Gateway on Pesticide Hazards and Safe Pest Management
How To Find Ingredients in Pesticide Products
Beyond Pesticides offers resources below to evaluate the health and ecological effects of specific chemical exposure from ACTIVE INGREDIENTS in pesticide products, as well as regulatory information and supporting scientific documents. Because various pesticide products can contain more than one active ingredient, it is important to READ the LABEL to determine chemical components.
With 192 different active ingredients and counting, it is essential to establish the connection between the use of these chemicals and their respective hazards.
View the step-by-step guide on how to search for the active ingredient(s) in pesticide products below:
- Go to U.S. EPA's Pesticide Product and Label System and enter the product name. The generic product name may vary.
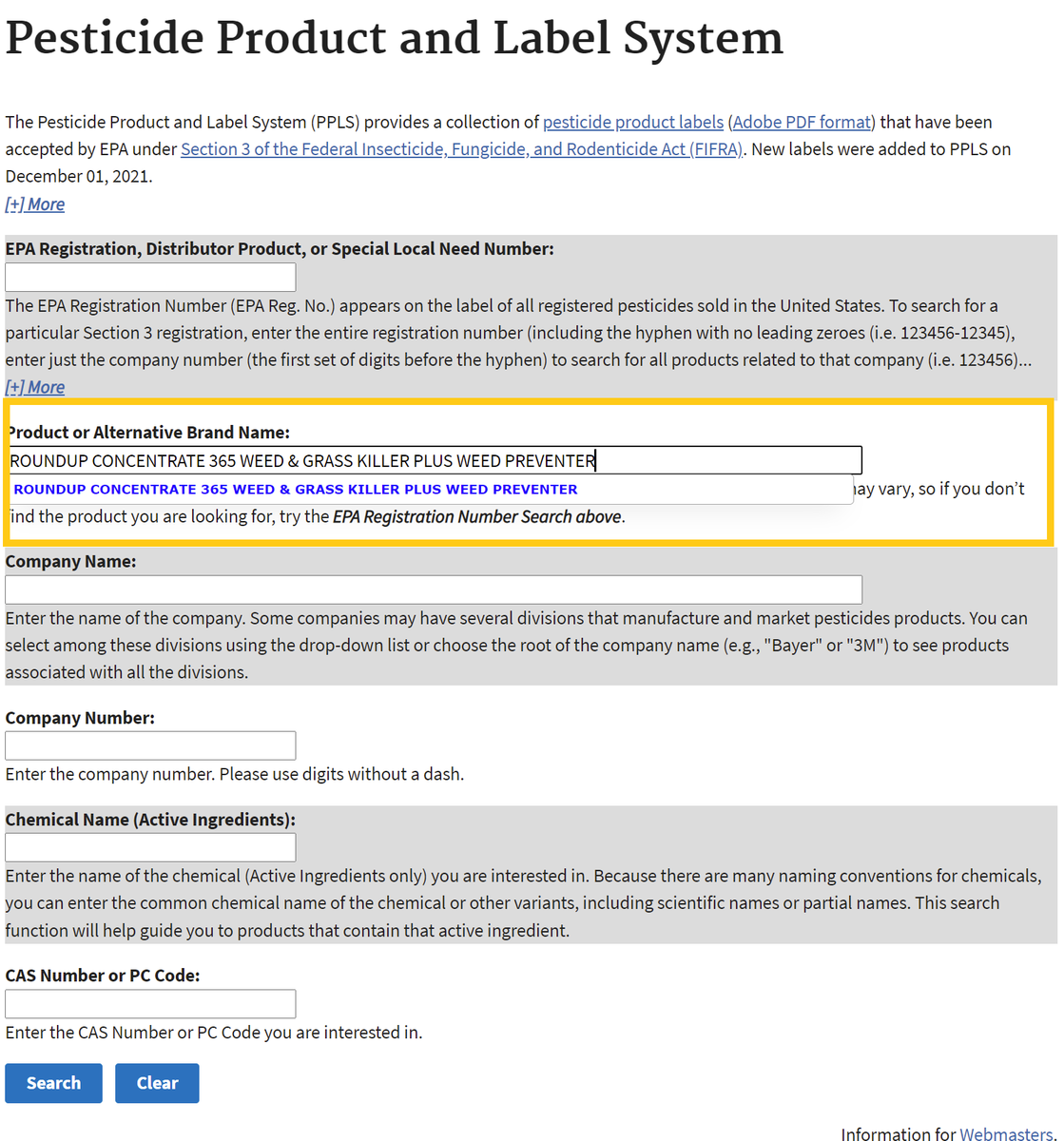
- After searching, click on the chemical ingredients tab or the link for the most recent label to find Active Ingredients.
Chemical List Label List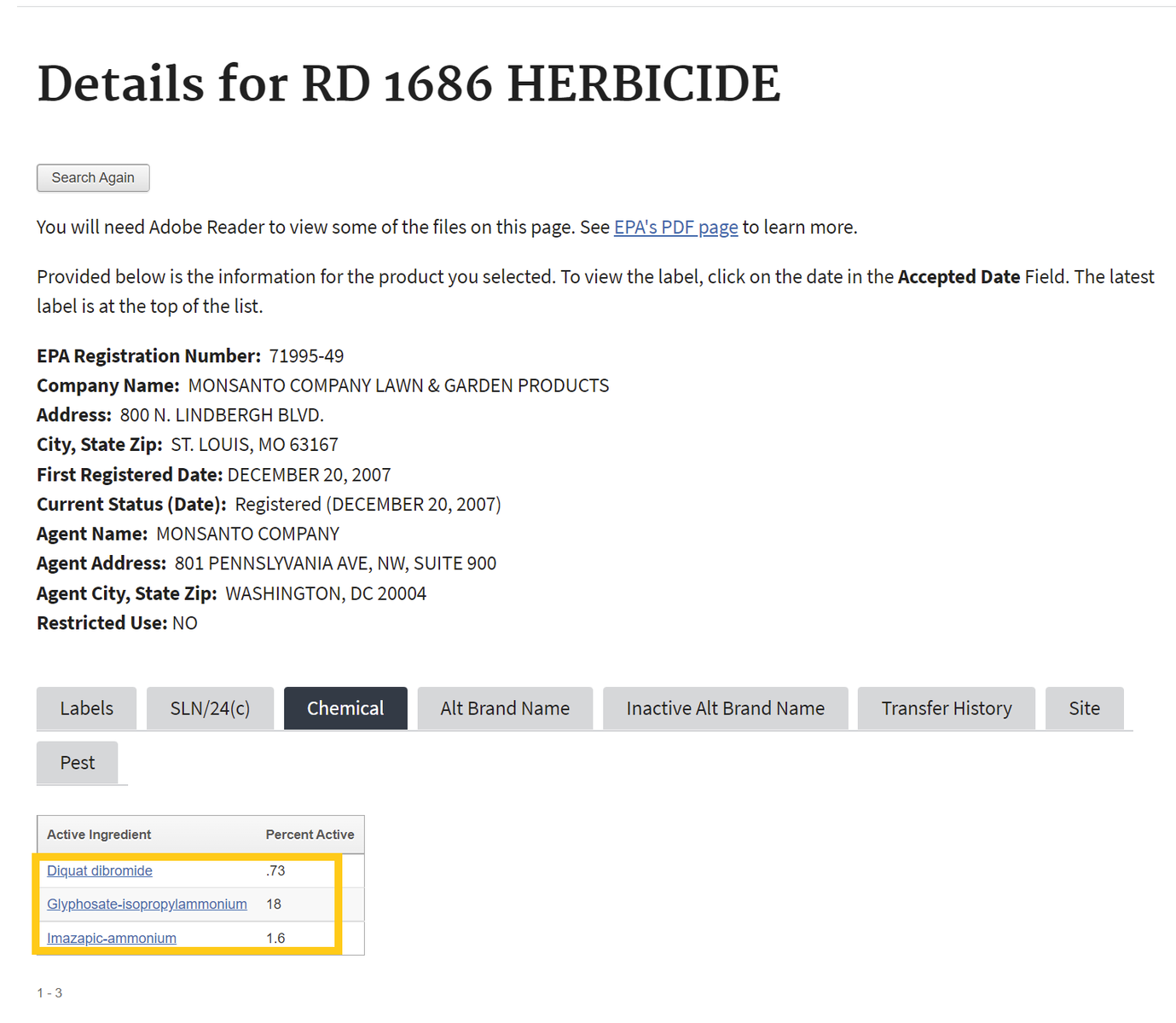
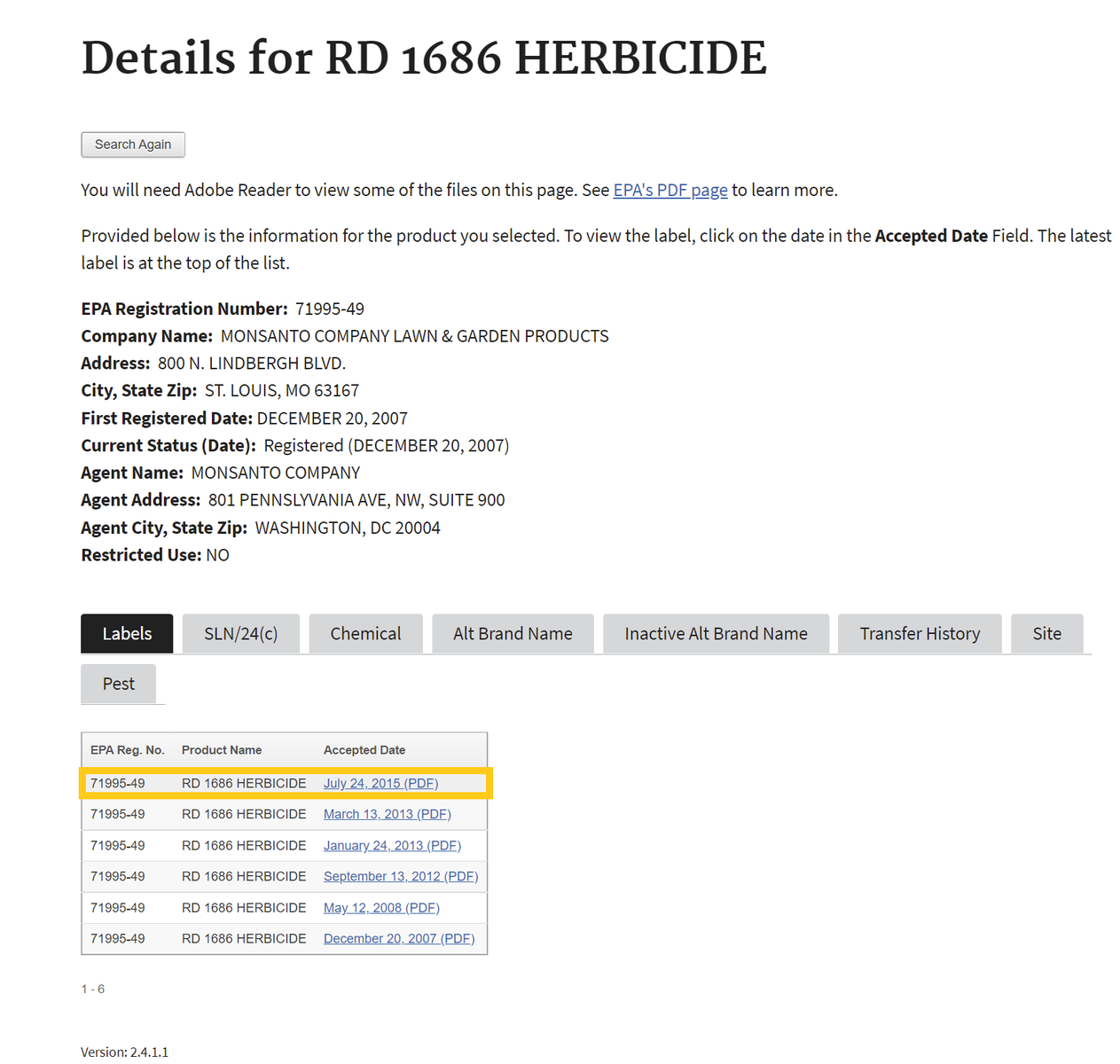
If one selects the chemical ingredients tab, skip to Step 4 . If not, proceed to step number 3 - To find the active ingredient(s) on the label, search for the page in the document containing the date of registration. Usually, the active ingredients section occurs within the first few pages of the label document.

- Return to the Beyond Pesticides Gateway and search for the active ingredient name in the yellow box to the right or from the list below.
Fluopyram
General Information
- Product Names:
- Chemical Class: Pyridinyl-ethybenzamide fungicide
- Uses: Agriculture, greenhouses, drip irrigation
- Beyond Pesticides rating: Toxic
Health and Environmental Effects
- Cancer: Yes (8, 43)
- Endocrine Disruption: Yes (8)
- Reproductive Effects: Not documented
- Neurotoxicity: Not documented
- Kidney/Liver Damage: Yes (8)
- Sensitizer/ Irritant: Not documented
- Birth/Developmental: Not documented
- Detected in Groundwater: Not documented
- Potential Leacher: Not documented
- Toxic to Birds: Not documented
- Toxic to Fish/Aquatic Organisms: Yes (8)
- Toxic to Bees: Not documented
Additional Information
- Regulatory Status:
- Supporting information:
- PAN Pesticides Database: Fluopyram (Pesticide Action Network)
- Studies:
- Direct pesticide exposure of insects in nature conservation areas in Germany. Brühl, C.A., Bakanov, N., Köthe, S., Eichler, L., Sorg, M., Hörren, T., Mühlethaler, R., Meinel, G. and Lehmann, G.U. Scientific reports, 11(1), pp.1-10.
- Flooding as a Vector for the Transport of Pesticides from Streams to Riparian Plants. Fiolka, F. et al. (2024) Flooding as a Vector for the Transport of Pesticides from Streams to Riparian Plants, American Chemical Society ES&T Water. Available at: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acsestwater.4c00571.
- Uptake and distribution of fluopyram and tebuconazole residues in tomato and bell pepper plant tissues. Matadha, N.Y. et al. (2019) Uptake and distribution of fluopyram and tebuconazole residues in tomato and bell pepper plant tissues, Environmental Science and Pollution Research. Available at: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11356-018-04071-4.
- Current-use pesticides in vegetation, topsoil and water reveal contaminated landscapes of the Upper Rhine Valley, Germany. Mauser, K.M., Wolfram, J., Spaak, J.W. et al. Current-use pesticides in vegetation, topsoil and water reveal contaminated landscapes of the Upper Rhine Valley, Germany. Commun Earth Environ 6, 166 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s43247-025-02118-2
- Distribution of fluopyram and tebuconazole in pomegranate tissues and their risk assessment. Yogendraiah Matadha, N., Mohapatra, S., & Siddamallaiah, L. (2021). Distribution of fluopyram and tebuconazole in pomegranate tissues and their risk assessment. Food chemistry, 358, 129909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129909
- Oxidative stress, intestinal damage, and cell apoptosis: Toxicity induced by fluopyram in Caenorhabditis elegans. Liu, Y., Zhang, W., Wang, Y., Liu, H., Zhang, S., Ji, X., & Qiao, K. (2022). Oxidative stress, intestinal damage, and cell apoptosis: Toxicity induced by fluopyram in Caenorhabditis elegans. Chemosphere, 286(Pt 3), 131830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131830
- Fluopyram activates systemic resistance in soybean. Rocha, L. F., Subedi, A., Pimentel, M. F., Bond, J. P., & Fakhoury, A. M. (2022). Fluopyram activates systemic resistance in soybean. Frontiers in plant science, 13, 1020167. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.1020167
- The Fate of Fluopyram in the Soil–Water–Plant Ecosystem: A Review. Rathod, P.H., Shah, P.G., Parmar, K.D. et al. The Fate of Fluopyram in the Soil–Water–Plant Ecosystem: A Review. Reviews Env.Contamination (formerly:Residue Reviews) 260, 1 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s44169-021-00001-7
- Combined toxicity of trifloxystrobin and fluopyram to zebrafish embryos and the effect on bone development. Zhang, T., Yuan, J., Guo, Y., Wang, X., Li, Q. X., Zhang, J., Xie, J., Miao, W., & Fan, Y. (2024). Combined toxicity of trifloxystrobin and fluopyram to zebrafish embryos and the effect on bone development. Aquatic toxicology (Amsterdam, Netherlands), 268, 106834. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2024.106834
- Currently used and legacy pesticides in the marine atmosphere from Patagonia to Europe. Debler, F., Gandrass, J., Paul Ramacher, M. O., Koenig, A. M., Zimmermann, S., & Joerss, H. (2025). Currently used and legacy pesticides in the marine atmosphere from Patagonia to Europe. Environmental pollution (Barking, Essex : 1987), 373, 126175. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2025.126175
- Insights into the chronic toxicity and mechanisms of fluorine-containing pesticides on earthworms. Shan, D. et al. (2025) Insights into the chronic toxicity and mechanisms of fluorine-containing pesticides on earthworms, Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1382668925001863.








.png)


