Gateway on Pesticide Hazards and Safe Pest Management
How To Find Ingredients in Pesticide Products
Beyond Pesticides offers resources below to evaluate the health and ecological effects of specific chemical exposure from ACTIVE INGREDIENTS in pesticide products, as well as regulatory information and supporting scientific documents. Because various pesticide products can contain more than one active ingredient, it is important to READ the LABEL to determine chemical components.
With 192 different active ingredients and counting, it is essential to establish the connection between the use of these chemicals and their respective hazards.
View the step-by-step guide on how to search for the active ingredient(s) in pesticide products below:
- Go to U.S. EPA's Pesticide Product and Label System and enter the product name. The generic product name may vary.
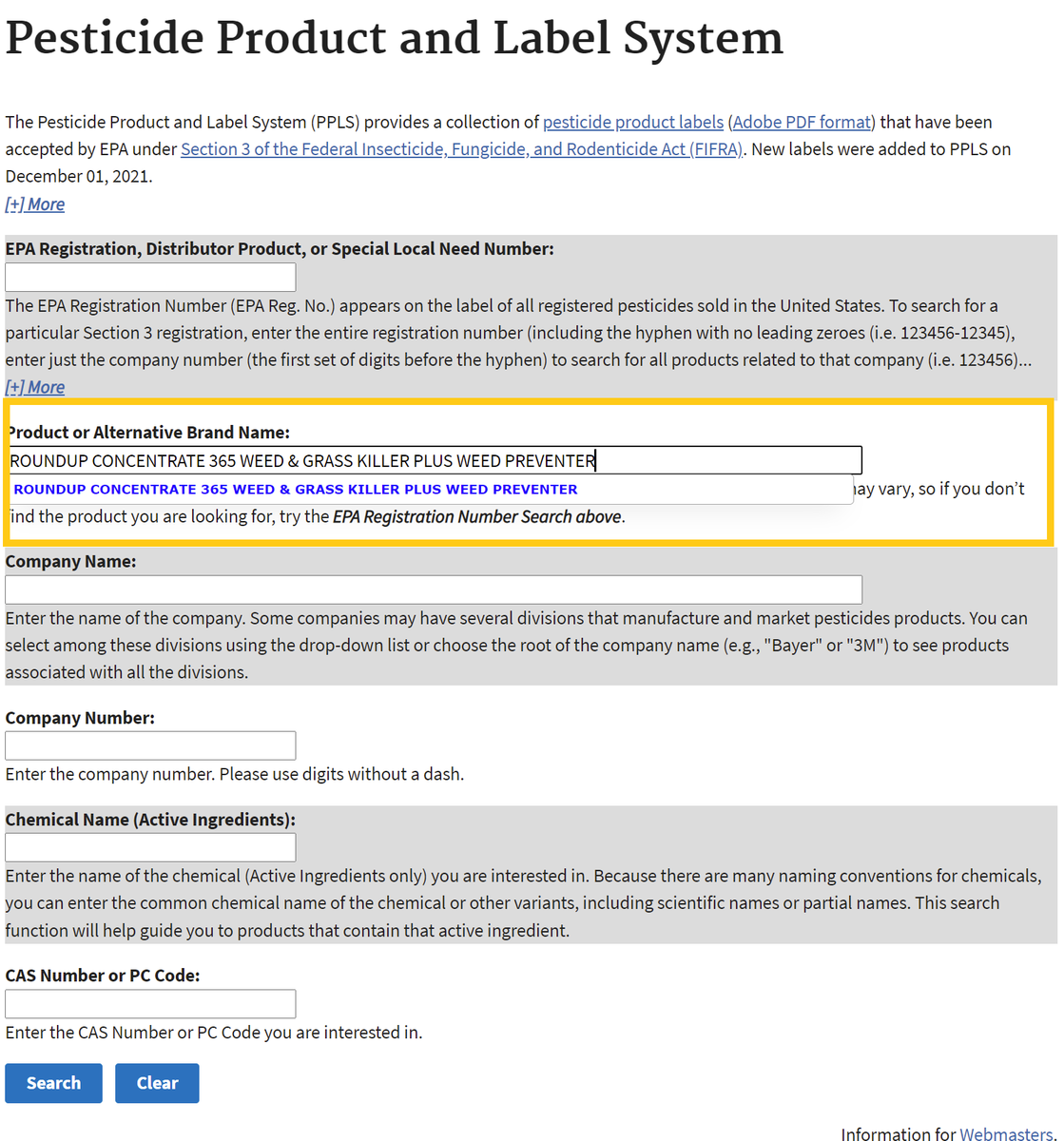
- After searching, click on the chemical ingredients tab or the link for the most recent label to find Active Ingredients.
Chemical List Label List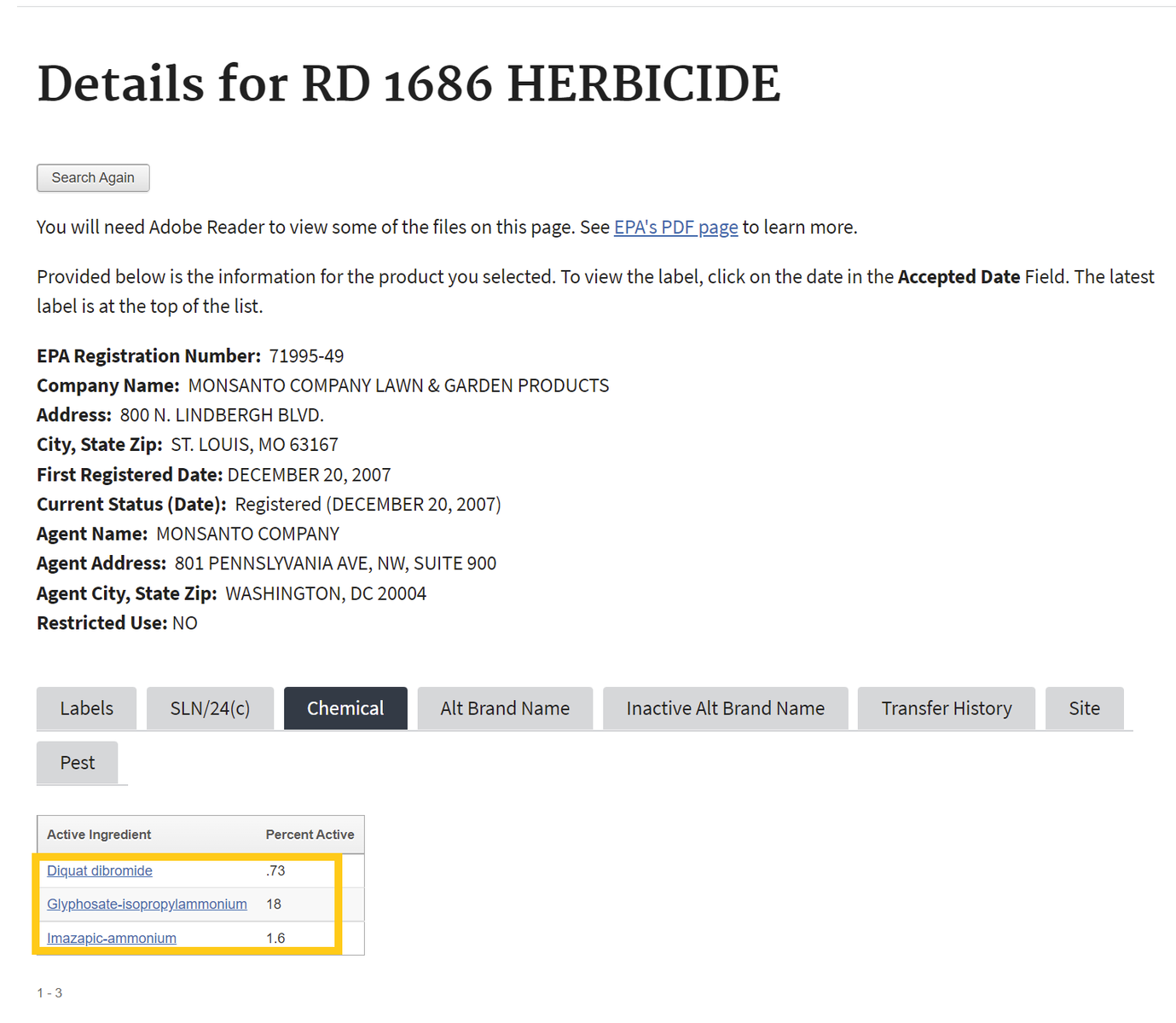
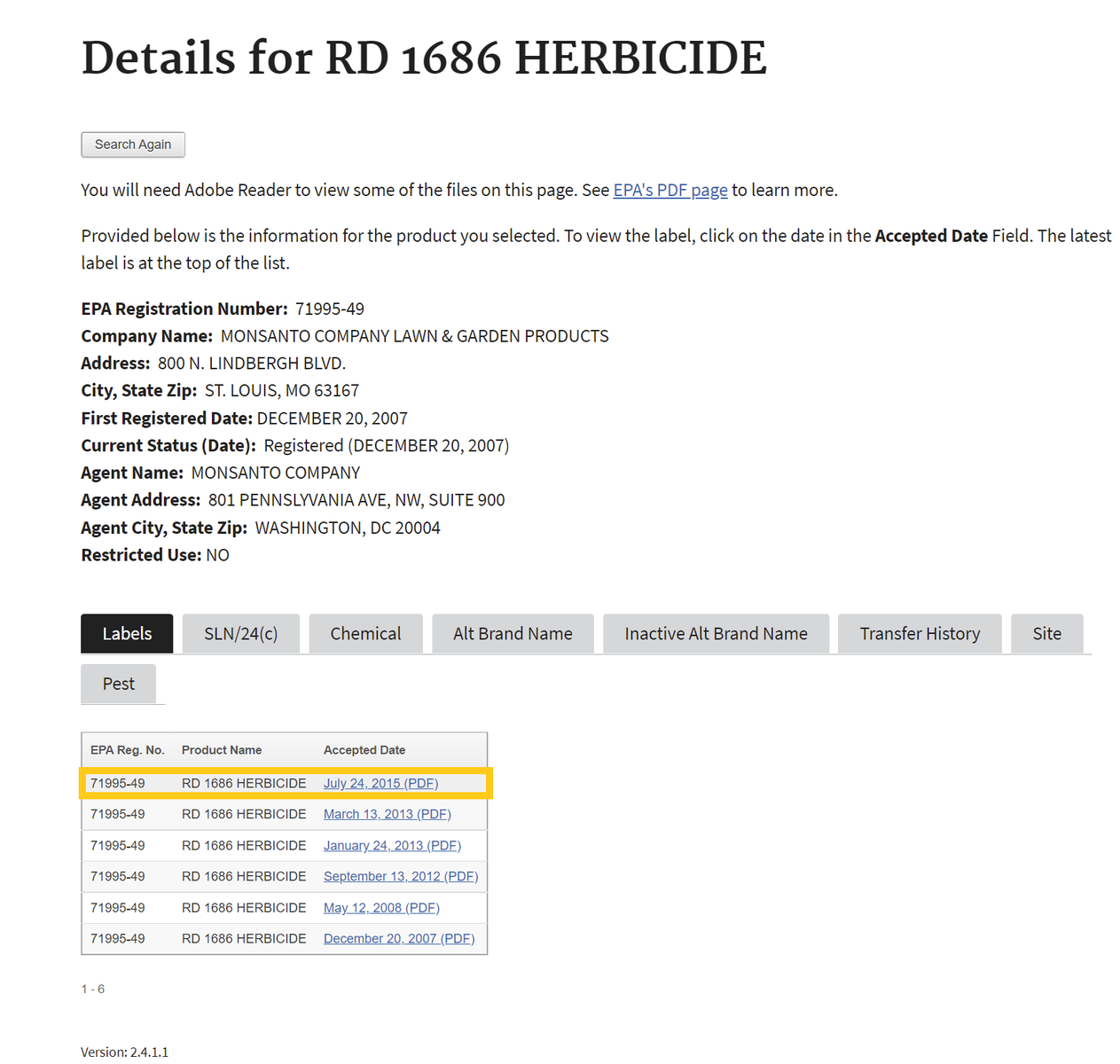
If one selects the chemical ingredients tab, skip to Step 4 . If not, proceed to step number 3 - To find the active ingredient(s) on the label, search for the page in the document containing the date of registration. Usually, the active ingredients section occurs within the first few pages of the label document.

- Return to the Beyond Pesticides Gateway and search for the active ingredient name in the yellow box to the right or from the list below.
Bacillus Thuringiensis (Bt)
including israelensis, kurstaki, aizawai, tenebrionis strains
General Information
- Fact Sheet: bacillus thuringiensis.pdf
- Product Names:
- Chemical Class: Microbial insecticide; Soil bacterium
- Uses: Used to control Coleoptera, Lepidoptera or Diptera insects in field, greenhouse, water-grown crops, ornamentals, nursery, forest, food/nonfood storage, and standing waters.
Approved uses in Organic Agriculture, Aquaculture, Least-toxic mosquito control. - Beyond Pesticides rating:
Health and Environmental Effects
- Cancer: No
- Endocrine Disruption: Insufficiently Studied
- Reproductive Effects: Insufficiently Studied
- Neurotoxicity: Insufficiently Studied
- Kidney/Liver Damage: Insufficiently Studied
- Sensitizer/ Irritant: Possible (226)
- Birth/Developmental: Insufficiently Studied
- Detected in Groundwater: Not Likely
- Potential Leacher: Insufficiently Studied
- Toxic to Birds: Not Likely
- Toxic to Fish/Aquatic Organisms: Possible: kurstaki and israelensis [moderate]; aizawai [high] (226)
- Toxic to Bees: Yes: aizawai strain (7)
Residential Uses as Found in the ManageSafe™ Database
Additional Information
- Regulatory Status:
- Supporting information:
- Beyond Pesticides' GE page
- Bt Factsheet (National Pesticide Information Center)
- Bt Fact Sheet (Northwest Coalition for Alternatives to Pesticides)
- PAN Pesticides Database: Bt (Pesticide Action Network)
- Studies:
- Field-evolved resistance by western corn rootworm to multiple Bacillus thuringiensis toxins in transgenic maize [Gassmann, A., et al. PNAS. 111(14):5141-5146]
- Bt Corn and Insect Resistance: An Economic Assessment of Refuges. Hurley, T.M., Babcock, B.A. and Hellmich, R.L. (2001) Bt Corn and Insect Resistance: An Economic Assessment of Refuges, Journal of Agricultural and Resource Economics. Available at: https://www.jstor.org/stable/40987102.
- Resistance to Bt Maize by Western Corn Rootworm: Effects of Pest Biology, the Pest–Crop Interaction and the Agricultural Landscape on Resistance. Gassmann, A.J. (2021) Resistance to BT maize by western corn rootworm: Effects of pest biology, the Pest–crop interaction and the agricultural landscape on resistance, Insects. Available at: https://www.mdpi.com/2075-4450/12/2/136.
- A Th2-type immune response and low-grade systemic inflammatory reaction as potential immunotoxic effects in intensive agriculture farmers exposed to pesticides . Lozano-Paniagua, D. et al. (2024) ‘A th2-type immune response and low-grade systemic inflammatory reaction as potential immunotoxic effects in intensive agriculture farmers exposed to pesticides’, Science of The Total Environment, 938, p. 173545. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.173545.








.png)


