27
Aug
Study Reveals Toxic Nanoparticles Persist in Food
(Beyond Pesticides, August 27, 2013) A new study by scientists at the University of Missouri College of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources is shedding light on the persistence of nanopesticides in our food. Researchers focused their attention on silver nanoparticles (nanosilver), a substance that has been linked to environmental harm, bacterial resistance, and not fully understood impacts on human health. Scientists say their findings represent a reliable method of testing foods for the harmful particles and hope to more broadly implement their technique in the future.
 The last decade has witnessed a large influx in the use of nanotechnology in consumer products, including food, clothing, cosmetics, fertilizers, and pesticides. The growth of this technology has elicited strong reactions from scientists across the globe, with many asserting that further research is urgently needed to evaluate the potential impacts of these novel substances. As Mengshi Lin, Ph.D, associate professor at the University of Missouri (MU) and co-author of the study states, “More than 1,000 products on the market are nanotechnology-based products. This is a concern because we do not know the toxicity of the nanoparticles. Our goal is to detect, identify and quantify these nanoparticles in food and food products and study their toxicity as soon as possible.”
The last decade has witnessed a large influx in the use of nanotechnology in consumer products, including food, clothing, cosmetics, fertilizers, and pesticides. The growth of this technology has elicited strong reactions from scientists across the globe, with many asserting that further research is urgently needed to evaluate the potential impacts of these novel substances. As Mengshi Lin, Ph.D, associate professor at the University of Missouri (MU) and co-author of the study states, “More than 1,000 products on the market are nanotechnology-based products. This is a concern because we do not know the toxicity of the nanoparticles. Our goal is to detect, identify and quantify these nanoparticles in food and food products and study their toxicity as soon as possible.”
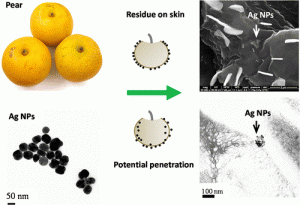
MU scientists began their testing by immersing several pears in a solution containing nanosilver at 20 nanometers (nm) and 70 nm, effectively mimicking a pesticide application. The team then repeatedly washed and rinsed the pears and observed the presence of nanoparticles on the pear’s skin and pulp. Results showed that both the 20 and 70nm nanosilver particles remained on the pears skin after 4 days, while the 20nm particles were in fact also able to penetrate the pear’s skin and reach the inside of the pear’s pulp. “The penetration of silver nanoparticles is dangerous to consumers because they have the ability to relocate in the human body after digestion,” Dr. Lin said. “Therefore, smaller nanoparticles may be more harmful to consumers than larger counterparts.”
The scientists note that, once ingested, nanoparticles can pass into the blood and lymph system, circulate through the body and reach potentially sensitive sites such as the spleen, brain, liver, and heart. Nanosilver’s presence in clothing and cosmetics provides another potential route of exposure. A recent study revealed that athletic wear impregnated with nanosilver can cause the substance to seep into a person’s skin through one’s sweat. A 2009 study showed that washing these types of nanosilver-impregnated textiles resulted in an unknown spread of the substance into the environment. Due to its small size, nanosilver is often not filtered out by conventional wastewater treatment plants. After entering the environment, past studies show nanosilver can have devastating impacts on wildlife, including deformities in fish and immune suppression in earthworms.
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has been criticized by scientists and consumer and environmental groups for its role in regulating emerging nanotechnology. A 2013 National Resources Defense Council (NRDC) report provided a scathing account of EPA’s “conditional” registration of nanosilver, which the agency approved under the assumption that its use would reduce the overall burden of conventional silver in the environment. However, despite its novel antibacterial properties, the material did not undergo a full range of required tests, and there is no labeling system that would alert consumers to the presence of this largely untested substance in consumer products. A 2012 industry newsletter placed EPA’s delay over nanotechnology regulation on White House officials in the Office of Management and Budget (OMB). Richard Denison, PhD, senior scientist at the Environmental Defense Fund explained, “My understanding is that there is a view in some circles in the White House that they do not want to stigmatize nanomaterials nor stifle the technology even by requiring the reporting of information that EPA needs to make judgments as to whether there are risks.”
The only surefire way to avoid nanomaterials in food is to buy USDA organic certified products. The National Organic Standards Board (NOSB) imposed a general ban over nanotechnology in its fall 2010 meeting, although USDA’s National Organic Program has never initiated rulemaking on the subject. The growth and success of organic agriculture shows that risky nanosilver pesticides are not necessary to feed the world. Organic practices that build soil and microbial diversity create natural pest resilience, and produce yields comparable to conventional agriculture. To find out more about the benefits certified organic products and production systems, visit Beyond Pesticides’ organic food program page.
Additional information on the regulatory history and risks associated with nanotechnology can be found on Beyond Pesticides’ nanosilver webpage.
Source: MU News Bureau
Image Source: Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry
All unattributed positions and opinions in this piece are those of Beyond Pesticides.










