Gateway on Pesticide Hazards and Safe Pest Management
How To Find Ingredients in Pesticide Products
Beyond Pesticides offers resources below to evaluate the health and ecological effects of specific chemical exposure from ACTIVE INGREDIENTS in pesticide products, as well as regulatory information and supporting scientific documents. Because various pesticide products can contain more than one active ingredient, it is important to READ the LABEL to determine chemical components.
With 192 different active ingredients and counting, it is essential to establish the connection between the use of these chemicals and their respective hazards.
View the step-by-step guide on how to search for the active ingredient(s) in pesticide products below:
- Go to U.S. EPA's Pesticide Product and Label System and enter the product name. The generic product name may vary.
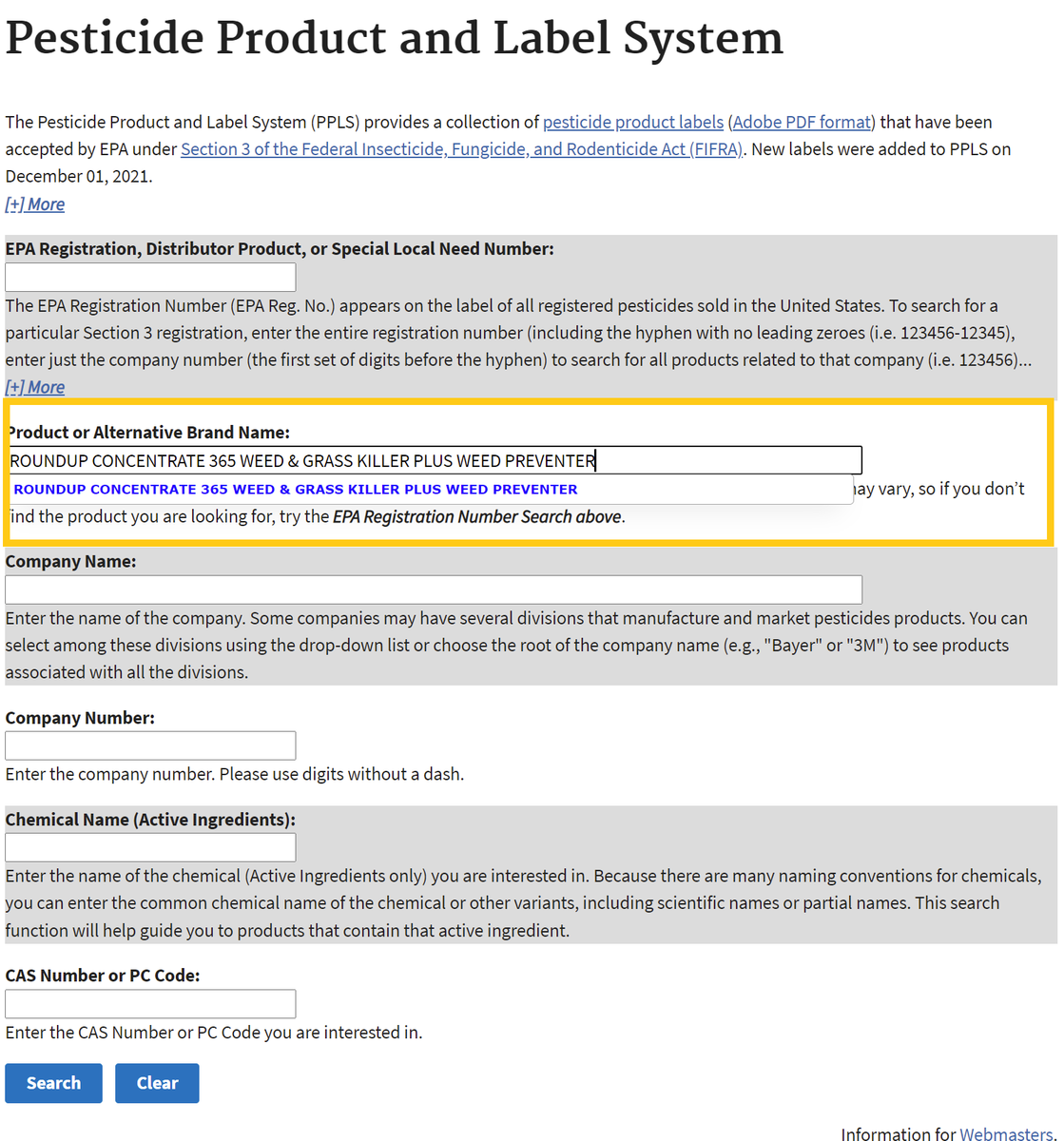
- After searching, click on the chemical ingredients tab or the link for the most recent label to find Active Ingredients.
Chemical List Label List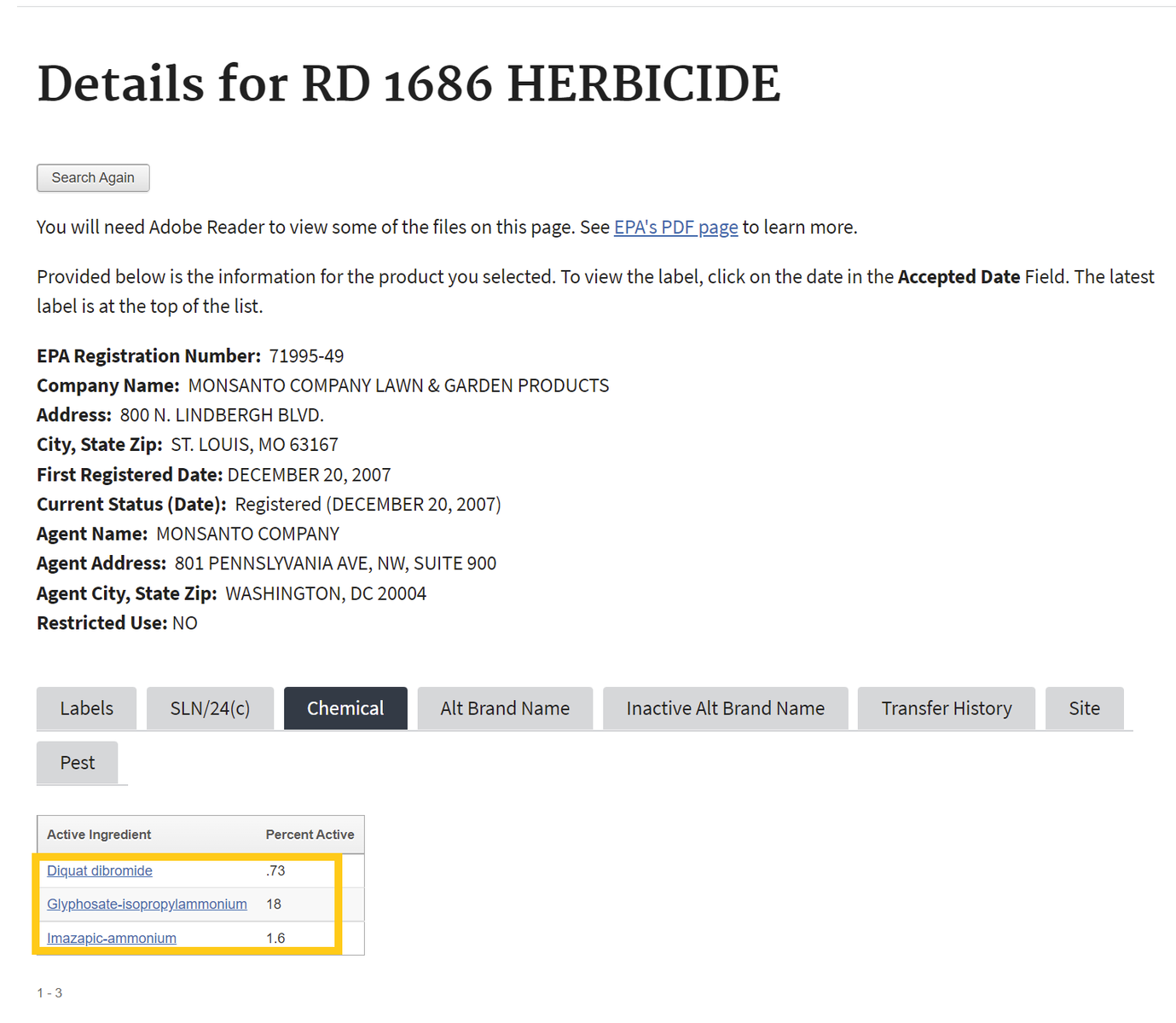
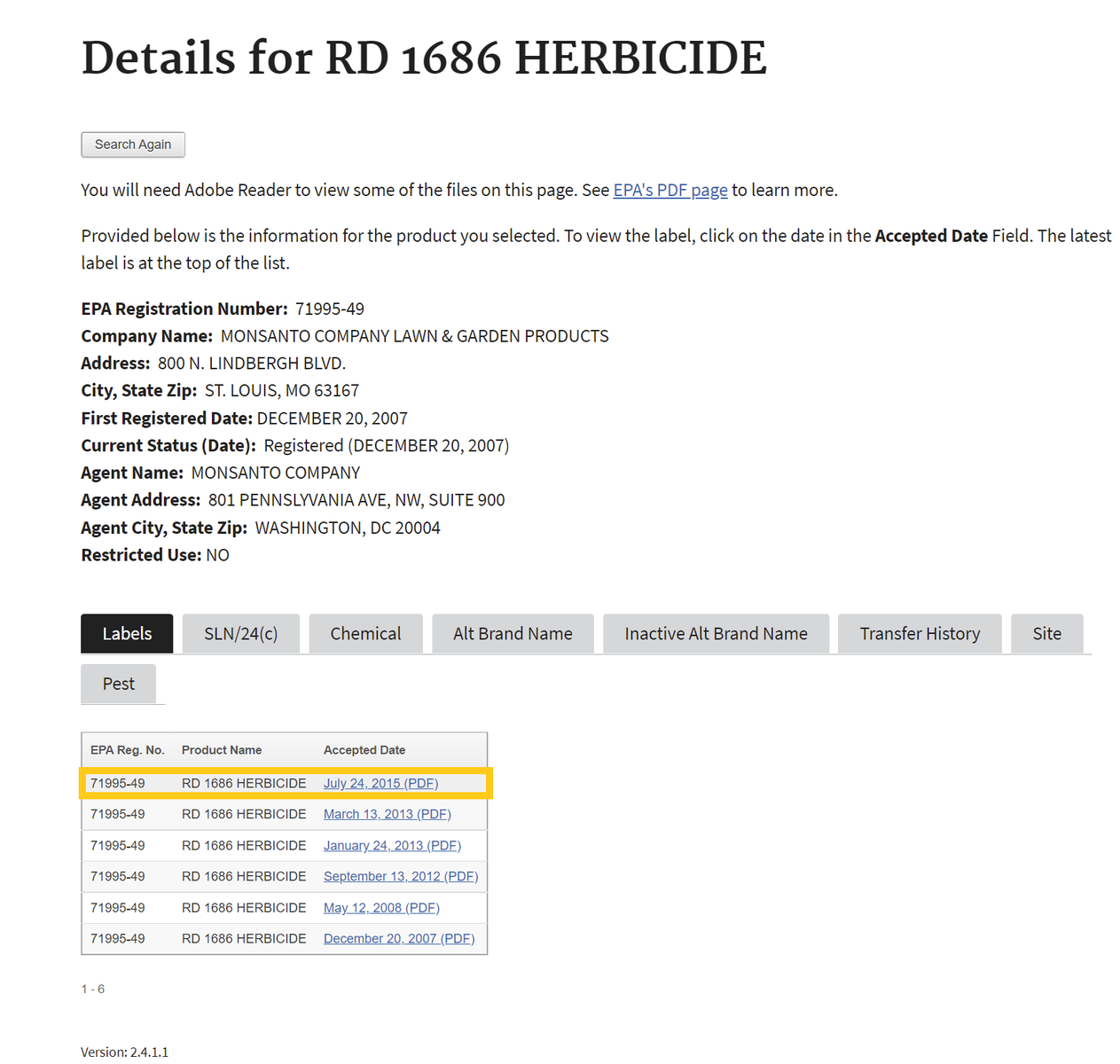
If one selects the chemical ingredients tab, skip to Step 4 . If not, proceed to step number 3 - To find the active ingredient(s) on the label, search for the page in the document containing the date of registration. Usually, the active ingredients section occurs within the first few pages of the label document.

- Return to the Beyond Pesticides Gateway and search for the active ingredient name in the yellow box to the right or from the list below.
1,3-Dichloropropene (Telone)
1,3-D
1,3-D is often formulated with chloropicrin both as a warning agent and to enhance plant pathogen and weed control.
General Information
- Product Names:
- Chemical Class: Soil fumigant
- Uses: Broad spectrum soil fumigant to control various soil-borne diseases, nematodes, and/or garden symphylans on a range of agricultural (fruiting, leafy, and root vegetable crops; legumes; corn and tobacco) and non-agricultural crops (ornamentals, non-bearing fruit/nut trees, forestry crops, lawns and turf, golf course). It also has drip irrigation uses on established vineyards.
- Alternatives: Organic Agriculture
- Beyond Pesticides rating: Toxic
Health and Environmental Effects
- Cancer: Yes (3, 8, 21, 240)
- Endocrine Disruption: Not documented
- Reproductive Effects: Not documented
- Neurotoxicity: Not documented
- Kidney/Liver Damage: Yes (8)
- Sensitizer/ Irritant: Yes (8)
- Birth/Developmental: Not documented
- Detected in Groundwater: Yes (8, 27)
- Potential Leacher: Yes (8, 27)
- Toxic to Birds: Yes (8)
- Toxic to Fish/Aquatic Organisms: Yes (8)
- Toxic to Bees: Not documented
Additional Information
- Regulatory Status:
- Supporting information:
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR). 2008. Toxicological Profile for 1,3-Dichloropropene. Atlanta, GA: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service.
- Strawberry Drip Fumigation. UC Pest Management Guidelines.
- The Center for Investigative Reporting. Dark Side of the Strawberry. RevealNews.org
- Studies:
- National Toxicology Program (NTP). 2011. Report on Carcinogens, 13th Edition
- Case report: Death caused by 1, 3-dichloropropene, a novel fumigant used in China. Zhou, Z., Guo, L., Wen, Z., Dai, P., Zhang, T., Wang, W. and Jian, X., 2023. Frontiers in Public Health, 11.
- Increasing confidence in new approach methodologies for inhalation risk assessment with multiple end point assays using 5-day repeated exposure to 1,3-dichloropropene. Paudel, I. et al. (2023) Increasing confidence in new approach methodologies for inhalation risk assessment with multiple end point assays using 5-day repeated exposure to 1,3-Dichloropropene, Toxicology. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0300483X23002299.
- Identification of volatile biomarkers for lung cancer from different histological sources: A comprehensive study. Lv, W. et al. (2024) Identification of volatile biomarkers for lung cancer from different histological sources: A comprehensive study, Analytical Biochemistry. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S000326972400071X.
- Impact of repeated fumigant applications on soil properties, crop yield, and microbial communities in a plastic-mulched tomato production system. Castellano-Hinojosa, A. et al. (2024) Impact of repeated fumigant applications on soil properties, crop yield, and microbial communities in a plastic-mulched tomato production system, Science of The Total Environment. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0048969724007988.
- Identifying Toxic Consumer Products: A Novel Data Set Reveals Air Emissions of Potent Carcinogens, Reproductive Toxicants, and Developmental Toxicants. Knox, K. et al. (2023) Identifying Toxic Consumer Products: A Novel Data Set Reveals Air Emissions of Potent Carcinogens, Reproductive Toxicants, and Developmental Toxicants, Environmental Science & Technology. Available at: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acs.est.2c07247.
- The association between 1,3-dichloropropene and asthma emergency department visits in California, USA from 2005 to 2011: a bidirectional-symmetric case crossover study. Gharibi, H. et al. (2019) The association between 1,3-dichloropropene and asthma emergency department visits in California, USA from 2005 to 2011: a bidirectional-symmetric case crossover study, Journal of Asthma. Available at: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/02770903.2019.1590596.
- Soil chemical fumigation alters soil phosphorus cycling: effects and potential mechanisms. Wang, Y. and Tang, D.W.S. (2024) Soil chemical fumigation alters soil phosphorus cycling: effects and potential mechanisms, Frontiers in Plant Science. Available at: https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/plant-science/articles/10.3389/fpls.2024.1289270/full.








.png)


