Gateway on Pesticide Hazards and Safe Pest Management
How To Find Ingredients in Pesticide Products
Beyond Pesticides offers resources below to evaluate the health and ecological effects of specific chemical exposure from ACTIVE INGREDIENTS in pesticide products, as well as regulatory information and supporting scientific documents. Because various pesticide products can contain more than one active ingredient, it is important to READ the LABEL to determine chemical components.
With 192 different active ingredients and counting, it is essential to establish the connection between the use of these chemicals and their respective hazards.
View the step-by-step guide on how to search for the active ingredient(s) in pesticide products below:
- Go to U.S. EPA's Pesticide Product and Label System and enter the product name. The generic product name may vary.
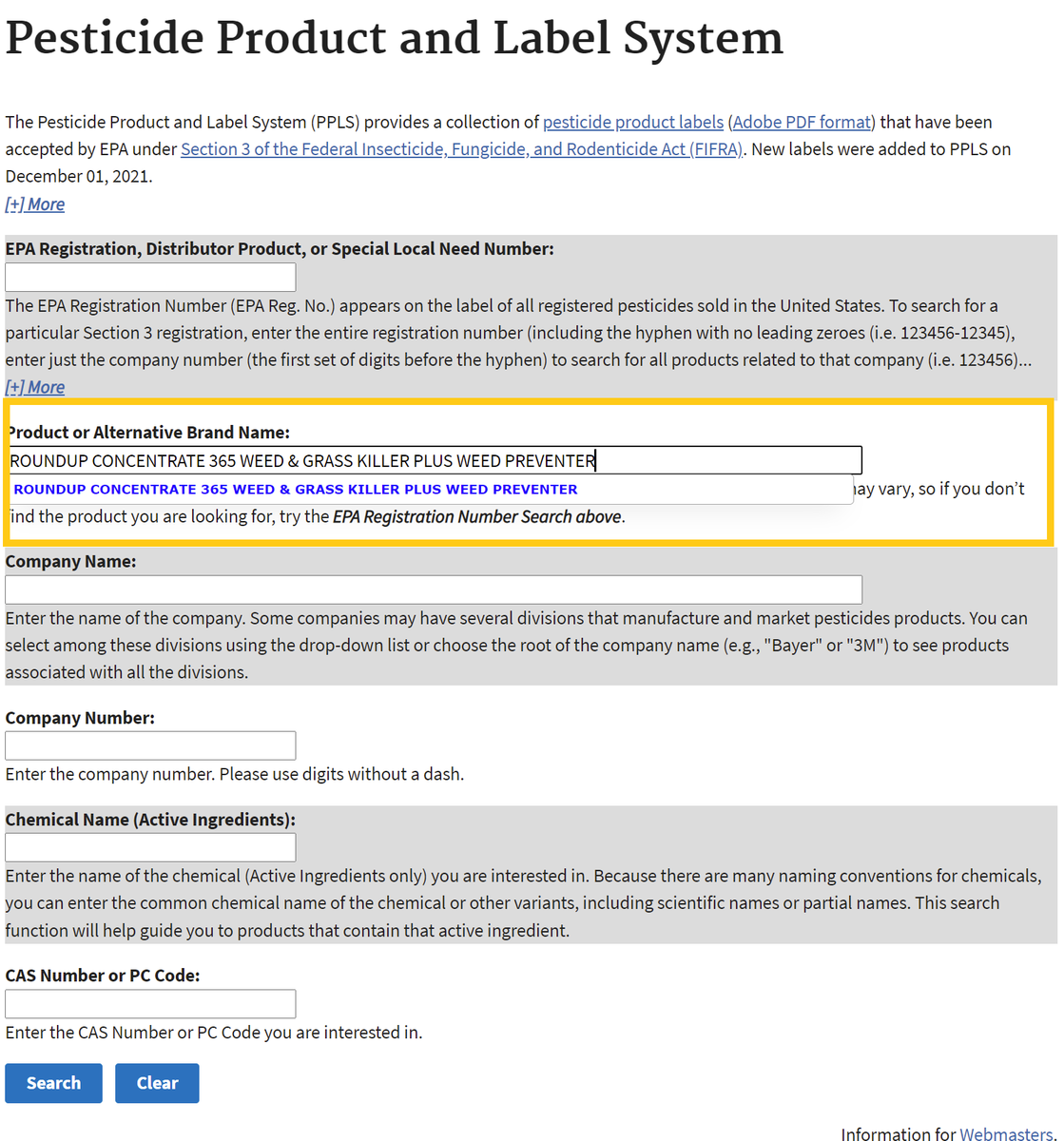
- After searching, click on the chemical ingredients tab or the link for the most recent label to find Active Ingredients.
Chemical List Label List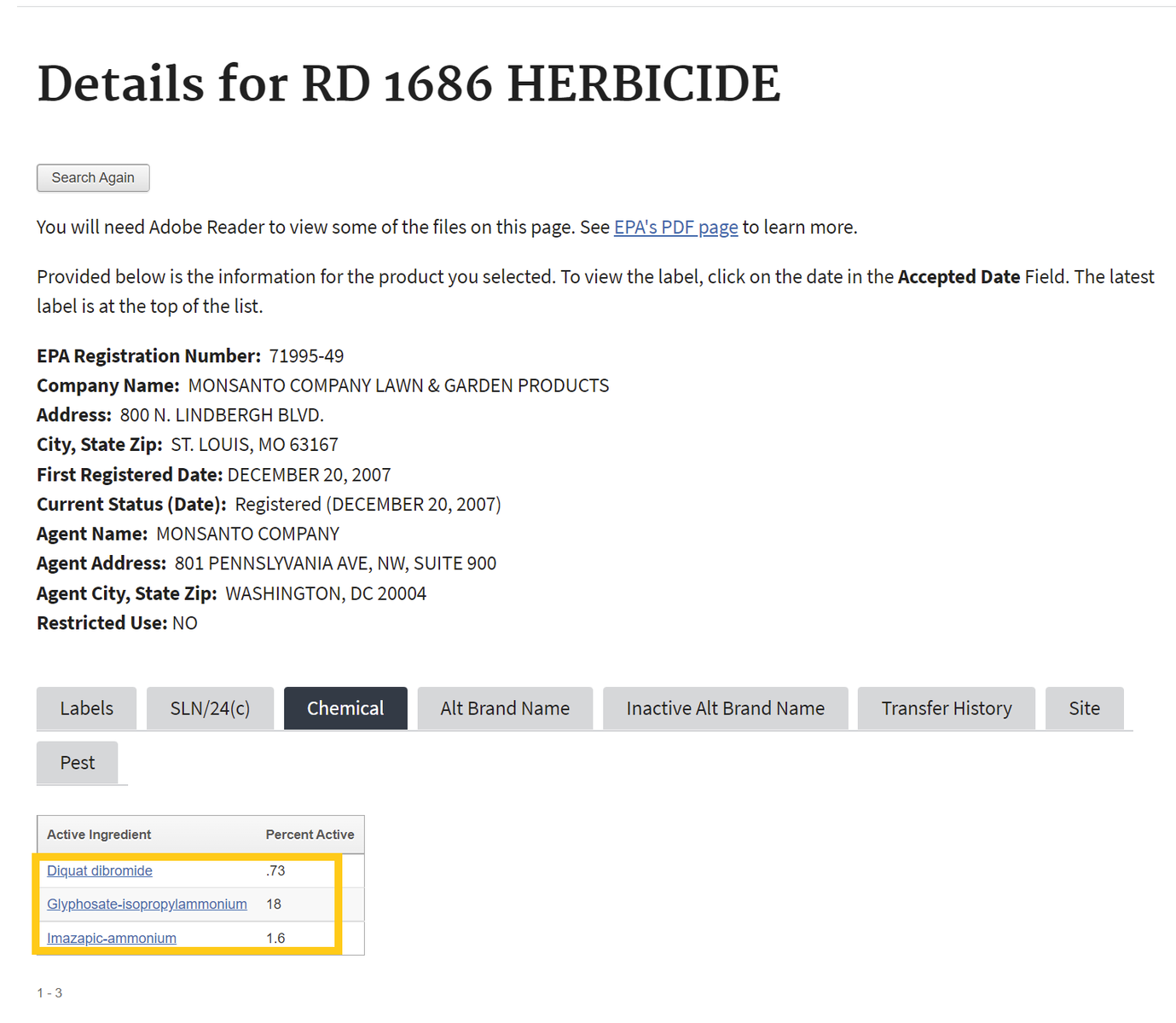
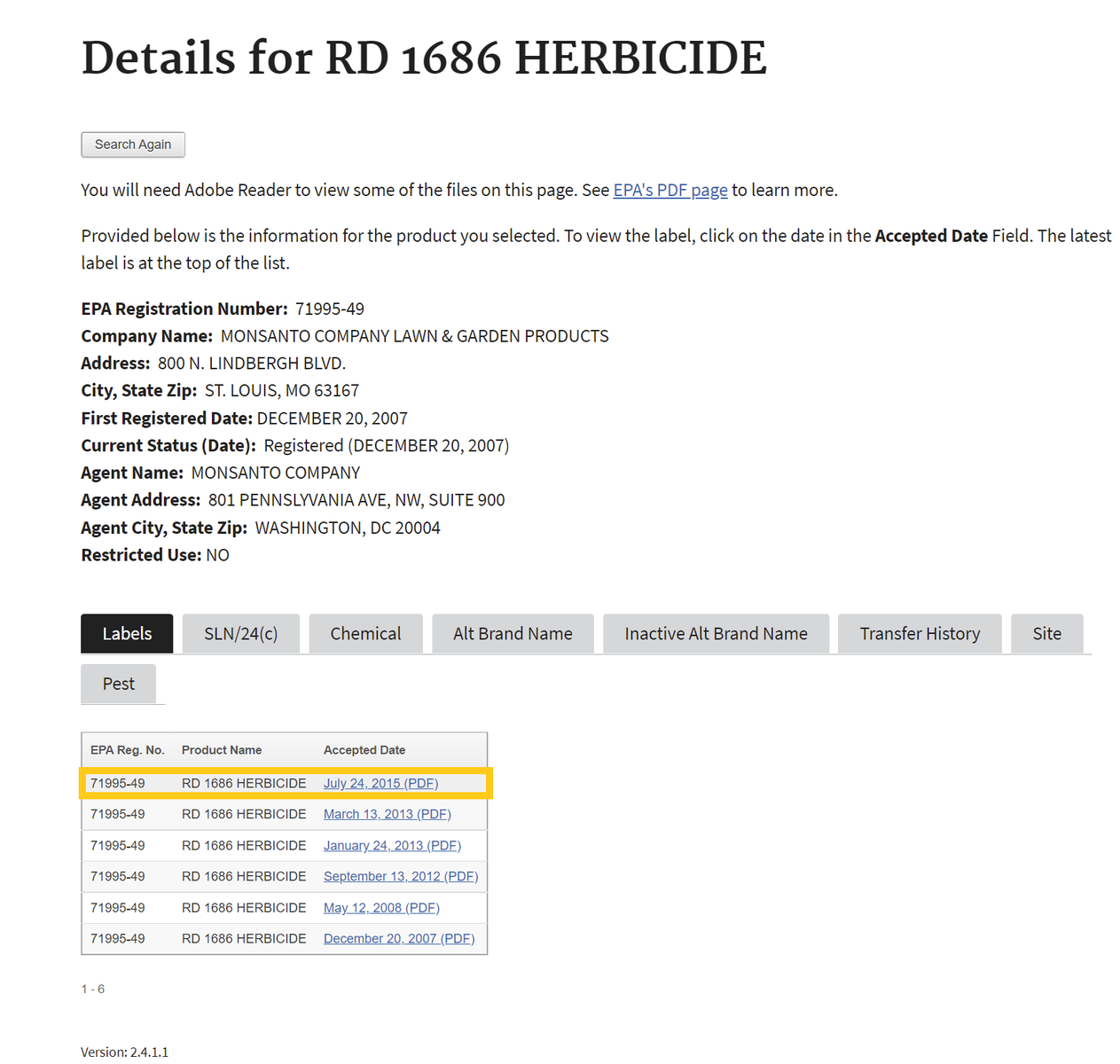
If one selects the chemical ingredients tab, skip to Step 4 . If not, proceed to step number 3 - To find the active ingredient(s) on the label, search for the page in the document containing the date of registration. Usually, the active ingredients section occurs within the first few pages of the label document.

- Return to the Beyond Pesticides Gateway and search for the active ingredient name in the yellow box to the right or from the list below.
Tebuconazole
General Information
- Product Names:
- Chemical Class: Azole fungicide
- Uses: Agriculture: grapes, garlic, cherries, peaches, more
- Alternatives: Organic agriculture
- Beyond Pesticides rating: Toxic
Health and Environmental Effects
- Cancer: Possible (43)
- Endocrine Disruption: Yes (36)
- Reproductive Effects: Not documented
- Neurotoxicity: Not documented
- Kidney/Liver Damage: Not documented
- Sensitizer/ Irritant: Not documented
- Birth/Developmental: Not documented
- Detected in Groundwater: Not documented
- Potential Leacher: Potential (43)
- Toxic to Birds: Not documented
- Toxic to Fish/Aquatic Organisms: Not documented
- Toxic to Bees: Not documented
Residential Uses as Found in the ManageSafe™ Database
Additional Information
- Supporting information:
- PAN Database: Tebuconazole (Pesticide Action Network North America)
- Studies:
- Adverse effects on sexual development in rat offspring after low dose exposure to a mixture of endocrine-disrupting pesticides.. Hass U, Boberg J, Christiansen S, Jacobsen PR, et al. 2012. Reprod Toxicol.34(2):261-74
- Birds feeding on tebuconazole treated seeds have reduced breeding output. Lopez-Antia, A., Ortiz-Santaliestra, M.E., Mougeot, F., Camarero, P.R. and Mateo, R., 2021. Environmental Pollution, 271, p.116292.
- Detrimental consequences of tebuconazole on redox homeostasis and fatty acid profile of honeybee brain. Mackei, M., Sebők, C., Vöröházi, J., Tráj, P., Mackei, F., Oláh, B., Fébel, H., Neogrády, Z. and Mátis, G., 2023. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 159, p.103990.
- Major Pesticides Are More Toxic to Human Cells Than Their Declared Active Principles. Mesnage, R. et al. (2014) Major pesticides are more toxic to human cells than their declared active principles, BioMed Research International. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3955666/.
- Snails as indicators of pesticide drift, deposit, transfer and effects in the vineyard. Druart, C. et al. (2011) Snails as indicators of pesticide drift, deposit, transfer and effects in the vineyard, Science of The Total Environment. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0048969711007224?via%3Dihub.
- Exposure to pesticides, persistent and non − persistent pollutants in French 3.5-year-old children: Findings from comprehensive hair analysis in the ELFE national birth cohort. Macheka, L. et al. (2024) Exposure to pesticides, persistent and non − persistent pollutants in French 3.5-year-old children: Findings from comprehensive hair analysis in the ELFE national birth cohort, Environment International. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0160412024004677.
- Uptake and distribution of fluopyram and tebuconazole residues in tomato and bell pepper plant tissues. Matadha, N.Y. et al. (2019) Uptake and distribution of fluopyram and tebuconazole residues in tomato and bell pepper plant tissues, Environmental Science and Pollution Research. Available at: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11356-018-04071-4.
- A Th2-type immune response and low-grade systemic inflammatory reaction as potential immunotoxic effects in intensive agriculture farmers exposed to pesticides . Lozano-Paniagua, D. et al. (2024) ‘A th2-type immune response and low-grade systemic inflammatory reaction as potential immunotoxic effects in intensive agriculture farmers exposed to pesticides’, Science of The Total Environment, 938, p. 173545. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.173545.
- Pesticide-Induced Inflammation at a Glance. Lopes-Ferreira, M. et al. (2023) ‘Pesticide-induced inflammation at a glance’, Toxics, 11(11), p. 896. doi:10.3390/toxics11110896.
- Different effects of polyethylene microplastics on bioaccumulation of three fungicides in maize (Zea mays L.). Qiu, S., Shen, H., Song, J. et al. Different effects of polyethylene microplastics on bioaccumulation of three fungicides in maize (Zea mays L.). Crop Health 2, 7 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s44297-024-00028-x
- The influence of polyethylene microplastics on pesticide residue and degradation in the aquatic environment. Wang, F., Gao, J., Zhai, W., Liu, D., Zhou, Z., & Wang, P. (2020). The influence of polyethylene microplastics on pesticide residue and degradation in the aquatic environment. Journal of hazardous materials, 394, 122517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122517
- Effects of triazole fungicides on androgenic disruption and CYP3A4 enzyme activity. Lv, X., Pan, L., Wang, J., Lu, L., Yan, W., Zhu, Y., Xu, Y., Guo, M., & Zhuang, S. (2017). Effects of triazole fungicides on androgenic disruption and CYP3A4 enzyme activity. Environmental pollution (Barking, Essex : 1987), 222, 504–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.11.051
- Triazole pesticides exposure impaired steroidogenesis associated to an increase in AHR and CAR expression in testis and altered sperm parameters in chicken. Serra, L., Bourdon, G., Estienne, A., Fréville, M., Ramé, C., Chevaleyre, C., Didier, P., Chahnamian, M., Ganier, P., Pinault, F., Froment, P., & Dupont, J. (2023). Triazole pesticides exposure impaired steroidogenesis associated to an increase in AHR and CAR expression in testis and altered sperm parameters in chicken. Toxicology reports, 10, 409–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2023.03.005
- Tebuconazole Induces Mouse Fetal Testes Damage via ROS Generation in an Organ Culture Method. Lee, W. Y., Lee, R., & Park, H. J. (2024). Tebuconazole Induces Mouse Fetal Testes Damage via ROS Generation in an Organ Culture Method. International journal of molecular sciences, 25(13), 7050. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25137050
- Oxidative Stress, Cytotoxic and Inflammatory Effects of Azoles Combinatorial Mixtures in Sertoli TM4 Cells. Petricca, S., Carnicelli, V., Luzi, C., Cinque, B., Celenza, G., & Iorio, R. (2023). Oxidative Stress, Cytotoxic and Inflammatory Effects of Azoles Combinatorial Mixtures in Sertoli TM4 Cells. Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland), 12(6), 1142. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12061142
- Evaluation of the Aquatic Toxicity of Several Triazole Fungicides. Boros, B.-V., Roman, D.-L., & Isvoran, A. (2024). Evaluation of the Aquatic Toxicity of Several Triazole Fungicides. Metabolites, 14(4), 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14040197
- Cardiotoxicity and triazole pesticides: therapeutic options for a neglected heart disease. Souza, D. and Roman-Campos, D. (2025) Cardiotoxicity and triazole pesticides: therapeutic options for a neglected heart disease, Expert Review of Cardiovascular Therapy. Available at: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/14779072.2025.2476124.
- In vivo tebuconazole administration impairs heart electrical function and facilitates the occurrence of dobutamine-induced arrhythmias: involvement of reactive oxygen species. Teixeira-Fonseca, J. L., Souza, D. S., Conceição, M. R. L., Marques, L. P., Durço, A. O., Silva, P. L. D., Joviano-Santos, J. V., Santos-Miranda, A., & Roman-Campos, D. (2024). In vivo tebuconazole administration impairs heart electrical function and facilitates the occurrence of dobutamine-induced arrhythmias: involvement of reactive oxygen species. Food and chemical toxicology : an international journal published for the British Industrial Biological Research Association, 187, 114596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2024.114596
- Tebuconazole induces ROS-dependent cardiac cell toxicity by activating DNA damage and mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Ben Othmène, Y., Monceaux, K., Karoui, A., Ben Salem, I., Belhadef, A., Abid-Essefi, S., & Lemaire, C. (2020). Tebuconazole induces ROS-dependent cardiac cell toxicity by activating DNA damage and mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Ecotoxicology and environmental safety, 204, 111040. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111040
- The fungicide tebuconazole modulates the sodium current of human NaV1.5 channels expressed in HEK293 cells. Marques, L. P., Santos-Miranda, A., Joviano-Santos, J. V., Teixeira-Fonseca, J. L., Alcântara, F. D. S., Sarmento, J. O., & Roman-Campos, D. (2023). The fungicide tebuconazole modulates the sodium current of human NaV1.5 channels expressed in HEK293 cells. Food and chemical toxicology : an international journal published for the British Industrial Biological Research Association, 180, 113992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2023.113992
- The fungicide Tebuconazole induces electromechanical cardiotoxicity in murine heart and human cardiomyocytes derived from induced pluripotent stem cells. Santos-Miranda, A., Joviano-Santos, J. V., Cruz-Nascimento, T., Neri, E. A., Souza, D. S., Marques, L. P., Krieger, J. E., & Roman-Campos, D. (2022). The fungicide Tebuconazole induces electromechanical cardiotoxicity in murine heart and human cardiomyocytes derived from induced pluripotent stem cells. Toxicology letters, 359, 96–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2022.02.005
- Tebuconazole induced oxidative stress and histopathological alterations in adult rat heart. Othmène, Y. B., Hamdi, H., Amara, I., & Abid-Essefi, S. (2020). Tebuconazole induced oxidative stress and histopathological alterations in adult rat heart. Pesticide biochemistry and physiology, 170, 104671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2020.104671
- Tebuconazole induced cardiotoxicity in male adult rat. Ben Othmène, Y., Hamdi, H., Annabi, E., Amara, I., Ben Salem, I., Neffati, F., Najjar, M. F., & Abid-Essefi, S. (2020). Tebuconazole induced cardiotoxicity in male adult rat. Food and chemical toxicology : an international journal published for the British Industrial Biological Research Association, 137, 111134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2020.111134
- Distribution of fluopyram and tebuconazole in pomegranate tissues and their risk assessment. Yogendraiah Matadha, N., Mohapatra, S., & Siddamallaiah, L. (2021). Distribution of fluopyram and tebuconazole in pomegranate tissues and their risk assessment. Food chemistry, 358, 129909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129909
- Fate of pesticide residues in beer and its by-products. Hakme, E., Kallehauge Nielsen, I., Fermina Madsen, J., Storkehave, L. M., Skjold Elmelund Pedersen, M., Schulz, B. L., … Duedahl-Olesen, L. (2023). Fate of pesticide residues in beer and its by-products. Food Additives & Contaminants: Part A, 41(1), 45–59. https://doi.org/10.1080/19440049.2023.2282557
- Currently used and legacy pesticides in the marine atmosphere from Patagonia to Europe. Debler, F., Gandrass, J., Paul Ramacher, M. O., Koenig, A. M., Zimmermann, S., & Joerss, H. (2025). Currently used and legacy pesticides in the marine atmosphere from Patagonia to Europe. Environmental pollution (Barking, Essex : 1987), 373, 126175. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2025.126175
- Widespread Pesticide Distribution in the European Atmosphere Questions their Degradability in Air. Mayer, L., Degrendele, C., Šenk, P., Kohoutek, J., Přibylová, P., Kukučka, P., Melymuk, L., Durand, A., Ravier, S., Alastuey, A., Baker, A. R., Baltensperger, U., Baumann-Stanzer, K., Biermann, T., Bohlin-Nizzetto, P., Ceburnis, D., Conil, S., Couret, C., Degórska, A., Diapouli, E., … Lammel, G. (2024). Widespread Pesticide Distribution in the European Atmosphere Questions their Degradability in Air. Environmental science & technology, 58(7), 3342–3352. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.3c08488
- Exposure to sublethal levels of insecticide-fungicide mixtures affect reproductive success and population growth rates in the solitary bee Osmia cornuta. Albacete, S., Sancho, G., Azpiazu, C., Sgolastra, F., Rodrigo, A., & Bosch, J. (2024). Exposure to sublethal levels of insecticide-fungicide mixtures affect reproductive success and population growth rates in the solitary bee Osmia cornuta. Environment international, 190, 108919. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2024.108919
- Wastewater surveillance for assessing human exposure to pesticides: Investigating populations living near flower bulb fields. Bijlsma, L. et al. (2025) Wastewater surveillance for assessing human exposure to pesticides: Investigating populations living near flower bulb fields, Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2213343725017865.
- Occurrence of Current-Use Pesticides in Paired Indoor Dust, Drinking Water, and Urine Samples from the United States: Risk Prioritization and Health Implications. Xie, Y., Li, J., Salamova, A., & Zheng, G. (2025). Occurrence of Current-Use Pesticides in Paired Indoor Dust, Drinking Water, and Urine Samples from the United States: Risk Prioritization and Health Implications. Environmental science & technology, 59(25), 12507–12519. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5c00961
- A wild bumble bee shows intraspecific differences in sensitivity to multiple pesticides. Tatarko, A. et al. (2025) A wild bumble bee shows intraspecific differences in sensitivity to multiple pesticides, Royal Society Open Science. Available at: https://royalsocietypublishing.org/doi/10.1098/rsos.250281.
- Potential neurotoxicity, immunotoxicity, and carcinogenicity induced by metribuzin and tebuconazole exposure in earthworms (Eisenia fetida) revealed by transcriptome analysis. Li, G., Li, D., Rao, H., & Liu, X. (2022). Potential neurotoxicity, immunotoxicity, and carcinogenicity induced by metribuzin and tebuconazole exposure in earthworms (Eisenia fetida) revealed by transcriptome analysis. The Science of the total environment, 807(Pt 1), 150760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150760








.png)


