Gateway on Pesticide Hazards and Safe Pest Management
How To Find Ingredients in Pesticide Products
Beyond Pesticides offers resources below to evaluate the health and ecological effects of specific chemical exposure from ACTIVE INGREDIENTS in pesticide products, as well as regulatory information and supporting scientific documents. Because various pesticide products can contain more than one active ingredient, it is important to READ the LABEL to determine chemical components.
With 192 different active ingredients and counting, it is essential to establish the connection between the use of these chemicals and their respective hazards.
View the step-by-step guide on how to search for the active ingredient(s) in pesticide products below:
- Go to U.S. EPA's Pesticide Product and Label System and enter the product name. The generic product name may vary.
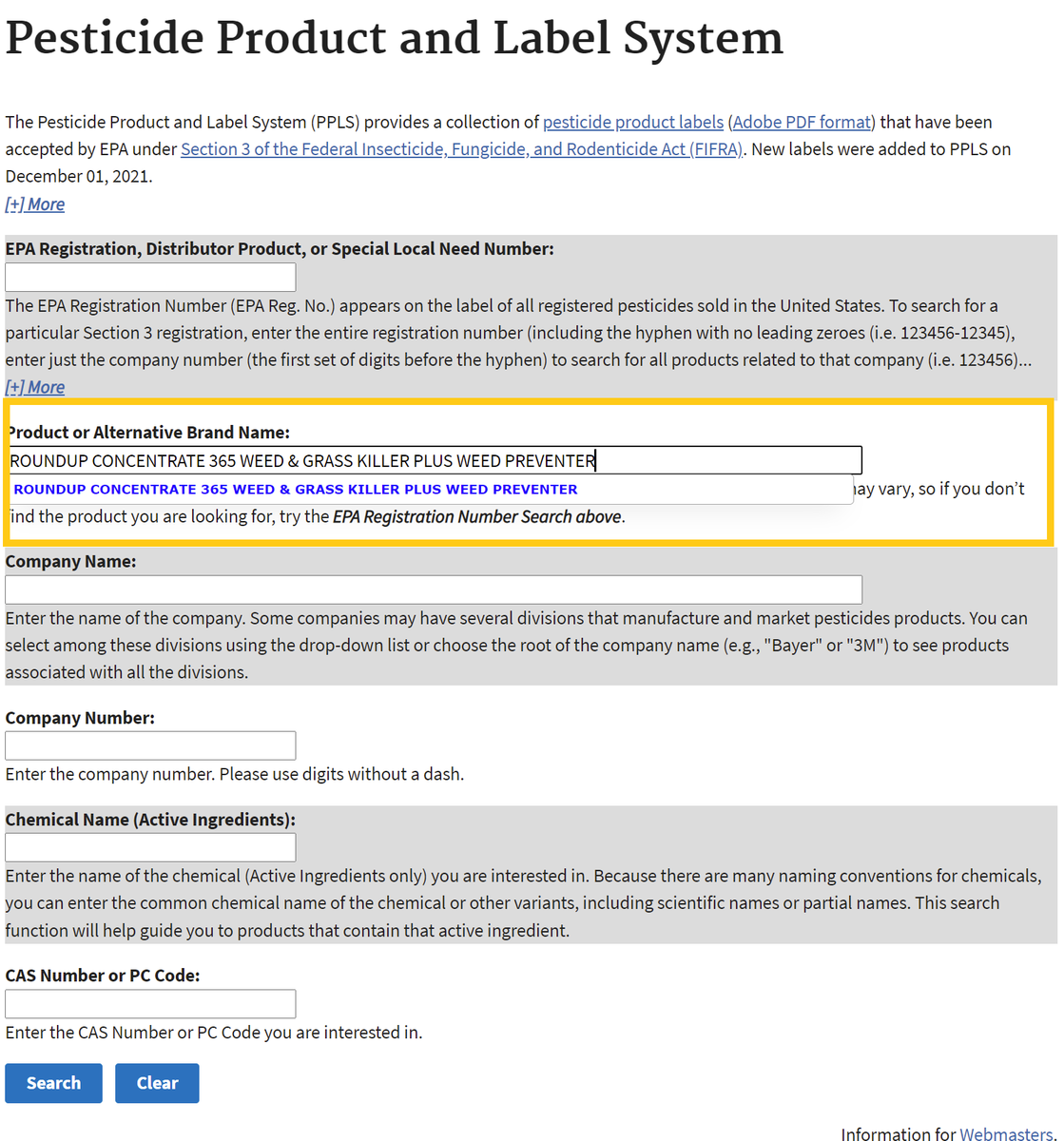
- After searching, click on the chemical ingredients tab or the link for the most recent label to find Active Ingredients.
Chemical List Label List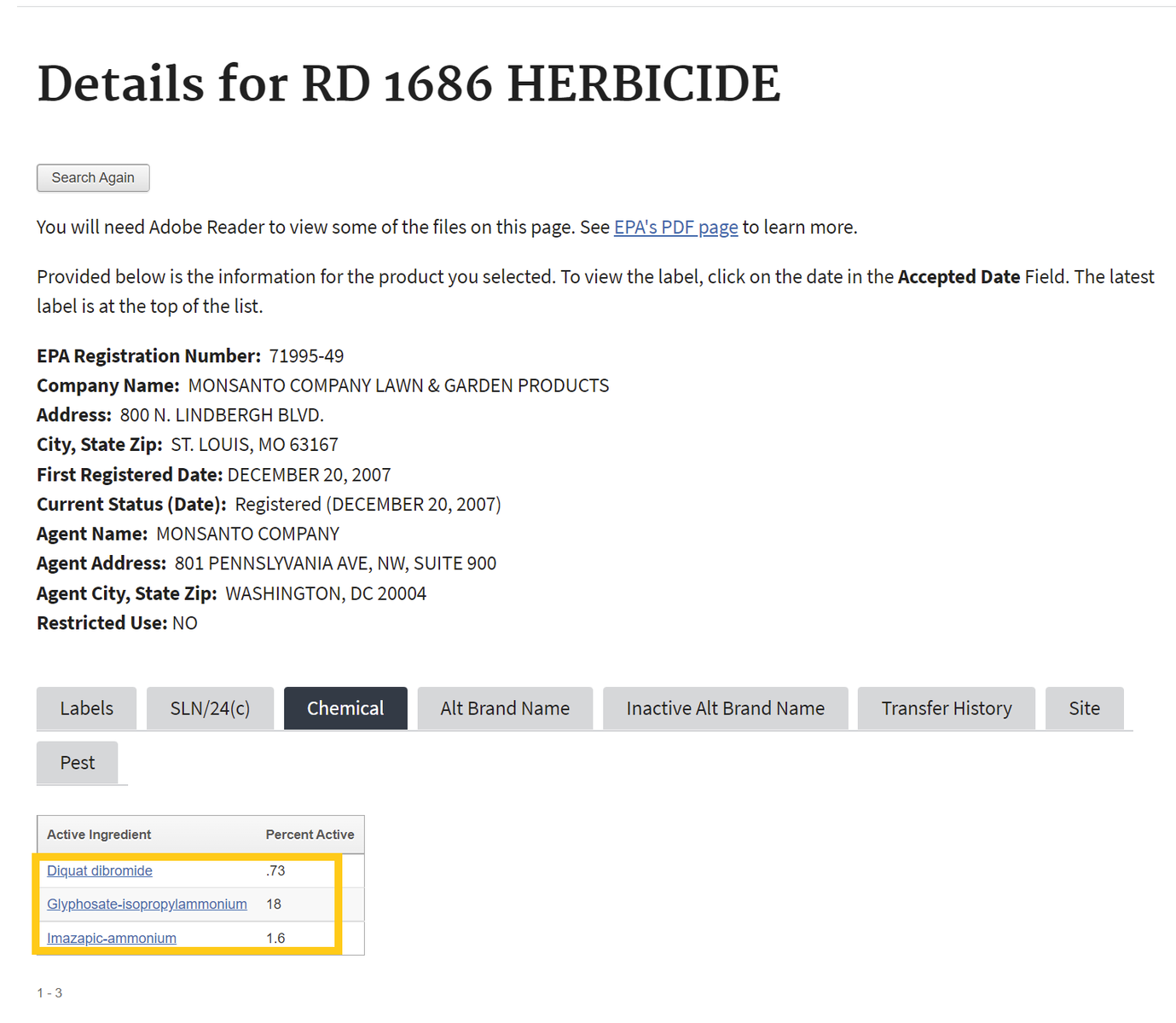
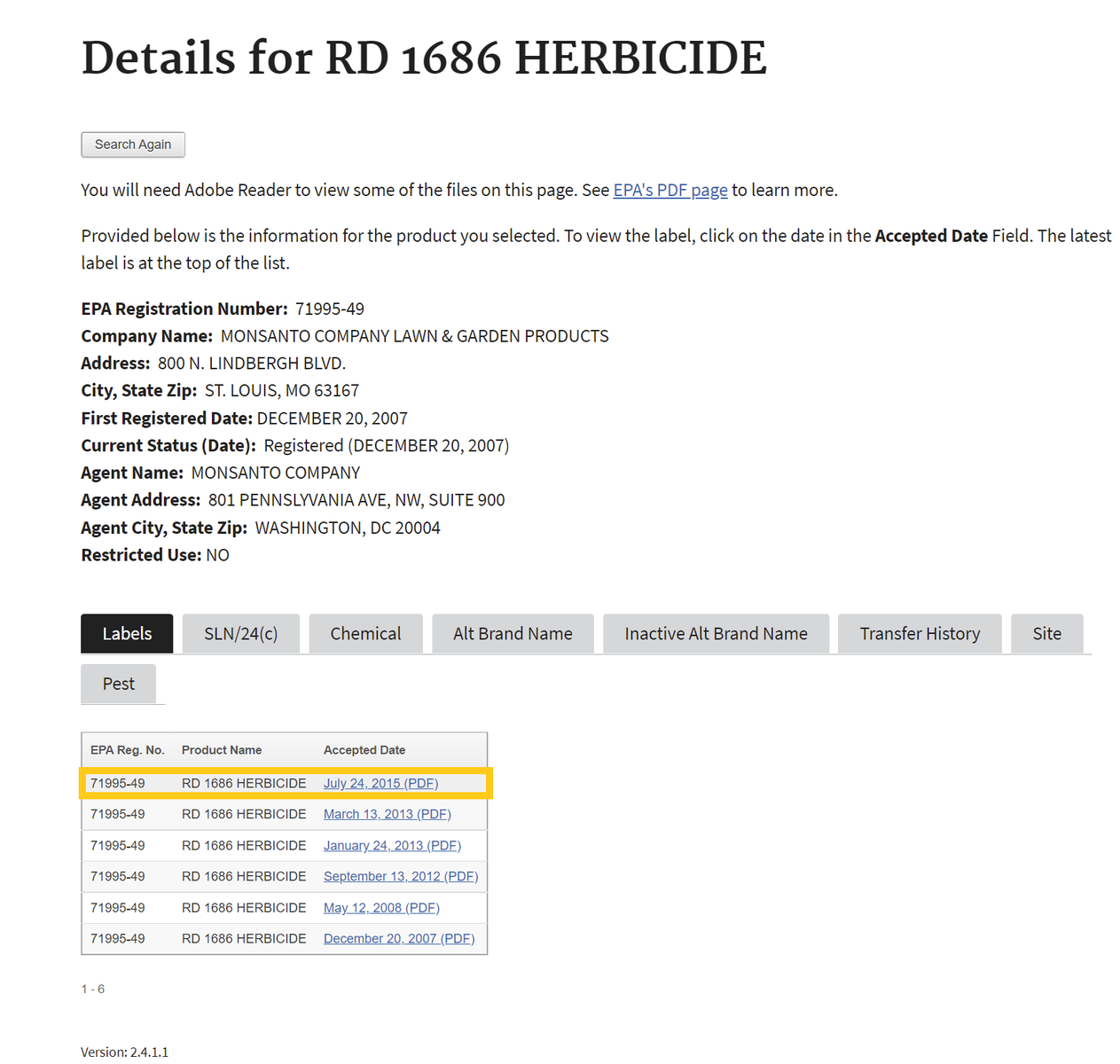
If one selects the chemical ingredients tab, skip to Step 4 . If not, proceed to step number 3 - To find the active ingredient(s) on the label, search for the page in the document containing the date of registration. Usually, the active ingredients section occurs within the first few pages of the label document.

- Return to the Beyond Pesticides Gateway and search for the active ingredient name in the yellow box to the right or from the list below.
Metolachlor
General Information
- Product Names:
- Chemical Class: Chloroacetanilide herbicide
- Uses: Control of grass and grasslike weeds and broadleaf weeds on terrestrial food crops: cabbage, pepper, radish and stone fruits; terrestrial food and feed crops: corn, cotton, legume vegetables, peanuts, peas, potato, safflower, sorghum, soybeans, treenuts, alfalfa (feed only); terrestrial non-food crops and outdoor residential: Rights-of-Way, golf courses, recreational areas and lawns, nonbearing fruits, ornamental and/or shade trees, ornamental plants and flowers, residential lawns; forest trees.
- Alternatives: Organic agriculture
- Beyond Pesticides rating: Toxic
Health and Environmental Effects
- Cancer: Possible (8)
- Endocrine Disruption: Suspected (43)
- Reproductive Effects: Yes (4)
- Neurotoxicity: Not documented
- Kidney/Liver Damage: Yes (4)
- Sensitizer/ Irritant: Yes (4)
- Birth/Developmental: Not documented
- Detected in Groundwater: Frequently (37)
- Potential Leacher: Not documented
- Toxic to Birds: Not documented
- Toxic to Fish/Aquatic Organisms: Yes (8)
- Toxic to Bees: Not documented
Additional Information
- Regulatory Status:
- EPA Reregistration Eligibility Decision (RED) signed (4/1995)
- Supporting information:
- Extoxnet Metolachlor Factsheet (Extension Toxicology Network)
- PAN Pesticide Database – Metolachlor (Pesticide Action Network)
- Studies:
- Assessment of genetic effects and pesticide exposure of farmers in NW Greece. Moshou, H., Karakitsou, A., Yfanti, F., Hela, D., Vlastos, D., Paschalidou, A.K., Kassomenos, P. and Petrou, I., 2020. Environmental Research, p.109558.
- Cancer incidence among pesticide applicators exposed to metolachlor in the Agricultural Health Study. Rusiecki, J.A., et al. 2006. Int J Cancer 118(12):3118-3123.
- Direct pesticide exposure of insects in nature conservation areas in Germany. Brühl, C.A., Bakanov, N., Köthe, S., Eichler, L., Sorg, M., Hörren, T., Mühlethaler, R., Meinel, G. and Lehmann, G.U. Scientific reports, 11(1), pp.1-10.
- Exposure to pesticides, persistent and non − persistent pollutants in French 3.5-year-old children: Findings from comprehensive hair analysis in the ELFE national birth cohort. Macheka, L. et al. (2024) Exposure to pesticides, persistent and non − persistent pollutants in French 3.5-year-old children: Findings from comprehensive hair analysis in the ELFE national birth cohort, Environment International. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0160412024004677.
- Estimating the aquatic risk from exposure to up to twenty-two pesticide active ingredients in waterways discharging to the Great Barrier Reef. Warne, M. et al. (2023) Estimating the aquatic risk from exposure to up to twenty-two pesticide active ingredients in waterways discharging to the Great Barrier Reef, Science of The Total Environment. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0048969723032552.
- The influence of polyethylene microplastics on pesticide residue and degradation in the aquatic environment. Wang, F., Gao, J., Zhai, W., Liu, D., Zhou, Z., & Wang, P. (2020). The influence of polyethylene microplastics on pesticide residue and degradation in the aquatic environment. Journal of hazardous materials, 394, 122517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122517
- A cocktail of contaminants: how mixtures of pesticides at low concentrations affect aquatic communities. Relyea R. A. (2009). A cocktail of contaminants: how mixtures of pesticides at low concentrations affect aquatic communities. Oecologia, 159(2), 363–376. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-008-1213-9
- Currently used and legacy pesticides in the marine atmosphere from Patagonia to Europe. Debler, F., Gandrass, J., Paul Ramacher, M. O., Koenig, A. M., Zimmermann, S., & Joerss, H. (2025). Currently used and legacy pesticides in the marine atmosphere from Patagonia to Europe. Environmental pollution (Barking, Essex : 1987), 373, 126175. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2025.126175
- Wastewater surveillance for assessing human exposure to pesticides: Investigating populations living near flower bulb fields. Bijlsma, L. et al. (2025) Wastewater surveillance for assessing human exposure to pesticides: Investigating populations living near flower bulb fields, Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2213343725017865.
- Bioaccumulation, metabolism and endocrine-reproductive effects of metolachlor and its S-enantiomer in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). Ou-Yang, K., Feng, T., Han, Y., Li, G., Li, J., & Ma, H. (2022). Bioaccumulation, metabolism and endocrine-reproductive effects of metolachlor and its S-enantiomer in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). The Science of the total environment, 802, 149826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149826
- Occurrence of Current-Use Pesticides in Paired Indoor Dust, Drinking Water, and Urine Samples from the United States: Risk Prioritization and Health Implications. Xie, Y., Li, J., Salamova, A., & Zheng, G. (2025). Occurrence of Current-Use Pesticides in Paired Indoor Dust, Drinking Water, and Urine Samples from the United States: Risk Prioritization and Health Implications. Environmental science & technology, 59(25), 12507–12519. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5c00961
- Acute and Subchronic Exposure of the Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio) to Herbicide S-Metolachlor. Rašković, Božidar, Vesna Poleksić, Gorica Vuković, Bojana Špirović Trifunović, Gavrilo Božić, Dejana Ćupić Miladinović, Zoran Marković, and Dragica Brkić. 2023. "Acute and Subchronic Exposure of the Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio) to Herbicide S-Metolachlor" Water 15, no. 23: 4182. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15234182








.png)


