
21
Mar
(Beyond Pesticides, March 21, 2024) Alarming levels of a hazardous pesticide plant growth regulator linked to reproductive and developmental effects, chlormequat, is found in 90% of urine samples in people tested, raising concerns about exposure to a chemical that has never been registered for food use in the U.S. but whose residues are permitted on imported food. Published in the Journal of Exposure Science and Environmental Epidemiology in February 2024 and led by Environmental Working Group toxicologist Alexis Temkin, PhD, a pilot study finds widespread chlormequat exposure to a sampling of people from across the country. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulations only permit the use of chlormequat on ornamental plants and not food crops grown in the U.S. As explained in the journal article, ‚ÄúIn April 2018, the U.S. EPA published acceptable food tolerance levels for chlormequat chloride in imported oat, wheat, barley, and some animal products, which permitted the import of chlormequat into the U.S. food supply.‚ÄĚ In 2020, EPA increased the allowable level of chlormequat in food. Then in April 2023, EPA proposed allowing the first-ever U.S. use of chlormequat on barley, oat, triticale (a hybrid of wheat and rye), and wheat. Existing regulatory standards explain the higher detections of the chemical in U.S. residents tested, as observed in the study and pending domestic use allowances will only increase exposure further. Advocates note that this study on one pesticide reflects systemic failures in the regulatory review process.¬†
Like many other pesticides, exposure to chlormequat raises significant concerns about the potential impact on public health, as animal studies have linked chlormequat to reduced fertility, harm to the reproductive system, and altered fetal growth, including negative impacts on reproduction and post-birth health, and proper weight and bone development. The study notes that published toxicological research has found potential health effects from chlormequat exposure at doses lower than the current regulatory limits set by the EPA and European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). 
Additionally, chlormequat residues are found in over 90% of conventional oat-based products, while organic food products showed minimal contamination. The report argues the necessity for ongoing biomonitoring to assess the potential health impacts of chlormequat exposure at environmentally relevant levels, especially during critical periods such as pregnancy. Advocates point to the chlormequat findings as evidence of the importance of supporting organic agriculture and organic food products as a means of avoiding harmful chemical exposure.
Research findings and methods
This study investigates the presence of chlormequat in urine samples collected from adults in the U.S. between 2017-2023. Study results detect chlormequat in most urine samples, with detection frequencies increasing from 69% in 2017 to 90% in 2023. Food products purchased in the U.S. and U.K. were also tested, with chlormequat found more frequently in U.S. non-organic oat products than wheat. U.K. oat food samples have 15 times higher chlormequat levels than U.S. samples. The study suggests exposure levels may rise further if chlormequat is approved for domestic agricultural use in the U.S. It raises potential health concerns given toxicology studies linking chlormequat exposure to reduced fertility and impacts on fetal growth.
Toxicological effects at doses lower than EPA’s allowed reference dose (and below the safety limit set by the European regulatory agency)
The pervasive presence of chlormequat in the U.S. population and its detection in conventional oat-based and some wheat-based products demand a comprehensive reevaluation of the risks associated with this chemical, which should raise alarm at the EPA‚Äôs current consideration of allowing chlormequat to be used in the U.S. on non-organic agricultural products. The report notes, ‚ÄúAdditionally, the regulatory thresholds do not consider the adverse effects of mixtures of chemicals that may impact the reproductive system, which have been shown to cause additive or synergistic effects at doses lower than for individual chemical exposures [22], raising concerns about the potential health effects associated with current exposure levels, especially for individuals on the higher end of exposure in general populations of Europe and the U.S.‚ÄĚ
Specifically, the report noted that animal studies showed:
- Mice and pigs exposed to doses under the EPA’s reference dose (allowed exhibited reduced fertility, harm to the reproductive system, and altered fetal growth.
- Pregnant mice exposed to a dose equal to the no observed adverse effect level used to set the EPA limit experienced altered fetal growth and metabolic/body composition changes in neonatal mice.
Additionally, the regulatory thresholds do not account for potential additive or synergistic effects from mixtures of chemicals that impact the reproductive system, as some studies have demonstrated.
This raises concerns that the current exposure levels in some populations, especially those with elevated exposures, could still pose health risks. The study argues that the toxicology research suggests a reevaluation of the safety thresholds may be warranted to better protect public health, and expanded biomonitoring is warranted. Beyond Pesticides advocates for consumers to avoid unnecessary exposure by eating organic food and certified organic food products and to support a systemic change to organic and regenerative organic agriculture.
Assessing chlormequat exposure in U.S. food products purchased between 2022 and 2023
To assess whether chlormequat levels detected in U.S. urine samples correspond to potential dietary exposure, analysis was conducted on oat and wheat-based food products acquired in the U.S. during 2022 and 2023. Results found that non-organic oat products contain chlormequat with a median concentration of 104 parts per billion (ppb). This variability could be attributed to differences in product sourcing, including domestic versus Canadian origins (chlormequat is widely used in Canadian grain crops, while not currently allowed in U.S. agriculture), and whether the oats were treated with chlormequat. In contrast, U.K. food samples demonstrated a higher prevalence of chlormequat, especially in wheat-based products like bread, where 90% of samples had detectable chlormequat levels, and in oat products, where levels were over 15 times higher than those found in U.S. samples. Beyond Pesticides reported in 2014 on U.K. contamination of bread supply, when it was found that over 60% of the country’s bread supply was tainted with chlormequat and glyphosate pesticide residues.  
The presence of chlormequat in urine samples prior to 2018 suggests exposure despite the absence of established food tolerance levels for this pesticide in the U.S. The study hypothesizes that such exposure likely resulted from dietary sources, considering chlormequat’s rapid degradation. According to the authors, ‚ÄúThese data indicate likely continuous exposure given the short half-life of chlormequat in vivo, with low levels from 2017 to 2022 and higher exposure levels in 2023.‚ÄĚ The formation of chlormequat from choline precursors in wheat and egg powder has been observed under the high temperatures used in food processing, leading to concentrations ranging from 5 to 40 ng/g. These findings imply that dietary exposure to chlormequat could stem from its formation during food processing and from imported products treated with chlormequat. Factors such as geographical location, dietary habits, and occupational exposure in environments like greenhouses could influence individual exposure levels.
This research underscores the need for a broader and more varied analysis of processed foods to thoroughly investigate potential dietary sources of chlormequat, especially in individuals with elevated exposure levels. Future research should encompass the examination of historical urine and food samples, alongside dietary and occupational surveys, to provide a comprehensive understanding of chlormequat exposure sources within the U.S. population. Given that chlormequat is presently restricted to imported oat and wheat products in the U.S., with its domestic use on non-organic crops under review by EPA, there is potential for increased chlormequat levels in the food supply and, consequently, higher exposure levels among the U.S. population.
This study constitutes the first biomonitoring of chlormequat presence in the urine of adults in the United States, expanding the scope of monitoring beyond limited research focused on the United Kingdom and Sweden. A comprehensive pesticide biomonitoring effort involving over 1,000 Swedish adolescents from 2000 to 2017 revealed a 100% detection rate for chlormequat, underscoring the widespread use of chlormequat in the UK, European Union (and Canada), and resulting human exposure levels. 
The discernible spike in urinary chlormequat concentrations in 2023, relative to preceding years, is potentially indicative of its recent introduction into the American food chain, a development that coincides with EPA  of permissible chlormequat levels in food in 2018 and an increase in these limits for oats in 2020.
In assessing whether the urinary chlormequat concentrations reflected potential dietary exposure, this research measured chlormequat levels in oat and wheat-based food products available in the U.S. market in 2022 and 2023. Oat products exhibited a higher frequency of chlormequat presence compared to wheat products, with significant variability in chlormequat content among oat-based items, potentially attributable to differences in sourcing of oats from the U.S. versus Canada. The study suggests that exposure to chlormequat predates 2018, prior to the establishment of food tolerance levels in the U.S., hypothesizing that such exposures were likely dietary in nature given chlormequat’s short half-life. The absence of chlormequat monitoring in U.S. food products and historical data complicates this assertion. However, the natural formation of chlormequat from choline precursors under high-temperature conditions typical of food processing has been documented, leading to chlormequat concentrations within a similar specific range. The variability in chlormequat levels observed in food samples, including those from the only organic oat-based product out of eight organic oat products tested, had low levels of chlormequat, aligning with this phenomenon of natural formation, and suggesting dietary exposure as a plausible source of the pre-2023 urinary chlormequat levels. The elevated levels detected in 2023 may result from dietary exposure to naturally occurring chlormequat and the consumption of imported, chlormequat-treated products. What is unequivocal is the widespread use of chlormequat in Canada, the U.K., and the European Union, where, as previously noted, human biomonitoring studies showed the U.K. and Sweden have almost 100% exposure in the population tested.¬†
Solutions found in buying organic oat and wheat products, supporting organic farming
Organic food products have been found to have zero contact with pesticides unless due to herbicidal drift from other farming operations. The best defense against pesticide exposure is, whenever possible, choosing to purchase and consume organic. For more information on pesticide residue exposure for different organic versus non-organic forms of common produce, please check out the pages on Eating with a Conscience and Buying Organic Products (on a budget!). For those with some background experience or interest in gardening, see Grow Your Own Organic Food for best practices, tips, and resources to get started. If you believe that you were exposed to pesticides, please click to access our section on Pesticide Emergencies.
Beyond Pesticides continues to closely monitor potential EPA actions to register chlormequat for use in the U.S. on non-organic crops. Click here to subscribe to action alerts and a weekly newsletter of the Daily News! 
All unattributed positions and opinions in this piece are those of Beyond Pesticides.
Sources
A pilot study of chlormequat in food and urine from adults in the United States from 2017 to 2023, Journal of Exposure Science and Environmental Epidemiology, February 15, 2024 https://www.nature.com/articles/s41370-024-00643-4 
A mixture of 15 phthalates and pesticides below individual chemical no observed adverse effect levels (NOAELs) produces reproductive tract malformations in the male rat, Environment International, November 2021 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0160412021002403
Maternal chlormequat chloride exposure disrupts embryonic growth and produces postnatal adverse effects, Toxicology, September 2020 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32622971/
Currently used pesticides and their mixtures affect the function of sex hormone receptors and aromatase enzyme activity, Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 2013 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0041008X13003013  
Posted in Agriculture, Alternatives/Organics, chemical sensitivity, Chemicals, chlormequat, contamination, Disease/Health Effects, Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), Infertility, multi-generational effects, Pesticide Mixtures, Pesticide Regulation, Pesticide Residues, Regenerative, Reproductive Health, Respiratory Diseases, Respiratory Problems, synergistic effects, Uncategorized by: Beyond Pesticides
No Comments
20
Mar
(Beyond Pesticides, March 20, 2024) A report by CBAN unpacks the ecosystem and wildlife health impacts of genetically engineered (GE) corn in the context of Mexico’s 2023 decision to stop its importation into the country. The phase out of genetically modified (GM) corn imports into Mexico was immediately challenged by the U.S. and Canadian governments as a trade violation under the 2020 U.S.-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA), which replaced the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) as the primary vehicle for North American trade policy. In August 2023, the U.S. Trade Representative set up a dispute settlement panel under USMCA to stop Mexico from going forward with its ban. There has been no public update from the Office of the U.S. Trade Representative as of this writing.
The CBAN report highlights the scientific rationale underpinning Mexico‚Äôs decision to ‚Äúsafeguard the integrity of native corn from GM contamination and to protect human health‚ÄĚ with this ban. In 2020, Mexico announced a four-year phase-out of the weed killer glyphosate, which along with other petrochemical herbicides is integral to GM corn production. When Mexico‚Äôs Minister of the Environment announced the phase-out, he said it is part of an effort to transform the country‚Äôs food system to one that is ‚Äúsafer, healthier and more respectful of the environment (m√°s seguro, m√°s sano y respetuoso con el medio ambiente).‚ÄĚ The Minister said that Mexico would be looking to Indigenous farming practices as an alternative. In addition to traditional agriculture, Beyond Pesticides points to organic agricultural practices as a systems approach that simultaneously prohibits the use of toxic petrochemical pesticides such as glyphosate and genetically engineered crops.
The CBAN report explains the background on the USMCA trade deal:
“The United States and Canada are challenging the measures in Mexico’s Presidential Decree of February 13, 2023 that pertain to the use of genetically modified [corn]:
- [A]n immediate ban on the use of GM corn for human consumption (white corn intended for use in dough and tortillas);
- [T]he revocation of existing GM corn authorizations and a halt to future approvals; and
- [A] phase-out of the use of GM corn for animal feed and processed food ingredients.
Mexico‚Äôs decree also phases out the use of the herbicide glyphosate but this measure is not being challenged by the US and Canada. Mexico already bans the cultivation of GM corn.‚ÄĚ
The USMCA was adopted with the stated goal of creating ‚Äúa more balanced environment for trade, will support high-paying jobs for Americans, and will grow the North American economy.‚ÄĚ
In deciding to ban GE corn, Mexico compiled a database of scientific studies that document the health impacts to insects, pollinators, and animals fed GE corn, as well as the adverse health impacts of glyphosate on humans. In addition to herbicide-tolerant GE crops, the CBAN report states, ‚ÄúMost GM corn plants are genetically modified to kill insect pests. The GM plants express a toxin from the soil bacteria Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) that is known to harm the guts of specific types of insects but not others. Farmers have long used Bt as a spray to kill pests but the Bt toxins in GM crops are different from this natural Bt in structure, function, and biological effects.‚ÄĚ The report continues, ‚ÄúIn fact, peer-reviewed studies across the scientific literature continue to find that Bt toxins in GM plants can harm insects (spiders, wasps, ladybugs, and lacewings, for example) that are not the intended targets.‚ÄĚ
Similar to the threat of pesticide drift is the threat of genetic drift -typically pollen from a GE crop field being carried by wind or pollinators like honey bees, which are known to travel six miles or further. The National Organic Standards Board, in a unanimous vote in the spring of 2012, sent a letter¬†to Secretary of Agriculture Tom Vilsack saying, ‚ÄúWe see the potential of contamination by genetically engineered crops as a critical issue for organic agricultural producers and the consumers of their products. There are significant costs to organic producers and handlers associated with preventing this contamination and market loss arising from it.‚Ä̬†
Within Mexico, there is over a decade of judicial and executive actions against the spread of GE and genetically modified crops, as well as the use of toxic petrochemical pesticides. As reported by Beyond Pesticides in 2013: ‚Äú[A] judge in Mexico issued an injunction against the planting and selling of genetically engineered (GE) corn seed, effective immediately, within the country‚Äôs borders. The decision comes nearly two years after the Mexican government temporarily rejected the expansion of GE corn testing, citing the need for more research. The decision prohibits agrichemical biotech companies, including Monsanto, DuPont Pioneer, Syngenta, PHI Mexico, and Dow AgroSciences, from planting or selling GE corn seed in Mexico.‚ÄĚ Then in 2020, Mexico announced the phase out of glyphosate from use or importation into the country by 2024. Mexico joins several other nations that have issued bans, including Germany (the country where Bayer was founded), Luxembourg, and Vietnam. See Genetic Engineering for a list of resources regarding state and local action against GE crops and the corresponding section on Daily News.
The U.S. government and corporate agribusinesses have a history of intervening when other countries or advocates in the U.S. move to ban glyphosate use or advance restrictions on genetically engineered or modified crops. Farmers and environmentalists have taken action in an effort to prevent the proliferation of new pesticide products, including Enlist Duo (glyphosate and 2,4 D hybrid with inert ingredients). A 2017 Daily News reported that: ‚Äú[A] coalition of farmers and environmental and public health organizations filed a lawsuit against the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) for approving agrochemical giant Dow Chemical‚Äôs toxic pesticide combo, Enlist Duo, among the newer more highly toxic pesticide mixtures used in genetically engineered (GE) herbicide-tolerant crops. Comprised of glyphosate and 2,4-D (50% of the mixture in the warfare defoliant Agent Orange), Enlist Duo is typically marketed alongside commercial crops like corn, cotton and soybeans that are engineered to withstand pesticide exposure, leading to problems of resistance and driving the evolution of super weeds.‚ÄĚ A 2023 Daily News reported, ‚ÄúBritish biotechnology company Oxitec is withdrawing its application to release billions of genetically engineered mosquitoes in California, according to a recent update from the California Department of Pesticide Regulation.‚ÄĚ EPA approved the us[e of] a nucleic acid‚ÄĒdouble-stranded RNA (dsRNA)‚Äďcalled ‚Äúinterfering RNA, or RNAi‚ÄĒto silence a gene crucial to the survival of the Colorado Potato Beetle (CPB), the scourge of potato farmers around the world. (See Daily News.)
Beyond Pesticides continues to support advocates who are passionate in our mission statement of abolishing toxic petrochemical pesticides by 2032. In the spirit of human and ecological health, advocates in our network believe that organic land management and farming principles are the primary pathway forward to make these toxic practices obsolete. See Organic Agriculture and Keeping Organic Strong to learn about the health and environmental benefits of organic land management principles and opportunities to strengthen the National Organic Program as the next National Organics Standards Board (NOSB) meeting begins at the end of this month. See Parks for a Sustainable Future to learn more about the importance of organic land management principles in the context of public parks at the city and county level.
All unattributed positions and opinions in this piece are those of Beyond Pesticides.
Source: Canadian Biotechnology Action Network
 
Posted in Contamination, Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), Genetic Engineering, International, Pesticide Drift, Pollinators, Uncategorized by: Beyond Pesticides
2 Comments
19
Mar
(Beyond Pesticides, March 19, 2024) This month the United Nations Environmental Programme (UNEP) announced the creation of a new initiative to combat the health and environmental impacts of toxic petrochemical pesticides in agriculture. Launched by seven countries‚ÄĒEcuador, India, Kenya, Laos, Philippines, Uruguay, and Vietnam‚ÄĒthe Financing Agrochemical Reduction and Management (FARM) Programme is a $379 million initiative that ‚Äúwill realign financial incentives to prevent the use of harmful inputs in food production.‚ÄĚ This international cohort aims to phase out the use of ‚Äútoxic persistent organic pollutants (POPs)‚ÄĒchemicals which don‚Äôt break down in the environment and contaminate air, water, and food.‚ÄĚ The work of FARM echoes Beyond Pesticides call for the banning of toxic petrochemical pesticides by 2032.
The program will help countries implement their commitment to eliminate POPs and plastics in agriculture. As it is described, ‚ÄúFARM…will support government regulation to phase out POPs-containing agrochemicals and agri-plastics and adopt better management standards, while strengthening banking, insurance and investment criteria to improve the availability of effective pest control, production alternatives and trade in sustainable produce.‚ÄĚ The 2001 Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants requires signatories to adopt a range of measures to reduce and, where feasible, eliminate the release of POPs. All FARM members are signatories and most ratified the Convention as of 2006, with Laos being the most recent to ratify in 2013.
‚ÄúThe five-year programme is projected to prevent over 51,000 tons of hazardous pesticides and over 20,000 tons of plastic waste from being released,‚ÄĚ according to the latest UNEP press release. ‚Äú[W]hile avoiding 35,000 tons of carbon dioxide emissions and protecting over 3 million hectares of land from degradation as farms and farmers convert to low-chemical and non-chemical alternatives,‚ÄĚ the release continues. FARM is supported by the Global Environmental Facility, UN Development Programme, UN Industrial Development Organization, and the African Development Bank. The goal of FARM is, ‚Äúfor banks and policy-makers to reorient policy and financial resources towards farmers to help them adopt low- and non-chemical alternatives to toxic agrochemicals and facilitate a transition towards better practices.‚ÄĚ Beyond Pesticides applauds this important step FARM countries are taking to transition away from pesticide dependency; however advocates reiterate the importance of organic land management principles as an opportunity to adopt a systems change framework rather than a product substitution framework that replaces toxic pesticides with less toxic pesticides. According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), POPs are ‚Äúintentionally produced chemicals currently or once used in agriculture, disease control, manufacturing, or industrial processes‚ÄĚ and ‚Äúunintentionally produced chemicals…that result from some industrial processes and from combustion.‚ÄĚ
There are cascading socio-ecological impacts of toxic pesticides, including POPs, that has been widely documented. (See Daily News.) Organochlorine compounds (OCs), including organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), are examples of persistent organic pollutants that cause adverse health impacts to wildlife including humpback whales and pandas. A 2021 study published in Environmental Pollution identifies, among female whale populations, ‚Äúlevels of POPs in blubber are higher in juveniles and subadults than in adults, primarily from the transference of contaminants from the mother to her calf.‚ÄĚ The study goes on to report previously unknown adverse health impacts, ‚Äúincluding reproductive toxicity, immune dysfunction, and increased susceptibility to disease.‚ÄĚ Meanwhile, a 2021 study published in Environmental Pollution found that the ‚ÄúQuinling Panda species [‚Äėthe rarest subspecies of giant pandas‚Äô] are generally exposed to moderate levels of OC pollution. Higher levels of OCs are present in captive pandas relative to wild pandas. The authors identify PCB and OCP residues as coming from atmospheric transportation. At the same time, the study identifies PCBs as a cancer risk to the pandas, in fact the most notable toxicant with the highest carcinogenic risk index of PCB 126 (the most potent highly toxic industrial byproduct that incites numerous adverse physiological effects).‚ÄĚ
Beyond individual animal species, POPs are emerging in remote ecosystems such as coral reefs and Arctic glaciers, leading to harmful impacts and long-term implications for biodiversity and human health. A 2021 study published in Chemosphere based on coral reefs in the South China Sea, ‚Äúindicate[d that] 17 of the 22 OCPs are detectable in seawater, and all 22 OCPs are detectable in ambient air samples from the SCS. The most prominent chemicals found in air and water samples are CHLs, HCBs, DDTs, and Drins. Although coastal corals have higher chemical concentrations than offshore species, the chemical composition is similar, with DDT and CHL¬†compounds dominant among tissue samples.‚ÄĚ The presence of OCPs in the South China Sea raises serious concerns about the long-term biodiversity impacts as they cause adverse health impacts on animals and humans alike, including ‚Äúrespiratory issues, nervous system disorders, and birth deformities to various common and uncommon cancers.‚ÄĚ A 2020 study published in Environmental Science and Technology found that POPs are found to be re-released after bioaccumulating in Arctic ice for decades, exacerbating the potential exposure levels facing marine animals, oceans, and humans as the climate crisis rages on and causes Arctic ice to melt in the coming decades. POPs are also found to have adverse health impacts on humans, including prenatal and early-life exposure leading to chronic illnesses such as developmental disorders to cancer. Persistent organic pollutants can also act like endocrine disruptors and studies link their exposure to female reproductive health disorders such as endometriosis.
As the U.S. EPA states, ‚ÄúMany POPs were widely used during the boom in industrial production after World War II, when thousands of synthetic chemicals were introduced into commercial use.‚ÄĚ After the war, the chemical industry looked to commercialize the petrochemical pesticide products for use in pest management and public health. ‚ÄúJust as U.S. industry and public forged an alliance to prepare for World War II, advocates must join with farmers, public health advocates, scientists, and elected officials to demand a new regulatory approach in service of public health, environmental justice, and addressing the climate crisis,‚ÄĚ says Max Sano, organic program associate at Beyond Pesticides. Advocates are steadfast in their belief that strengthening federal organic policy and standards will address the proliferation of toxic petrochemical pesticides into soil, waterways, and ecosystems. See Keeping Organic Stronger to learn how to engage in the National Organic Standards Board April meeting and public comment periods to engage in protecting and expanding climate-health-soil protections for the National Organic Program. See Pesticide-Induced Disease Database and Gateway on Pesticide Hazards and Safe Pest Management to view an ongoing list of scientific studies that link pesticide exposure, such as POPs, to chronic illnesses to learn how to engage with elected officials and participate in regulatory reviews with the aim of strengthening their regulation and minimizing additional exposure levels.
All unattributed positions and opinions in this piece are those of Beyond Pesticides.
Source: United Nations Environment Programme
Posted in Breakdown Chemicals, Chemicals, International, organochlorines, Plastic, Uncategorized, United Nations by: Beyond Pesticides
No Comments
18
Mar
(Beyond Pesticides, March 18, 2024) Comments are due by 11:59 pm EDT on April 3, 2024. Organic standard setting provides for democratic input, full transparency, and continuous improvement. The current public comment period is an important opportunity for the public to engage with the organic rulemaking process to ensure that the National Organic Standards Board (NOSB) and the USDA National Organic Program uphold the values and principles set forth in the Organic Foods Production Act (OFPA). With the threats to health, biodiversity, and climate associated with petrochemical pesticide and fertilizer use in chemical-intensive land management, advocates stress that this is critical time to keep organic strong and continually improving.
Organic maintains a unique place in the food system because of its high standards, public input, inspection system, and enforcement mechanism. But, organic will only grow stronger if the public participates in voicing positions on key issues to the NOSB, a stakeholder advisory board. Beyond Pesticides has identified key issues for the upcoming NOSB meeting below!
The NOSB is receiving written comments from the public on key issues through April 3, 2024. This precedes the upcoming public comment webinar on April 23 and 25 and the deliberative hearing on April 29 through May 1‚ÄĒconcerning how organic food is produced.¬†Written comments must be submitted by 11:59 pm EDT on April 3¬†through the¬†“click-and-submit” form linked¬†or via¬†Regulations.gov.
Sign up for a 3-minute comment to let U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) know how important organic is at the webinar by April 3. Links to the virtual comment webinars will be provided approximately one week before the webinars.  
>>Submit your written comment HERE to the National Organic Standard Board by April 3. (See high-priority issues below.)
The NOSB is responsible for guiding USDA in its administration of The Organic Foods Production Act (OFPA), including the materials allowed to be used in organic production and handling. The role of the NOSB is especially important as we depend on organic production to protect our ecosystem, mitigate climate change, and enhance our health. 
A draft meeting agenda is available¬†here.‚ÄĮ¬†And a detailed agenda, along with the proposals, are available¬†here.¬†
Written comments are due by 11:59 pm ET on Wednesday, April 3, 2024, as well as registration for oral comments. Oral comment sign-ups fill up fast! >> Sign up for oral comments here.  
The NOSB plays an important role in bringing the views of organic consumers and producers to bear on USDA, which is not always in sync with organic principles and not giving sufficient support to the critical need to end the use of petrochemical pesticides and fertilizers. There are many important issues on the NOSB agenda this Spring.¬†For a complete discussion, see¬†Keeping Organic Strong¬†and the¬†Spring 2024 Beyond Pesticides’ issues¬†webpage. ¬†
Some of our high-priority issues for the upcoming NOSB meeting: 
- Reject the petition to allow unspecified ‚Äúcompostable materials‚ÄĚ in compost allowed in organic production. Compost made in organic production should use plant and animal waste, and not synthetic materials that could introduce hazardous contaminants like¬†PFAS¬†and¬†microplastics. The current regulations require compost to be made from manure and plant wastes, allowing only synthetics on the National List‚ÄĒthat is, those that have specifically been approved by the NOSB and USDA through a public comment process. The only synthetic inputs into compost that are currently allowed are newspaper and other paper. A¬†petition seeks to allow ‚Äúcompost feedstocks‚ÄĚ that might include, for example, ‚Äúcompostable‚ÄĚ food containers.¬†
Both organic and nonorganic farms¬†have been taken out of production¬†because of PFAS contamination, and microplastics can have a¬†synergistic effect¬†with PFAS. Even worse are potential contaminants we don’t know. Current PFAS contamination came from past use of biosolids not known to be a source of ‚Äúforever chemicals.‚ÄĚ Biosolids‚ÄĒfortunately never allowed in organic production‚ÄĒshould be a lesson to remember.¬†¬†
- Eliminate nonorganic ingredients in processed organic foods as a part of the sunset review. Materials listed in ¬ß205.606 in the organic regulations are nonorganic agricultural ingredients that may comprise 5% of organic-labeled processed foods. The intent of the law is to allow restricted nonorganic ingredients (fully disclosed and limited) only when their organic form is not available. However, materials should not remain on ¬ß205.606 if they can be supplied organically, and we can now grow virtually anything organically. The Handling Subcommittee needs to ask the question of potential suppliers, ‚ÄúCould you supply the need¬†if the organic form is required?‚ÄĚ The materials on ¬ß205.606 up for sunset review this year are made from agricultural products that can be supplied organically and thus should be taken off the National List of allowed materials.¬†
 
- Ensure that so-called ‚Äúinert‚ÄĚ ingredients in the products used in organic production meet the criteria in OFPA with an NOSB assessment.¬†The NOSB has passed repeated recommendations instructing USDA’s National Organic Program (NOP) to replace the generic listings for ‚Äúinerts‚ÄĚ that may be biologically and chemically active¬†(currently using¬†EPA Lists 3, 4A, and 4B ‚Äúinerts‚ÄĚ) with specific substances approved for use. NOP must allocate resources for this project. Recent appropriations have increased for NOP, and some of this money must be used for the evaluation of ‚Äúinert‚ÄĚ ingredients to ensure compliance with the law and to maintain the integrity of the USDA organic label.
OFPA provides stringent criteria for allowing synthetic materials to be used in organic production. In short, the NOSB must judge‚ÄĒby a supermajority‚ÄĒthat the material would not be harmful to human health or the environment, is necessary to the production or handling of agricultural products, and is consistent with organic farming and handling. These criteria have been applied to ‚Äúactive‚ÄĚ ingredients, but not to ‚Äúinert‚ÄĚ ingredients, which make up the largest part of pesticide products‚ÄĒup to 90% or more.
A comparison of the hazards posed by active and ‚Äúinert‚ÄĚ ingredients used in organic production reveals that in seven of 11 categories of harm, more ‚Äúinerts‚ÄĚ than actives pose a hazard. The NOSB and NOP must act on ‚Äúinerts‚ÄĚ NOW and meet OPFA standards.
>> Submit your written comment HERE to the National Organic Standard Board by April 3. 
Comment to NOSB
I would like to address three priority issues in this comment that are of concern to me as a stakeholder in organic.
(1) Reject the petition to allow unspecified ‚Äúcompostable materials‚ÄĚ in compost allowed in organic production.
Compost made in organic production should use plant and animal waste, and not synthetic materials that could introduce hazardous contaminants like PFAS and microplastics. The current regulations require compost to be made from manure and plant wastes, allowing only synthetics on the National List‚ÄĒthat is, those that have specifically been approved by the NOSB and USDA through a public comment process. The only synthetic inputs into compost that are currently allowed are newspaper and other paper. A petition seeks to allow ‚Äúcompost feedstocks‚ÄĚ that might include, for example, ‚Äúcompostable‚ÄĚ food containers.¬†
Both organic and nonorganic farms have been taken out of production because of PFAS contamination, and microplastics can have a synergistic effect with PFAS. Even worse are potential contaminants we don‚Äôt know. Current PFAS contamination came from past use of biosolids not known to be a source of ‚Äúforever chemicals.‚ÄĚ Biosolids‚ÄĒfortunately never allowed in organic production‚ÄĒshould be a lesson to remember.
(2) Eliminate nonorganic ingredients in processed organic foods as a part of the sunset review.
Materials listed in ¬ß205.606 in the organic regulations are nonorganic agricultural ingredients that may comprise 5% of organic-labeled processed foods. The intent of the law is to allow restricted nonorganic ingredients (fully disclosed and limited) only when their organic form is not available. However, materials should not remain on ¬ß205.606 if they can be supplied organically, and we can now grow virtually anything organically. The Handling Subcommittee needs to ask the question of potential suppliers, ‚ÄúCould you supply the need if the organic form is required?‚ÄĚ The materials on ¬ß205.606 up for sunset review this year are made from agricultural products that can be supplied organically and thus should be taken off the National List of allowed materials.
(3) Ensure that so-called ‚Äúinert‚ÄĚ ingredients in the products used in organic production meet the criteria in OFPA with an NOSB assessment.
The NOSB has passed repeated recommendations instructing USDA‚Äôs National Organic Program (NOP) to replace the generic listings for ‚Äúinerts‚ÄĚ that may be biologically and chemically active¬† (currently using EPA Lists 3, 4A, and 4B ‚Äúinerts‚ÄĚ) with specific substances approved for use. NOP must allocate resources for this project. Recent appropriations have increased for NOP, and some of this money must be used for the evaluation of ‚Äúinert‚ÄĚ ingredients to ensure compliance with the law and to maintain the integrity of the USDA organic label.
OFPA provides stringent criteria for allowing synthetic materials to be used in organic production. In short, the NOSB must judge‚ÄĒby a supermajority‚ÄĒthat the material would not be harmful to human health or the environment, is necessary to the production or handling of agricultural products, and is consistent with organic farming and handling. These criteria have been applied to ‚Äúactive‚ÄĚ ingredients, but not to ‚Äúinert‚ÄĚ ingredients, which make up the largest part of pesticide products‚ÄĒup to 90% or more.
A comparison of the hazards posed by active and ‚Äúinert‚ÄĚ ingredients used in organic production reveals that in seven of 11 categories of harm, more ‚Äúinerts‚ÄĚ than actives pose the hazard. The NOSB and NOP must act on ‚Äúinerts‚ÄĚ NOW and meet the standards of the Organic Foods Production Act.
Thank you for your consideration of my comments.
Posted in Agriculture, Alternatives/Organics, Announcements, Biosolids, compost, contamination, National Organic Standards Board/National Organic Program, Organic Foods Production Act OFPA, Pesticide Regulation, PFAS, Take Action, Uncategorized, US Department of Agriculture (USDA) by: Beyond Pesticides
No Comments
15
Mar
(Beyond Pesticides, March 15, 2024) Toxic pesticides harm all beings and ecosystems, including coral reefs. Large benthic foraminifera (LBF) are single-celled organisms found on reefs that face adverse metabolic impacts after exposure to the weed killer glyphosate, fungicide tebuconazole, and insecticide imidacloprid, according to a study published in Marine Pollution Bulletin. The study found that ‚Äúeven the lowest doses of the fungicide and herbicide caused irreparable damage to the foraminifera and their symbionts.‚ÄĚ Beyond Pesticides reiterates our mission of banning toxic petrochemical pesticides by 2032 and that this goal applies to land and water exposure to pesticides. LBFs are typically used as bioindicators for coral health because they are found in substantial quantities and gathering data is not intrusive or damaging to reef health.
Researchers in this study screened three different pesticides (one insecticide, one fungicide, and one herbicide) at three different concentration levels. The experiments were performed in six well-samples, each with 10mL of filtered artificial seawater and a singular LBF. The control plates are artificial seawater and the experimental plates include artificial seawater with the addition of three pesticides (imidacloprid, glyphosate, and tebuconazole). Each pesticide was applied at low, medium, and high doses to measure the direct impacts of each pesticide after dilution in seawater. The research team conducted two different experiments, one based on pulse-amplitude-modulation (PAM) fluorometry and the other to measure isotopic uptake. For the PAM fluorometry experiment the researchers ‚Äúmeasured the photosynthetic performance of the photosymbionts [an organism in a photosymbiotic relationship] for two weeks at days 1, 3, 5, 7 and 14 using variable chlorophyll fluorescence imaging of photosystem II (PSII; Imaging PAM Microscopy Version‚ÄďWalz GmbH; excitation at 620 nm). Measurement of the variable fluorescence over the maximum quantum yield fluorescence (Fv/fm) estimates the efficiency of photosystem II []. Fv/fm serves as a proxy for the vitality of the photosymbionts [] and therefore it can be used as an indicator of the health of the foraminifera themselves [].‚ÄĚ In terms of the isotopic uptake experience, ‚ÄúTwo-way ANOVAs (level of significance p = 0.05) were run to test if the type of pesticide, the concentration and/or incubation time significantly affected uptake of 15N and 13C, respectively. Significant results were further analyzed for group differences using Tukey’s post hoc test (level of significance p = 0.05).‚ÄĚ
This study differs from existing literature in how the researchers quantified the impact based on amount of pesticide products rather than solely on the individual pesticides that make up the main ingredient of the targeted products. ‚ÄúRoundup¬© [with the active ingredient glyphosate] only contains 1 % glyphosate, in Pronto¬©Plus the active substance tebuconazole has 13.6 % and in Confidor¬© the imidacloprid concentration is 20 %, according to the manufacturer’s information,‚ÄĚ says the research team. ‚ÄúBased on that, the concentration of active pesticide substances, which can be found in the environment are not a factor of 10 smaller than ours tested, they are approximately the same concentration or even 10 times higher.‚ÄĚ The scientists in this study found that, ‚Äúthe photosynthetic area decreased as the amount of pesticide added increased and as the incubation time increased.‚ÄĚ Glyphosate-based Roundup Ready in particular ‚Äúcaused a reduction of the photosynthetic area in all foraminifera…independent of concentration.‚ÄĚ The scientists also found that, ‚ÄúForaminiferal [inorganic carbon] 13C uptake was significantly reduced at the highest pesticide concentration compared to the control (p < 0.001). The herbicide and fungicide showed comparable reductions of 13C uptake (p = 0.945), the reduction caused by the insecticide was less pronounced.‚ÄĚ
Oceans and water advocates continue to remind elected officials that we cannot talk about climate action without talking about oceans and waterways stewardship. Bodhi Patil, a UN-recognized oceans solutionist and co-creator of Ocean Uprise, a global activist accelerator initiative, guides his advocacy with the understanding that ocean health is human health. ‚ÄúMitigating toxic pollutants, excess fertilizers, pesticides, and chemicals entering upstream water bodies and flowing into downstream reef ecosystems is a direct way to reduce the stressors on critically important coral reefs‚ÄĚ says Bodhi. ‚ÄúImproved water quality and reduced water pollution will contribute to their long-term health and climate resiliency. We have to think about the ocean as a being that is connected to all waterways, because she is!‚ÄĚ
Advocates have worked tirelessly to codify ocean rights in a United Nations-recognized framework as the impacts of toxic pesticides continue to impact ocean creatures big and small. In 2023, due to the years of advocacy by people like Bodhi, 193 nations approved the draft version of the High Seas Treaty (also known as Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction), an international framework that establishes universal rights to protect the oceans from harm. To date, 88 countries have signed the treaty and two countries (Chile and Palau) have ratified the treaty in their national legislatures. At least 60 countries must ratify the High Treaty for it to become international law. The exorbitant loss of over 90% of planktonic organisms from the 1940 baseline is analogous to the decline in terrestrial pollinator loss over the past several decades. Additionally, ‚ÄúIn its 2017 risk assessment for the most widely used neonicotinoid, imidacloprid, EPA found, ‚Äė[C]oncentrations of imidacloprid detected in streams, rivers, lakes and drainage canals routinely exceed acute and chronic toxicity endpoints derived for freshwater invertebrates.‚Äô The agency evaluated an expanded universe of adverse effects data and finds that acute (short-term) and chronic (long-term) toxicity endpoints are lower (adverse effects beginning at 0.65 őľg/L (micrograms per liter)-acute and 0.01 őľg/L-chronic effects) than previously established aquatic life benchmarks (adverse effects from 34.5 őľg/L-acute and 1.05őľg/L-chronic effects).‚ÄĚ Beyond Pesticides has reported on the linkage to the climate crisis and toxic petrochemical pesticide use in relation to aquatic organisms, oceans, and water.
Beyond Pesticides acknowledges the intersectional nature of the climate crisis and that pesticide drift and exposure (including glyphosate and imidacloprid) is a problem that applies to both terrestrial and marine environments. To avoid the introduction of toxic pesticides into ecosystems at the place of origin, advocates are calling on strengthening organic standards and providing new incentives to expand the domestic production and consumption of organic foods and products. See Keeping Organic Strong to learn how to engage with the National Organic Standards Board Spring 2024 meeting. Whether or not you live in a coastal city or along a waterway, see Parks for a Sustainable Future to learn about how to transition a higher education institution or a local parks department to organic land management principles.
All unattributed positions and opinions in this piece are those of Beyond Pesticides.
Source: Marine Pollution Bulletin
Posted in Aquatic Organisms, Glyphosate, Imidacloprid, Oceans, tebuconazole, Uncategorized, Water by: Beyond Pesticides
No Comments
14
Mar
¬†(Beyond Pesticides, March 14, 2024)¬† A recent review in the New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM) highlights the urgent need to address the widespread chemical pollution stemming from the petrochemical industry, underscoring the dire implications for public health. Tracey Woodruff, PhD, author and professor at the University of California San Francisco (UCSF), emphatically states in an email comment to Beyond Pesticides, “We need to recognize the very real harm that petrochemicals are having on people‚Äôs health. Many of these fossil-fuel-based chemicals are endocrine disruptors, meaning they interfere with hormonal systems, and they are part of the disturbing rise in disease.” Beyond Pesticides echoes this concern, noting that endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) include many pesticides and are linked to a plethora of health issues such as infertility, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, obesity, early puberty, as well as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), Parkinson‚Äôs, Alzheimer‚Äôs, and childhood and adult cancers.¬† (See Beyond Pesticides‚Äô Disease database here and news coverage here). The review further calls on the clinical community to advocate for policy changes aimed at mitigating the health threats posed by petrochemical-derived EDCs and climate change. Beyond Pesticides urgently calls for the elimination of petrochemical pesticides and fertilizers and advocates for a systemic shift to organic regenerative agriculture.¬† This call to action is grounded in the understanding that the petrochemical industry’s growth poses existential threats to climate, human health, and biodiversity.¬†¬†
Dr. Woodruff‚Äôs article adds to a series, ‚ÄúFossil Fuel Pollution and Climate Change,‚ÄĚ that NEJM launched in 2021. The journal joined with more than 200 health journals worldwide in publishing a joint editorial ‚Äúcalling for urgent action to limit greenhouse gas emissions to protect human health, adding to growing demands from around the globe.‚Ä̬†
Highlighting the explosive growth in petrochemical production, including plastics, pesticides, and fertilizers, Dr. Woodruff’s report draws a direct line between these activities and a growing burden of chemical exposure responsible for at least 1.8 million deaths annually. As the demand for oil and gas declines due to the shift toward renewable energy sources, multinational fossil-fuel corporations have ramped up the production of plastics and other petrochemicals. This transition is highlighted in the report as a significant factor driving both climate change and increased exposure to health-impacting chemicals through contaminated air, water, food, and a range of manufactured products (including plastics, pesticides, and consumer goods). This body of work is among numerous studies pointing to the far-reaching effects of endocrine disruption on both humans and wildlife. Endocrine disruptors can cause significant harm even at very low exposure levels, with embryonic and fetal development stages being particularly vulnerable to their adverse effects. The report notes, ‚ÄúConsequently, experts believe there is no risk-free level of exposure to these chemicals across the population.‚Ä̬† The report underscores the omnipresent nature of petrochemical-derived EDCs, noting that national biomonitoring data and epidemiologic studies have detected around 150 chemicals in human bodily fluids, including during pregnancy.¬† ‚ÄúThis represents a fraction of potential EDC exposures, since standard detection technology measures less than 1% of totally chemicals in use,‚ÄĚ the authors note.¬†¬†
Of serious concern is the disproportionate impact on communities of color and low-income communities, contributing to health inequities. While the report sheds light on this disparity, it stops short of delving into the environmental justice issues specific to petrochemical pesticide use, which significantly affects farmworkers and their families (see here and here). While the report focuses on what healthcare clinicians can do to reduce EDC exposures for their patients (and includes a helpful example of an environmental exposure history and suggestions of how patients can protect themselves), Dr. Woodruff acknowledges that ‚Äúmost exposures are beyond individual control‚ÄĚ and even when one chemical is removed from consumer products, the result is often a substitution of a similar toxic chemical. ¬†
Regulatory Failure 
After a nearly two decade defiance of a federal mandate to institute pesticide registration requirements for endocrine disruptors, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) accepted public comments until last month on establishing a testing protocol for pesticides. (See here for comprehensive Beyond Pesticide comments). Advocates, including Beyond Pesticides, are criticizing the agency‚Äôs proposed evaluation as too narrow. EPA never completed protocol for testing potential endocrine-disrupting pesticides that disrupt the fundamental functioning of organisms, including humans, causing a range of chronic adverse health effects that defy the common misconception (and EPA risk assessment assumption) that dose makes the poison (‚Äúa little bit won‚Äôt hurt you‚ÄĚ), when, in fact, minuscule doses (exposure) wreak havoc with biological systems. Beyond Pesticides detailed comments call for EPA to suspend or deny any pesticide registration until the agency has sufficient data to demonstrate no unreasonable adverse endocrine system risk per the mandate in Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA), as amended by the 1996 Food Quality Production Act. Under FIFRA, there is an inherent presumption of risk, a pesticide is presumed to pose an unreasonable risk until reliable data demonstrate otherwise. If the agency lacks the data and/or resources to fully evaluate endocrine system risks to human health and wildlife, then the agency is obliged to deny registration of said pesticide. Further, it is not the agency but pesticide registrants that have the burden to demonstrate with adequate data that their products will not pose unreasonable adverse effects, including the inherently presumed endocrine-disrupting effects. ¬†
Beyond Pesticide’s Call for an End to Petrochemical Pesticide and Synthetic Fertilizer Use by 2032 
The petrochemical industries‚Äô growth is a driver of three existential threats: climate, human health, biodiversity. In addition to the petroleum used to produce synthetic pesticides, Beyond Pesticides has reported on the plastic saturation of the planet, including through the use of plastic coating of some synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, as well as treated seeds. The reliance on petroleum-based pesticides, fertilizers, and plastics reveals a deep connection of chemical-intensive agriculture to the climate crisis and biodiversity decline and establishes a vivid contrast to organic agriculture which eschews these inputs.‚Äč‚Ä謆¬†
The plastic problem is vast and complex. A 2022 study in Environmental Science & Technology reports that plastics caused chemical pollution has the potential to ‚Äúalter vital Earth system processes on which human life depends.‚Ä̬† The inherent “chemically inert” property of plastics, once thought benign, has proven to be a double-edged sword. Under certain conditions, plastics are not benign at all; they can leach toxic chemicals into their surroundings. Moreover, plastics do not easily break down into their constituent compounds after their intended life. The result is a world where microplastics, pieces less than five millimeters in diameter, have suffused every ecosystem, as the Guardian reported from the heights of Everest to the depths of the oceans, and even in Antarctica. These microplastics, along with the toxicants they may carry, have entered the food chain, impacting marine organisms, terrestrial livestock, and humans through multiple exposure routes.¬†
Rising petrochemical production spells disaster for efforts to curb greenhouse gas emissions and avert climate catastrophe‚Äč‚Äč.¬† Agriculture is a major consumer of other plastic products, using them for purposes ranging from mulching to irrigation. The United States alone uses approximately 816 million pounds of agricultural plastics annually, with significant environmental implications due to the lack of recycling policies and the resultant soil contamination that affects crop yield and ecosystem health‚Äč‚Äč. As Center for International Environmental Law in its December 2022 reissued report, Sowing a Plastic Planet: How Microplastics in Agrochemical Are Affecting¬† our Soils, Our Food, And Our Future writes, ‚ÄúNon-plastic alternatives already exist for most of the agricultural uses of microplastics (organic and organic regenerative agriculture). Accordingly, there is no justification for allowing the continued use of microplastics in fertilizers and pesticides.‚Ä̬† In response to these and other challenges, the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and other bodies have advocated for a return to traditional, organic farming practices that eschew synthetic materials in favor of organic mulch materials, cover crops, and nonchemical management strategies. These practices reduce dependence on fossil fuel-based inputs and thus, the negative climate, health, and environmental impacts.¬† Beyond Pesticides supports the transition to organic regenerative agriculture as a comprehensive solution to the myriad problems posed by chemical and plastic use in farming. Organic agricultural approaches offer numerous benefits over chemical methods, including enhanced safety for people and the environment, improved soil health, a more nutritious and nutrient dense food supply, in many cases, superior yields and and can mitigate the effects of agricultural greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. As the Rodale Institute notes, conventional farming isn‚Äôt just contributing to the climate crisis, organic farming is essential to address it and wrote, ‚ÄúOrganic methods can produce competitive yields in good weather and outperform conventional in times of drought or flooding, and organic uses less energy and generates fewer emissions while revitalizing the soil and sequestering carbon.‚ÄĮ If we‚Äôre going to decrease farming‚Äôs impact‚ÄĒand we must decrease farming‚Äôs impact‚ÄĒthen we need organic. Because farming doesn‚Äôt only contribute to climate change; it‚Äôs greatly affected by it. And it is getting harder and harder to grow food in extreme weather.‚Ä̬†¬†
Solutions to Existential Crises of Climate, Human Health, and Biodiversity 
Beyond Pesticides noted in January 2023 that there is no solution to this wide array of crises that includes continued fossil fuel use. The organization wrote: ‚ÄúWhile the solutions are in reach, tremendous public action is needed to stop the fossil fuel and agrichemical industries from their short-sighted pursuit of profit at any cost‚Ķ. Arguments are made that high intensity, industrial chemical agriculture is the only way to feed the world, and fossil fuels are the only way to provide energy. Scientific data has spelled out exactly what we are in for if we continue to endorse these dangerous myths.‚ÄĚ With chemicals, like pesticides, long advanced by the synthetic pesticide and fertilizer industry as the answer to feeding the world, the United Nations ‚ÄĮSpecial Rapporteur on the right to food‚ÄĮconcluded in 2017‚ÄĮthat industrialized agriculture has not succeeded in eliminating world hunger, and has only hurt human health and the environment in its wake.‚ÄĮ¬†
Beyond Pesticides established the Parks for a Sustainable Future program to assist with the transition to organic land management in communities across the U.S. The organization also strives to maintain the integrity of organic standards through Keeping Organic Strong campaign and historical work to transition agriculture to organic practices. In 2022, Beyond Pesticides sponsored a Climate Change Calls for Phase Out of Fossil Fuels Linked to Petrochemical Pesticides and Fertilizer series of national virtual seminars (with archived videos) covering health, biodiversity, and climate. For more on climate-friendly organic agriculture, see Daily News and the groundbreaking work of the Rodale Institute, as captured in its Farming Systems Trial ‚ÄĒ 40-Year Report, which shows the efficacy and benefits of organic agriculture. California Certified Organic Farmers Association‚Äôs Roadmap to an Organic California provides a policy framework for advancing agricultural programs that combat climate change.¬†¬†¬†
All unattributed positions and opinions in this piece are those of Beyond Pesticides. 
 Sources:
Health Effects of Fossil Fuel-Derived Endocrine Disruptors, Dr. Tracey Woodruff, The New England Journal of Medicine, March 7, 2024  
‚ÄėExplosive growth‚Äô in petrochemical production poses risks to human health, The Guardian, March 6, 2024
Sowing a Plastic Planet: How Microplastics in Agrochemical Are Affecting  our Soils, Our Food, And Our Future, Center for International Environmental Law, Reissued December 2022  
Posted in Agriculture, Alternatives/Organics, Body Burden, Cancer, Chemicals, Climate, Climate Change, contamination, Dow Chemical, Drinking Water, DuPont, Endocrine Disruption, Farmworkers, Groundwater, Herbicides, Livestock, Lung Cancer, multi-generational effects, National Organic Standards Board/National Organic Program, Oceans, PFAS, phthalates, Plastic, Reproductive Health, soil health, Synthetic Fertilizer, Synthetic Turf, Uncategorized by: Beyond Pesticides
1 Comment
13
Mar
(Beyond Pesticides, March 13, 2024) A comprehensive study released in Journal of Cleaner Production in August 2023 identifies the potential for organic agriculture to mitigate the impacts of agricultural greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in the fight to address the climate crisis. In ‚ÄúThe spatial distribution of agricultural emissions in the United States: The role of organic farming in mitigating climate change,‚ÄĚ the authors determine that ‚Äúa one percent increase in total farmland results in a 0.13 percent increase in GHG emissions, while a one percent increase in organic cropland and pasture leads to a decrease in emissions by about 0.06 percent and 0.007 percent, respectively.‚ÄĚ This descriptive study affirms the urgency of Beyond Pesticides‚Äô mission to ban toxic petrochemical pesticides by 2032, given the projected adverse impacts that conventional agricultural dependence on these toxic pesticides will continue to have on people, wildlife, and ecosystems.
The study refers to various studies focused on a comparative analysis of conventional to organic farming on energy use, greenhouse gas emissions (GHGe), nutrient leaching, soil quality, and biodiversity. The consensus is that organic farming is more sustainable than conventional agriculture. For example, ‚Äú[S]everal studies comparing conventional to organic agriculture found that the latter used 10%‚Äď70% less energy per unit of land for all analyzed crops.‚ÄĚ However, measurements on a meta-analysis of soil quality and biodiversity show ‚Äúsignificant variability across studies with 16% of them showing a negative effect of organic farming on species richness.‚ÄĚ Drawing on this past research, the authors of this study accomplish what the previous research could not: ‚Äúprovide categorical supporting evidence… for the general expectation that organic farming is more environmentally sustainable than conventional farming.‚ÄĚ
These researchers used U.S. state-level data from 1997 to 2010, excluding the years 1998, 1999, and 2009 due to bad data. Additionally, researchers drew GHGe data from the World Resources Institute, economic data (e.g. ‚Äúreal per capita GDP (in chained 2009 dollars), output share for utilities, manufacturing, oil and natural gas, and transportation‚ÄĚ as a percentage of state GDP) from the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis, Department of Commerce. Additional data was gathered from the U.S. Department of Transportation‚Äôs Federal Highway Administration, the U.S. Department of Agriculture‚Äôs Economic Research Service, and the U.S. Census Bureau.
To determine a statistical relationship between GHGe and organic farming in the U.S., the researchers use a model based on the STIRPAT (Stochastic Regression on Population, Affluence, and Technology) approach. Researchers summarize the benefits of this analytical method, ‚ÄúGiven the importance of transportation to farming, this would help examine whether the potential environmental benefits of organic food production, if any, are substantial enough to outweigh the environmental harm of transportation output embodied in organic farming.‚ÄĚ ¬†See Subsection 3.2 under Methods for a full breakdown of the empirical specifications of their methodology.
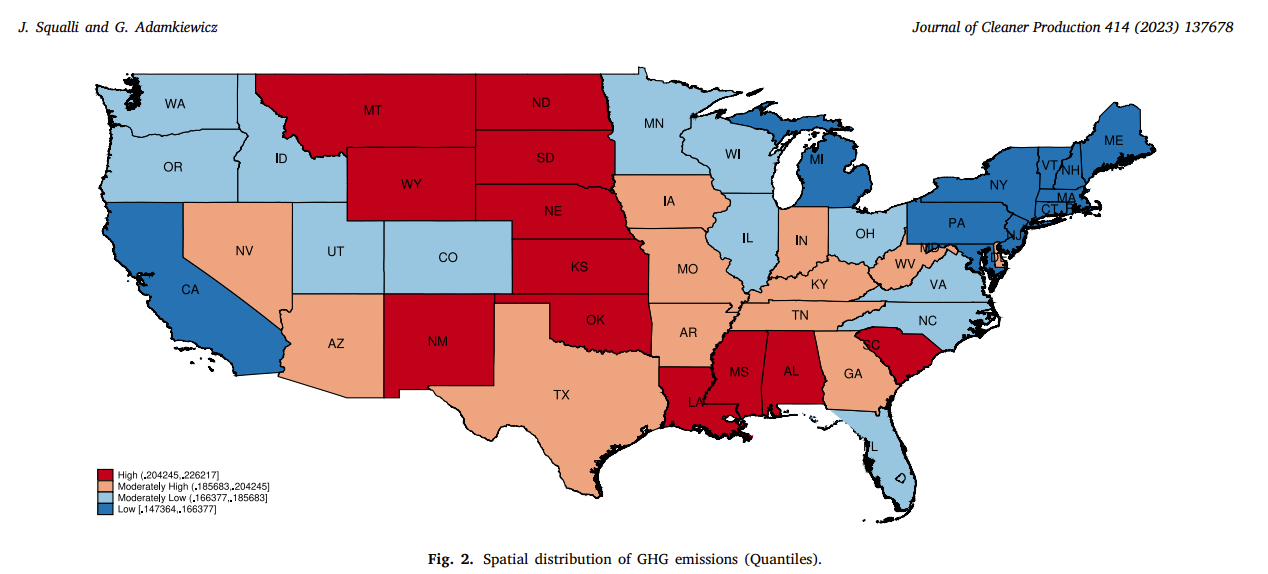
The spatial distribution (as seen above in Figure 2) of the statistical comparison between conventional and organic agricultural across all fifty states amounts to three overarching findings:
- “The spatial distribution of agricultural GHG emissions in the United States is uneven: High-emissions states are concentrated in the Great Plains extending south to NM and the southeastern area of the United States. Meanwhile, low-emissions states are in California and the northeastern region extending to MI in the north and MD in the south.
- Agriculture is a significant contributor to GDP within the high-emissions states, but organic agriculture represents only a small proportion of total farmland: The contribution of agriculture to GDP in high-emissions Great Plains states ranges from 1.11% to 5.94%, while organic agriculture as a share of total farmland ranges from 0.02% to 0.33%. In the southeastern states, the contribution of agriculture to GDP ranges from 0.39% to 1.41%, and organic agriculture ranges from 0.003% to 0.005%.
- Agriculture has a substantially lower contribution to GDP within low-emissions states, but organic agriculture represents a large proportion of total farmland: The contribution of agriculture to GDP ranges from 0.063% to 0.95%, while organic farming as a share of total farmland ranges from 0.14% to 3.13%.‚ÄĚ
Years of reporting by Beyond Pesticides corroborates the findings in the study that organic agriculture is a monitorable and critical solution to address cascading crises relating to climate change and public health. Rodale Institute‚Äôs Farming Systems Trial ‚Äď 40-Year Report highlights the success of regenerative organic agriculture:
- Organic systems achieve 3‚Äď6 times the profit of conventional production;
- Yields for the organic approach are competitive with those of conventional systems (after a five-year transition period);
- Organic yields during stressful drought periods are 40% higher than conventional yields;
- Organic systems leach no toxic compounds into nearby waterways (unlike pesticide-intensive conventional farming)
- Organic systems use 45% less energy than conventional agriculture, and
- Organic systems emit 40% less carbon into the atmosphere.
There are also numerous reports that highlight the threat of toxic petrochemical pesticides and fertilizers to the broader climate crisis. For example, a 2020 study documents the use of synthetic fertilizers as a driver of nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions. This phenomenon is of critical concern to advocates given that, ‚ÄúGrowth in nitrous oxide emissions over these last four decades has been considerable, with human-caused release, mostly from fertilizer use on cropland, increasing by 30%. Compared to pre-industrial levels, nitrous oxide levels increased 20% from all sources.‚ÄĚ While nitrous oxide emissions only make up 6 percent of total greenhouse gas emissions in the U.S., ‚Äúthe impact of one pound of N2O on warming the atmosphere is 265 times that of one pound of carbon dioxide.‚ÄĚ In Sub-Saharan Africa, meanwhile, years of soaring fertilizer costs (for both organic and conventional products) that began with the pandemic and continue with currency fluctuations wracked by geopolitical actions, including the Russia-Ukraine War, prevent many farmers from maintaining soil health to produce agricultural products. The climate crisis is also causing significant harm to bumblebees, according to a 2023 study that adds to research tying together the compounding impacts of extreme temperature fluctuations and toxic insecticide exposure in relation to their physical fitness and pollinating capabilities.
Beyond Pesticides strongly advocates for strengthening organic regulations to ensure the positive impact of organic principles in addressing the compounding ecological, public health, and climate crises. See Keeping Organic Strong as the National Organic Standards Board to find the opportunity to suggest changes to the National Organic Program through public hearings, comment periods, and written testimonials that will open up in April.
All unattributed positions and opinions in this piece are those of Beyond Pesticides. 
Source: Journal of Cleaner Production
Posted in Agriculture, Alternatives/Organics, Biodiversity, Climate Change, State/Local, Synthetic Fertilizer, Uncategorized by: Beyond Pesticides
No Comments
12
Mar
(Beyond Pesticides, March 12, 2024) A study released in Science of the Total Environment unpacks the threat of emerging chemicals of concern (CECs), including toxic pesticides, in the groundwater of Tunisia. Researchers highlight that the impact of pesticide drift and leaching into groundwater reserves is not siloed to the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region, but a key concern for most industrialized countries, including the United States. Authors of this study build on literature of CECs already conducted in the region that have broader implications for the spillover effects of pesticide regulation in broader contexts. This descriptive study and accompanying Environmental Risk Assessment (ERA) demonstrate the urgency of Beyond Pesticides’ mission to ban toxic petrochemical pesticides by 2032 because of the pervasiveness of toxic residues, be it pesticides, antibiotics, or other substances, from groundwater systems to human bodies.
The researchers performed the tests in thirteen wells in the Grombalia shallow aquifer, an area of northeast Tunisia that feeds into the Wadi El Bay watershed, which is defined as a ‚Äúhigh population density [with] intensive agricultural activity [in ‚Äėone of the most polluted areas in Tunisia‚Äô].‚ÄĚ The researchers gathered data ‚Äúduring two seasons and were analyzed with two high resolution mass spectrometry approaches: target and suspect screening. The latter was screening banned pesticides.‚ÄĚ For more information on the suspect screening approach for pesticide analysis, see Subsection 2.4 under the Materials and Methods.
The researchers identified 20 target pesticides in this study: Anabasine,¬†atrazine, bendiocarb, bentranil,¬†carbaryl,¬†carbofuran, DEET, desethylatrazine, desethylterbuthylazine, dimethomorph, fenfuram,¬†imidacloprid, isoproturon, methfuroxam, mexacarbate, propamocarb, propoxur, pyroquilon, spiroxamine, and¬†terbuthylazine. Table 2 delineates the concentrations of the most frequently detected pesticides in groundwater samples, which include DEET, mexacarbate, propoxur, desethylatrazine, and terbuthylazine. The authors are particularity concerned with the presence of ‚Äúseveral carbamate insecticides‚Ķdue to their acute and chronic toxicity.‚ÄĚ The main source of carbamate insecticides are from agricultural use, which is not surprising given that the Grombalia region‚Äôs economy is mainly based on citrus: ‚Äú77.3 percent of the irrigated area [in this region] is planted with citrus [].‚ÄĚ
‚ÄúThe most frequently quantified pesticides belong to the family of¬†triazine herbicides and carbamate insecticides. Triazines have been highly used on several agricultural crops. The occurrence of triazine herbicides in groundwater has been found very commonly [] with most likely no potential human-health concerns at the observed levels of detection [],‚ÄĚ authors report in Section 3.1.2 on the results and discussion subsection on pesticides. According to the report: ‚ÄúThe frequent detection of triazines can also be expressed as a function of their groundwater ubiquity score (GUS) index, used to predict the behavior of pollutants in groundwater. Triazines are the compounds with the highest GUS index and detection frequency, indicating their high leachability.¬†Atrazine¬†and its¬†degradation product¬†desethylatrazine are by far the most abundant herbicides detected in shallow groundwater []. Atrazine was not detected in the sampling sites, while its metabolite desethylatrazine was detected in 13 samples in both sampling campaigns []. Some researchers have shown that pesticide metabolites are often detected in groundwater at higher concentrations compared to parent compounds [] and that their presence can be more toxic than their parents. []‚ÄĚ This last line on pesticide metabolites is consistent with findings from numerous studies which demonstrate the relationship between groundwater and pesticide residue exposure and infiltration in the United States, for example, ‚Äú90 percent of Americans having at least one pesticide biomarker (includes parent compound and metabolites) in their body,‚ÄĚ according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Beyond the focus on pesticides, the study also documents the occurrence of CECs, which include ‚Äúcommonly prescribed drugs [‚Äėantimicrobials, analgesics, anti-inflammatories‚Äô], artificial sweeteners [sucralose], insecticides [fipronil], and UV filters.‚ÄĚ Sixty-nine compounds of CECS and one transformation product [metabolites or degradation products of the precursor analyte‚Äô] and 20 pesticides were detected per well, ‚Äúranging between 43 and 7384¬†ng¬†L‚ąí1¬†and 7.3 and 80¬†ng¬†L‚ąí1, respectively. The unit ng L-1 refers to one nanogram of a substance per liter of water.
Researchers in this study found it pertinent to study toxic substance exposure in Tunisian groundwater since a vast majority of the population accesses water resources through wells linked to aquifers. A 2023 Gallup poll indicates a record dissatisfaction with water quality across 81 percent of the population, particularly in southern regions of the country. ‚ÄúIndustrial waste from phosphate mining‚ÄĒphosphogypsum‚ÄĒhas led to spikes in cancer rates, infertility, and miscarriage in the region. Once famed for its thriving marine ecosystems, fish stocks have plummeted. Groundwater has been polluted, with diminishing reserves for households.‚ÄĚ One of the reasons these researchers focused on an area in northeast Tunisia was because of the lack of existing data regarding toxic substance residues in groundwater reserves generally.
There is extensive reporting by Beyond Pesticides on the human, wildlife, and ecological health implications of pesticide leaching into groundwater. For instance, marine ecosystems along the U.S. West Coast are threatened by forest management practices that permit the use of pesticides including certain herbicides (indaziflam, hexazinone, and atrazine), fungicides (fluopicolide and pyraclostrobin), and insecticides (bifenthrin and permethrin). In Arizona, the State Auditor General reported deep concern over the insufficient amount of groundwater monitoring for pesticides by the Arizona Department of Environmental Quality between 2017 and 2021 which flew in the face of legal requirements.
Beyond Pesticides continues to call on Secretary of Interior Deb Haaland to expand USGS mapping of pesticide use and monitoring and inform the U.S. Environmental Protection (EPA) Administrator Michael Regan that pesticides shown to contaminate rivers and streams must be banned. The regulation of and rulemaking around pesticide infiltration in groundwater is more complicated in the aftermath of Sackett v. EPA (2023), a Supreme Court case that limited EPA‚Äôs authority to protect critical wetland ecosystems through a narrower definition of, ‚ÄúWaters of the United States (WOTUS). In the 5-4 SCOTUS decision, regulation of groundwater (including protections against pesticide residue) was undermined once WOTUS was defined by the language, ‚Äúcontinuous surface connection to bodies.‚ÄĚ
Beyond the patchwork of state and national law that impacts water and pesticide regulation, investing in the protection of organic agricultural and land management principles is a critical approach to prevent the overwhelmingly majority of toxic petrochemical pesticides from leaching into groundwater in the first place. Beyond Pesticides affirms the decades of advocacy that went into establishing organic agriculture standards through the Organic Foods Production Act of 1990. This legislation established mechanisms for compliance, oversight, and enforcement of the national List of Allowed and Prohibited Substances to protect the public against toxic pesticides that EPA permits acceptable use in conventional, industrial agriculture. See Keeping Organic Strong as the National Organic Standards Board will offer the public the opportunity to suggest changes to the National Organic Program through public hearings, comment periods, and written testimonials in April.
All unattributed positions and opinions in this piece are those of Beyond Pesticides. 
Source: Science of the Total Environment
Posted in Atrazine, Bendiocarb, Carbaryl, Chemical Mixtures, Chemicals, contamination, DEET, Groundwater, Uncategorized, Water by: Beyond Pesticides
1 Comment
11
Mar
(Beyond Pesticides, March 11, 2024) Inside a recent disagreement between the Office of the Inspector (OIG) and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency‚Äôs (EPA) Office of Pesticide Programs (OPP) on the agency‚Äôs review of pet flea and tick collars‚ÄĒleading to thousands of deaths and poisonings‚ÄĒis a basic question of the adequacy of pesticide regulation. The disagreement is over the cause of 105,354 incident reports, including 3,000 pet deaths and nearly 900 reports of human injury, and the February 2025¬†OIG report‚Äôs conclusion that ‚Äú[EPA] has not provided assurance that they can be used without posing unreasonable adverse effects to the environment, including pets.” While the disagreement focuses on a number of EPA process failures, Beyond Pesticides urges that the findings advance the need for the agency to address a key element of chemical mixtures in pesticide products not currently evaluated, potential synergistic effects‚ÄĒthe increased toxic potency created by pesticide and chemical combinations not captured by assessing product ingredients individually.¬†
Key to the dispute is what many see as a foundational failure of EPA to evaluate the effect of pesticide mixtures and full formulations of pesticide end products, a longstanding criticism of the agency‚Äôs pesticide registration process, which focuses on pesticide products‚Äô active ingredients. The manufacturer identifies the active ingredient as the compound in the product formulation that kills the target pest‚ÄĒeven though the other ingredients (called inerts) may be toxic. The concern stems from two scenarios present with the Seresto collar in which EPA is not evaluating (i) the mixture of chemicals in the product purchased by consumers, including the so-called inert ingredients (other chemical agents to increase performance, such as adjuvants, surfactants, solvents, carriers, etc.) and contaminants (both not disclosed on the product label); and (ii) the effect of the mixture of two or more active ingredients in the pesticide product, which may increase the product‚Äôs overall toxicity.
In the case of the Seresto flea and tick collar, there is concern that EPA missed the true toxicity of the product by not fully evaluating whether there is a synergistic effect that increases the product‚Äôs overall toxic effect. Seresto contains two active insecticide ingredients‚ÄĒthe neurotoxic insecticide‚ÄĮflumethrin, and the notorious neonicotinoid‚ÄĮimidacloprid¬†with adverse effects on the endocrine system and environment.
As Beyond Pesticides pointed out in 2021, when the pet poisonings and deaths made headlines, a‚ÄĮ2012 study‚ÄĮfound that flumethrin and imidacloprid have a synergistic effect in attacking fleas. However, EPA dismissed or ignored this science,‚ÄĮstating in a 2016‚ÄĮEPA bulletin, ‚ÄúThe risk of the combination of the two active ingredients, flumethrin and imidacloprid, was not assessed because the two chemicals act in completely different ways.‚ÄĚ
Synergistic effects have been widely reported. For example, Beyond Pesticides has reported that researchers found elevated neurotoxic effects from exposure to the glyphosate/Roundup formulation with the so-called inert ingredient polyethoxylated tallowamine (POEAs), also shown to kill human cells. 
>>Tell EPA to start protecting people and pets from pesticide poisoning. 
Despite all the concerns, at the time the poisoning and deaths of pets made headlines in 2021, the agency¬†defended the product’s registration, telling the media that, despite these incidents, EPA deemed Seresto collars ‚Äú’eligible for continued registration’ based on best available science, including incident data…¬†No pesticide is completely without harm, but EPA ensures that there are measures on the product label that reduce risk.‚ÄĚ
Overall, the OIG highlights known shortcomings¬†in EPA’s pesticide registration program,¬†including (but not limited to):¬†
- Failure to address combined effects of multiple pesticides; 
- Failure to investigate impacts on pets; 
- Failure to adopt standard operating procedures and a methodology to determine when pet products may pose unreasonable adverse effects to the environment; 
- Failure to collect complete incident data that would allow EPA to fully understand the risks and take appropriate action; and 
- Failure to assure the public of the safety of the products. 
Furthermore, EPA continues to rely on labeling to reduce risk, despite its failure to protect pets, children, farmworkers, pollinators, and biodiversity. Advocates point out that If the labeling is not protecting people, then the agency is not fulfilling its responsibility to protect public health and safety and the pesticide products should not be allowed on the market
>>Tell EPA to start protecting people and pets from pesticide poisoning. 
Letter to EPA
More proof of multiple systemic failures by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) Office of Pesticide Programs (OPP) to protect people and their pets from pesticides was presented in a report of the Office of Inspector General (OIG) report, published on February 29, 2024.
The report, The EPA Needs to Determine Whether Seresto Pet Collars Pose an Unreasonable Risk to Pet Health, concludes that, ‚ÄúThe EPA‚Äôs response to reported pesticide incidents involving Seresto pet collars has not provided assurance that they can be used without posing unreasonable adverse effects to the environment, including pets.‚ÄĚ At the time the animal effects made headlines in 2021, the agency defended the product‚Äôs registration, telling the media that, despite these incidents, EPA deemed Seresto collars ‚Äú‚Äėeligible for continued registration‚Äô based on best available science, including incident data. . . . No pesticide is completely without harm, but EPA ensures that there are measures on the product label that reduce risk.‚ÄĚ‚ÄĮDespite the scathing criticism, EPA maintains the position that it conducted an adequate review of the two active insecticide ingredients in the pet collars‚ÄĒ the neurotoxic insecticide‚ÄĮflumethrin, and the notorious neonicotinoid‚ÄĮimidacloprid with adverse effects on the endocrine system and environment.
The OIG points out that EPA‚Äôs handling of the flea and tick collars‚ÄĒimplicated in 105,354 incident reports, including 3,000 pet deaths and nearly 900 reports of human injury‚ÄĒhighlights known shortcomings in EPA‚Äôs pesticide registration program, including (but not limited to):
– Failure to address combined effects of multiple pesticides;
– Failure to investigate impacts on pets;
– Failure to adopt standard operating procedures and a methodology to determine when pet products may pose unreasonable adverse effects to the environment;
– Failure to collect complete incident data that would allow EPA to fully understand the risks and take appropriate action; and
– Failure to assure the public of the safety of the products.
Furthermore, EPA continues to rely on labeling to reduce risk, despite its failure to protect pets, children, farmworkers, pollinators, and biodiversity. When EPA cannot protect against ongoing harm to humans and the biosphere with the labeling it approves on pesticide products, it must remove the pesticide product from the market. When faced with evidence of harm from a pesticide, despite its labeling restrictions and warnings, EPA must take steps to halt its use. 
The deaths and poisonings associated with Seresto animal collars requires EPA to immediately establish the necessary protocol to evaluate full formulations of products it allows on the market for additive and synergistic effects. When will you do this?
Thank you for your consideration.
Letter to U.S. Congress
More proof of multiple systemic failures by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) Office of Pesticide Programs (OPP) to protect people and their pets from pesticides was presented in a report of the Office of Inspector General (OIG) report, published on February 29, 2024. 
The report, The EPA Needs to Determine Whether Seresto Pet Collars Pose an Unreasonable Risk to Pet Health, concludes that, ‚ÄúThe EPA‚Äôs response to reported pesticide incidents involving Seresto pet collars has not provided assurance that they can be used without posing unreasonable adverse effects to the environment, including pets.‚ÄĚ At the time the animal effects made headlines in 2021, the agency defended the product‚Äôs registration, telling the media that, despite these incidents, EPA deemed Seresto collars ‚Äú‚Äėeligible for continued registration‚Äô based on best available science, including incident data… No pesticide is completely without harm, but EPA ensures that there are measures on the product label that reduce risk.‚ÄĚ‚ÄĮDespite the scathing criticism, EPA maintains the position that it conducted an adequate review of the two active insecticide ingredients in the pet collars‚ÄĒ the neurotoxic insecticide‚ÄĮflumethrin, and the notorious neonicotinoid‚ÄĮimidacloprid with adverse effects on the endocrine system and environment.
The OIG points out that EPA‚Äôs handling of the flea and tick collars‚ÄĒimplicated in 105,354 incident reports, including 3,000 pet deaths and nearly 900 reports of human injury‚ÄĒhighlights known shortcomings in EPA‚Äôs pesticide registration program, including (but not limited to):
– Failure to address combined effects of multiple pesticides;
– Failure to investigate impacts on pets;
– Failure to adopt standard operating procedures and a methodology to determine when pet products may pose unreasonable adverse effects to the environment;
– Failure to collect complete incident data that would allow EPA to fully understand the risks and take appropriate action; and
– Failure to assure the public of the safety of the products.
Furthermore, EPA continues to rely on labeling to reduce risk, despite its failure to protect pets, children, farmworkers, pollinators, and biodiversity. When EPA cannot protect against ongoing harm to humans and the biosphere with the labeling it approves on pesticide products, it must remove the pesticide product from the market. When faced with evidence of harm from a pesticide, despite its labeling restrictions and warnings, EPA must take steps to halt its use. 
Please let EPA know that the deaths and poisonings associated with Seresto animal collars requires it to immediately establish the necessary protocol to evaluate full formulations of products it allows on the market for additive and synergistic effects.
Thank you for your consideration.
Posted in Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), Flumethrin, Imidacloprid, synergistic effects, Synthetic Pyrethroids, Uncategorized by: Beyond Pesticides
11 Comments
08
Mar
(Beyond Pesticides, March 8, 2024) A major problem has vexed pesticide regulators and researchers for decades: Humans and other organisms almost always have multiple pesticides in their bodies, but techniques for assessing their combined effects, or cumulative body burden from multiple chemical classes are not typically available. A new study from Chinese and British researchers provides the first combined assessment of multiple classes of pesticides in human blood. The authors believe they are the first to develop a way to quantify multiple types of pesticides in human serum (clear liquid part of blood) as opposed to urine or from other sample collection methods. This is a tool that authors say is a more accurate way of assessing the real world exposure and ultimately the adverse impact of pesticide use on human health.
The researchers had a small sample of 31 men and 34 pregnant women in Wuxi, China. They chose 73 pesticides and a few of their breakdown products to identify from three categories: fungicides, neonicotinoid insecticides, and triazine herbicides. Their testing protocol confirms their expectation that food‚ÄĒprimarily produce‚ÄĒis the major source of pesticide exposures. This result reinforces Beyond Pesticides‚Äô mission of supporting the shift in agriculture to pesticide-free methods and regenerative practices. Eating organic food is the most effective way to reduce the body burden of pesticides.
The researchers detect a total of 40 pesticides and 10 related chemicals in the sample. No sample was free of all pesticides. More than 80 percent contained more than 10 pesticides. The researchers note that this adds to the evidence that pesticides are ubiquitous in human bodies. As Beyond Pesticides often stresses, it defies belief that these chemicals could have no effect on human (and ecosystem) health.
Based on the sampling data, the team calculates each subject’s estimated daily intake (EDI) of each pesticide, adding those together to find a cumulative EDI. They then compare the EDI with acceptable daily intake (ADI) standards for each pesticide set by various countries and international organizations, including the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the World Health Organization. ADI is an estimate of how much of a substance a person could consume daily over a lifetime without suffering adverse health effects. Then they derive a cumulative hazard quotient (HQ), which is an estimate of the health effects resulting from exposures above the ADI.
Of the three pesticide categories, fungicides occurr most often and at the highest levels. Boscalid, a carbamid compound, is the most common fungicide in the samples. Upon its registration in 2003, EPA described it as ‚Äúpractically nontoxic.‚ÄĚ But it inhibits succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) a chemical whose structure and functions, in the words of one review, are highly conserved in ‚Äúnearly all extant eukaryotes‚ÄĚ‚ÄĒthat is, everything but bacteria and their unicellular cousins, the archaea. Therefore, what it does to one organism it may very well do to all (including humans). Studies in zebrafish show unambiguously that boscalid affects central nervous system development and function and glucose metabolism, causes oxidative stress, and disrupts reproductive hormones.
Four of the fungicides are triazoles, which the authors note can cross the blood-brain barrier and infiltrate cerebrospinal fluid. The current study is the first to find them in human serum. Triazoles affect a steroid synthesis pathway in fungi that is the same in humans. Triazoles are known to damage cardiac tissue and trigger oxidative stress in rats.
Simazine is the most common triazine herbicide in the samples. The triazine family includes the notorious endocrine disrupter atrazine; simazine is used for weed control in fruit and nut orchards, berry fields and cornfields, and aquatic environments. EPA regulates simazine according to its similarity to atrazine. It was approved in 1972 for algae control in swimming pools, hot tubs and whirlpools until 1994, when EPA withdrew this registration based on ‚Äúunacceptable cancer and non-cancer health risks to children and adults.‚ÄĚ However, by 2022, EPA declared in a rule establishing tolerances for certain crops that ‚Äúcancer risk is not a concern and a quantitative cancer risk was not conducted.‚ÄĚ Researchers have found effects of simazine on the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis leading to, for example, ‚Äúconstant estrus [in heat]‚ÄĚ and ‚Äúcontinuous estrogen stimulation of mammary gland‚ÄĚ in female rats. Endocrine disruption is a well-established factor in the development of many cancers.
Neonicotinoids are widely recognized to be neurotoxic to many beneficial insects such as bees as well as humans, but they may also have other harmful effects, including disruption of metabolic functions involving lipids and leading to obesity and cardiovascular disease. A previous study in Wuxi by different researchers identified nine neonicotinoids in human serum along with nine lipids already known to be affected by environmental contaminants, including dioxins, polychlorinated biphenyls, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and organophosphorus flame retardants. The authors of the current study found eight neonicotinoids in their samples, three of which had not been observed in human serum before. They also observed that, like some fungicides, neonicotinoids can cross the blood-brain barrier.
The authors found that there is a clear linear relationship between maximum residue levels allowed in foods, also called tolerances, and the serum levels of pesticides in their study subjects‚ÄĒthe higher the allowable residue in food, the higher the serum level of that pesticide. This means that setting these tolerances lower or eliminating them altogether would go a long way toward reducing pesticide exposures, as would better monitoring and enforcement of such regulations in the U.S., especially on imported foods.
One important aspect of the current study is the identification of numerous troubling pesticides not previously found in human serum, findings that adds to the urgency of further investigation. But the study did not directly demonstrate that any of the pesticides they analyzed are causing adverse health effects. The study’s main significance is that it establishes a method for measuring, comparing, and determining cumulative levels of numerous pesticides in human serum. This method can help determine the extent and severity of those pesticides’ consequences individually and cumulatively.
Perhaps unintentionally, the study also highlights the inadequacy of methods calculating exposures and health hazards using the crude estimates of EDI, ADI, HQ and maximum residue levels/tolerances. These concepts are imprecise almost to the point of ‚Äúhand waving.‚ÄĚ They rest on the assumption that there are some levels of pesticides in the body that are harmless‚ÄĒwhich, even if true, fails to account for the total risks and hazards presented by the ubiquitous body burdens of multiple pesticides. The most rational course to protect humans and ecosystems from pesticide exposures is to switch agriculture to organic methods as soon as possible. For more on the public health outcomes linked to pesticide exposure, see Beyond Pesticides‚Äô Pesticide-Induced Diseases Database.¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬† ¬†¬†
All unattributed positions and opinions in this piece are those of Beyond Pesticides
Sources:
Exposure levels and health implications of fungicides, neonicotinoid insecticides, triazine herbicides and their associated metabolites in pregnant women and men. Nanxiu Shang, Yingying Yang, Yilin Xiao, Yukang Wu, Kaixuan Li, Xiaoman Jiang, Edmond Sanganyado, Qing Zhang, Xinghui Xia, Environmental Pollution, Volume 342, 1 February 2024. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0269749123020717
A comprehensive review of 1,2,4-triazole fungicide toxicity in zebrafish (Danio rerio): A mitochondrial and metabolic perspective. Tao Huang, Haibo Jiang, Yuanhui Zhao, Jia He, Hongguang Cheng, Christopher J. Martyniuk, Science of The Total Environment 2022. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0048969721062550
Biomonitoring and risk assessment of human exposure to triazole fungicides panel. Luiz P.A. Marciano, Luiz F. Costa, Naiane S. Cardoso, Josiane Freire, Fernando Feltrim, Geovana S. Oliveira, Fernanda B.A. Paula, Alessandra C.P. Silvério, Isarita Martins, Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology, Volume 147, February 2024. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0273230024000060
Serum concentrations of neonicotinoids, and their associations with lipid molecules of the general residents in Wuxi City, Eastern China. Qianyu Chen, Yayun Zhang, Jianhua Li, Guanyong Su, Qi Chen, Zhen Ding, Hong Sun, Journal of Hazardous Materials, Volume 413, 5 July 2021
See Beyond Pesticides info:
Disproportionate Risks: The Effects of Pesticide Exposure Among the Population.  https://www.beyondpesticides.org/resources/disproportionate-risks/overview
Read More on Beyond Pesticides’ Agricultural Justice Page. https://www.beyondpesticides.org/programs/agricultural-justice
Pesticide-Induced Diseases: Body Burden. https://www.beyondpesticides.org/resources/pesticide-induced-diseases-database/body-burden
Of Note During Organic Month, Study Finds Organic Diet and Location Affect Pesticide Residues in the Body. https://beyondpesticides.org/dailynewsblog/2023/09/of-note-during-organic-month-study-finds-organic-diet-and-location-affect-pesticide-residues-in-the-body/
Posted in Atrazine, Endocrine Disruption, Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), Fungicides, neonicotinoids, simazine, Triazines, Uncategorized, World Health Organization by: Beyond Pesticides
No Comments
07
Mar
(Beyond Pesticides, March 7, 2024) As the threats to health, biodiversity, and climate converge in agricultural policy and practices, the question of defining the fundamental changes necessary to reverse these existential crises takes on life-sustaining importance. Despite the existence of an organic community with governing stakeholders (farmers, consumers, conservationists, retailers, processors, inspectors, and scientists) that has evolved over at least seven decades and is codified in the Organic Foods Production Act (OFPA) of 1990, the term ‚Äúregenerative‚ÄĚ is now increasingly being advanced as a loosely defined alternative to the organic standard and label, which is transparent, defined, certified, enforced, and subject to public input. The publication AgFunderNews (AFN) last month published its updated ‚Äú2024 list of agrifood corporates making regenerative agriculture commitments,‚ÄĚ a who‚Äôs who of the largest food and agribusiness corporations worldwide. The list includes companies such as ADM, Cargill, Danone, General Mills, Tyson, Unilever, Walmart, and more with commitments to millions of acres in their supply chain practicing ‚Äúregenerative‚ÄĚ agriculture with target dates ranging from 2024 to 2050.
The AFN author reporting on the ‚Äúregenerative‚ÄĚ trend states, ‚Äú[O]ne big challenge is that ‚Äėregenerative agriculture‚Äô still has no set definition. While that still holds true, the bigger observation in 2024 is the number of companies leaning heavily on sustainability jargon to describe goals. With¬†greenwashing pretty rampant nowadays, it will be important to check beneath the PR-friendly language at the actual acres, dates, practices and prescriptions.‚ÄĚ
Organic advocates point out that even if there was an agreed upon definition that was transparent to the public, the defined standard would require an inspection, certification, and enforcement mechanism that allows for public input and oversight, similar to the policy and structure established for organic claims under OFPA.
In January, Civil Eats reported that the State Innovation Exchange (SiX), a progressive answer to the industry-financed American Legislative Exchange Council (ALEC), organized a two-day workshop with over 30 state legislators from across the nation to provide ‚Äúlegislative approaches to promoting regenerative farming and ranching practices, which [SiX] believes can galvanize support across partisan and rural-urban divides.‚ÄĚ How will this compare with the organic statute and its mandate for organic systems plans that are soil-based with prohibitions on synthetic fertilizers, sewage sludge (biosolids), irradiation, excluded methods such as genetically engineered crops, and a national List of Allowed and Prohibited Substances? Is this building on organic standards to improve upon existing practices with more equitable and accessible production methods that meet the existential crises, including the climate crisis? Or, is this a weakening of the existing standards? Beyond Pesticides has advocated that the elevation of organic management practices with incentives and support because of the social good it provides in protecting life and saving resources that now go into treating petrochemical pesticide-induced illness and rebuilding after fires, floods, and mudslides, as well as loss of land.
As reported in Civil Eats, senior agriculture and food systems director at State Innovation Exchange (SiX), Kendra Kimbirauskas, finds it important to provide space for state legislators to ‚Äúarm [them] with the resources needed to tackle ‚Äėtough decisions‚Äô in their State Houses….and expose them to perspectives outside the typical agriculture lobbying groups on abstruse measures and less-obvious implications of bills.‚ÄĚ SiX facilitates a cohort of elected officials and state legislators from 43 states in a subset of their Agriculture and Food Systems program called Cohort for Rural Opportunity and Prosperity (CROP). ‚ÄúSiX connects lawmakers to policy advocates and agriculture-based organizations to share information and strategies in creating more effective policies.‚ÄĚ
With the looming crises, organic advocates acknowledge that providing counternarratives to the petrochemical industry and industrial agriculture interests is important to systems change and ‚Äúcreating effective policies,‚ÄĚ so long as it meets the urgency of the moment to protect public and ecological health. On the matter of biodiversity collapse, the United Nation‚Äôs (UN‚Äôs) Conference of the Parties (COP) to the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) stated in the 2022 COP15 meeting.: ‚ÄúDespite ongoing efforts, biodiversity is deteriorating worldwide, and this decline is projected to worsen with business-as-usual. The loss of biodiversity comes at a great cost for human well-being and the global economy.‚Ä̬†Beyond Pesticides has documented many aspects of this decline in biodiversity, and the implications for ecosystem, human, and planetary health. Similarly, the¬†28th United Nations Climate Change Conference of the Parties (COP28) in December 2023 signaled ‚Äúthe eventual end of the oil age.‚Ä̬†As reported previously, under organic management, healthy soil can absorb and store 1,000 pounds of carbon per acre foot of soil annually. This translates to about 3,500 pounds of carbon dioxide per acre drawn down from the air and sequestered into organic matter in soil. (It is noteworthy that use of¬†synthetic fertilizers actually compromises the carbon-capture¬†ability of some kinds of terrain, such as salt marshes.) A fact often overlooked by policy makers in generating climate strategies is that¬†carbon-sequestering soil practices are federally mandated¬†in certified organic agriculture.
As¬†reported by Beyond Pesticides in October 2021¬†before COP26, the¬†use of synthetic fertilizers is a particular and noxious contributor¬†to the rising planetary temperature. This happens largely through these products‚Äô emissions of nitrous oxide, or NOx¬†‚ÄĒ another potent greenhouse gas that also pollutes the air and feeds the development of ozone.¬†
While not necessarily representative of the broader movement, some regenerative agricultural practitioners and their products have been found to fall short of organic standards and open the door to loopholes for toxic pesticide use that undermines the sanctity of alternative agricultural systems compared to the conventional status quo. For instance, ‚Äúregenerative‚ÄĚ agriculture could embrace genetically engineered, herbicide-tolerant crops that require heavy use of herbicides. In 2019, industrial food titan General Mills committed to converting one million acres of farmland to regenerative practices by 2030. Their strategy allows for the transitional use of glyphosate-based herbicides in their regenerative agriculture strategy, which does not align with organic standards of proving that restricted pesticides have not touched land for three years.¬†
Additionally, a 2019 report by Friends of the Earth indicates the relationship between no-till practices (often analogous to ‚Äúregenerative‚ÄĚ agriculture) and the use of pesticides such as glyphosate: ‚Äú86 percent of No-Till Farmer¬†readers said they planned to plant Roundup Ready corn in 2017, while 80 percent planned to plant Roundup Ready soybeans, and some 92 percent planned to use glyphosate for weed control.‚ÄĚ This connection between no-till, regenerative, agriculture and the application of pesticides is also true in Vermont, where farmers are advised to grow and spray cover crops with the Glyphosate-based herbicide Roundup. ‚ÄúGlyphosate is applied to the [genetically engineered] corn crop as it grows, adding the compound not only to the soil (from where it can migrate to ground or surface waters) but also, because glyphosate is a systemic herbicide, to the whole of the plant that livestock will ultimately eat. Then, farmers are using the herbicide on the same fields again to kill off cover crops once those have grown and served their purposes.‚ÄĚ As a result, the application of glyphosate ‚Äúrose from roughly 13,000 pounds annually in 2009 to nearly 30,000 in 2016,‚ÄĚ exacerbating the health risks to nearby waterways and ecosystems.
Based on a wide array of analyses, organic land management as a baseline is crucial to address compounding crises relating to climate change, biodiversity, public health, and economic stability, while eliminating petrochemical pesticide use by 2032. There are examples of regenerative agriculture certifications that take this approach, including Rodale Institute and Regenerative Organic Alliance‚Äôs Regenerative Organic Certified (ROC) label. Researchers in California quantified the reduction of total pesticide use in organic and conventional farms, noting that there was a ‚Äú18‚Äď31% likely reduction in spraying of pesticides on organically managed fields compared to conventional, and a 27% likely reduction in use of pesticide products with high acute human toxicity for organic versus conventional fields‚ÄĚ from 2013 to 2019. Biodiversity and pollinator health are also shown to be more prevalent on organic versus conventional farms, according to a 2018 Swedish study that corroborates previous studies in 2011 and 2012.
In terms of safety for human consumption, organic farming has also proven to reduce the likelihood of foodborne human pathogens based on data ‚Äúcompar[ing] dung beetle populations, soil bacteria diversity, and feces removal rates on 70 organic and conventional broccoli farm fields.‚ÄĚ Additionally, a 2020 Public Health Nutrition study ‚Äď a first-in-the-nation comparison of pesticide levels in conventional versus organic milk ‚Äď found that ‚Äúall conventional, non-organic milk samples have residues of current-use pesticides, antibiotics, and growth hormones not present in organic samples,‚ÄĚ including atrazine, permethrin, cypermethrin, chlorpyrifos, diazinon, amoxicillin, sulfamethazine, and sulfathiazole. Legacy pesticides, including ppDDT and ppDDE, were found in both organic and non-organic samples, but these ‚Äúresidue levels remain higher in conventional milk samples than organic.‚ÄĚ
To engage in opportunities to strengthen the National Organic Program, see our section on Keeping Organic Strong. Stay tuned for updated resources on the April 2024 NOSB meeting in Milwaukee, WI! Each year we provide information on the meeting agendas, pertinent proposals, sign-up periods to submit comments to the Board, as well as historical context and potential strategies in alignment with our Actions of the Week. Some of these Actions of the week include ‚ÄúTell[ing] NOP to adopt an origin of livestock rule that protects dairy farmers and consumers,‚ÄĚ ‚ÄúTell[ing] your U.S. Representative and Senators to address climate change in the Farm Bill by incorporating a large-scale, national transition to certified organic agriculture and restoration and resilience strategies that prohibit the use of petrochemical pesticides and fertilizers,‚ÄĚ ‚ÄúTell[ing] Secretary of Agriculture Vilsack to implement the NOSB recommendation to remove incentives to convert native ecosystems to organic farms,‚ÄĚ and ‚ÄúTell[ing] EPA and USDA that ‚Äėregenerative‚Äô agriculture must be organic.‚ÄĚ
All unattributed positions and opinions in this piece are those of Beyond Pesticides.   
Sources: Civil Eats, Ag Funders Network
Posted in Agriculture, California, Cargill, Climate, General Mills, Regenerative, soil health, TruGreen, Uncategorized, Wal-Mart by: Beyond Pesticides
No Comments
06
Mar
(Beyond Pesticides, March 6, 2024) With over 2,500 pet deaths and 900 reports of adverse effects to people, an Office of Inspector General (OIG) report, published on February 29, 2024, reveals multiple systemic failures by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency‚Äôs (EPA) Office of Pesticide Programs (OPP), citing inadequate safety reviews of Seresto pet collars. The report, The EPA Needs to Determine Whether Seresto Pet Collars Pose an Unreasonable Risk to Pet Health, concludes, ‚ÄúThe EPA‚Äôs response to reported pesticide incidents involving Seresto pet collars has not provided assurance that they can be used without posing unreasonable adverse effects to the environment, including pets.‚ÄĚ At the time the animal effects made headlines in 2021, the agency defended the product‚Äôs registration, telling the media that, despite these incidents, EPA deemed Seresto collars ‚Äú‚Äėeligible for continued registration‚Äô based on best available science, including incident data… No pesticide is completely without harm, but EPA ensures that there are measures on the product label that reduce risk.‚ÄĚ‚ÄĮDespite the scathing criticism, EPA maintains the position that it conducted an adequate review of the two active insecticide ingredients in the pet collars‚ÄĒthe neurotoxic insecticide‚ÄĮflumethrin, and the notorious neonicotinoid‚ÄĮimidacloprid‚ÄĒproven to have adverse effects on the endocrine system as environmental contaminants.¬†
In the report, the OIG states, ‚ÄúSpecifically, the OPP [Office of Pesticide Programs] did not conduct domestic animal risk assessments for either flumethrin or imidacloprid as it had committed to do in initial and final work plans for both pesticides. Furthermore, according to a long-tenured EPA scientist we interviewed, the EPA‚Äôs 1998 Guideline 870.7200 for companion animal safety studies is inadequate, and the OPP lacks standard operating procedures and a methodology to help determine when pet products may pose unreasonable adverse effects to the environment.‚ÄĚ With this statement, the report calls out EPA for its failure to adequately assess the safety of Seresto flea and tick collars, originally formulated by Bayer and now manufactured by Elanco. The OIG demands that EPA, ‚ÄúIssue amended proposed interim registration review decisions for both flumethrin and imidacloprid that include domestic animal risk assessments for flumethrin and imidacloprid; written determinations on whether the Seresto pet collar poses unreasonable adverse effects in pets; and an explanation of how the Office of Pesticide Programs came to its determinations. Allow for public comment by placing these documents in the applicable registration review dockets.‚ÄĚ EPA defends its process and points to mitigation measures it adopted and announced in July 2023. The agency says that it was unable to determine the cause of the animal deaths, except for some possible mechanical strangulations that were associated with a failure of the collar‚Äôs release mechanism. However, the agency did find some neurological effects and struck an agreement with Elanco to issue label warnings and improve the quality of incident data collected by the manufacturer.¬†
The New Lede reported, ‚ÄúThe (Seresto) collars have been the subject of more than 105,354 incident reports, including the 3,000 pet deaths, more than any other EPA regulated product in history, according to the EPA‚Äôs incident database.‚ÄĚ The OIG investigation began in response to these and ‚Äúnearly 900 reports of human pesticide incidents related to the Seresto pet collars‚ÄĚ received from 2012 through 2022.¬†¬†
Synergistic Effects of Flumethrin and Immidacloprid Not Evaluated 
As Beyond Pesticides previously reported, Seresto collars are plastic pet collars embedded with pesticides designed to kill fleas, ticks, and lice by emitting the poisons from the collar; they contain the active ingredients flumethrin and imidacloprid. Flumethrin, a chemical in the pyrethroid class of synthetic neurotoxic insecticides, has been linked repeatedly to neurological issues, such as seizures and learning disabilities in children, to gastrointestinal distress, and to damage to invertebrates, according to EPA‚Äôs own analysis¬† In a March 2021 call to action, Beyond Pesticides reported that a 2012 study found [flumethrin and imidacloprid] have a synergistic effect, meaning they are more toxic together on fleas. However, EPA consistently fails to evaluate synergistic effects of pesticides, a 2016‚ÄĮEPA bulletin concluded: ‚ÄúThe risk of the combination of the two active ingredients, flumethrin and imidacloprid, was not assessed because the two chemicals act in completely different ways.‚ÄĚ Similarly, as Beyond Pesticides has pointed out repeatedly, EPA does not do an adequate job of evaluating the risks and harms of exposures to multiple pesticide compounds, as well as those of so-called¬† ‚Äúinert‚ÄĚ or ‚Äúother‚ÄĚ pesticide ingredients that are not disclosed on the product label.¬†
 
As the OIG report discovered in its findings, EPA demonstrated:  
- Lack of Adherence to Registration Process: The EPA’s Office of Pesticide Programs (OPP) has failed to adhere to certain aspects of the pesticide registration review process for the active ingredients, flumethrin and imidacloprid, in Seresto collars. Specifically, the OPP did not conduct domestic animal risk assessments as initially planned, as required by their work plans for both pesticides. This failure raises concerns about the agency’s commitment to ensuring the safety of pet products.¬†
 
- Inadequate Guidelines and Procedures: The OPP lacks standard operating procedures and a methodology to determine when pet products may pose unreasonable adverse effects to the environment. According to a long-tenured EPA scientist, the agency’s 1998 Guideline 870.7200 for companion animal safety studies is inadequate and described ‚Äúas a ‚Äúglaring weakness‚ÄĚ that has become publicly obvious with the Seresto pet collar incidents. More efficient, advanced, and accurate methods for ensuring a margin of safety have been developed.‚Ä̬†¬† ¬†
 
- Incomplete Incident Data Collection: The EPA has collected incident data related to Seresto pet collars through its Incident Data System (IDS). However, the IDS does not capture all the necessary data for the agency to assess the unreasonable adverse effects of pet products. This incomplete data collection hampers the EPA’s ability to fully understand the risks associated with Seresto collars and take appropriate action.¬†
 
- Lack of Public Assurance: The EPA’s lack of action in response to reported incident data and its failure to capture comprehensive data through the IDS does not provide the public with sufficient assurance that Seresto pet collars are safe for use. The agency’s inaction raises concerns about its commitment to protecting the environment and the well-being of pets.¬†
The OIG report notes, ‚Äú [T}he U.S. House of Representatives Committee on Oversight and Government Reform, which is now the Committee on Oversight and Accountability, Subcommittee on Economic and Consumer Policy launched an investigation‚Ķin 2022, the subcommittee released a report of its investigation, which outlined the EPA‚Äôs awareness of these incidents and the potential harm caused by the collars and the EPA‚Äôs own conclusion after an independent review conducted in 2016 that the collars ‚Äúprobably or possibly‚ÄĚ caused 45 percent of the reported pet deaths.‚Ä̬†
The measures EPA announced after its July 2023 review include the following: 
- Adding label warnings on common adverse effects that have been reported, along with instructions to remove the collar if those effects occur and on how to report the incident.  
- Requiring the registrant to report incident and sales data on an annual basis and provide additional information about incidents whenever possible.  
- Improving the quality of data reported when receiving reported incidents from consumers. 
The committee’s report also highlighted that the Seresto collar was banned in Canada following an assessment by federal regulators. The assessment concluded that the collar “probably or possibly” caused 77% of reported incidents categorized as “death” or “major” when used on pets.¬†
OIG Report Recommendations 
The OIG report makes eight recommendations, which include directing the EPA to improve data gathering and update the EPA‚Äôs Incident Data System so that it can ‚Äúadequately assess incident reports and make timely decisions,‚ÄĚ implement procedures for how to conduct domestic animal risk assessments, a measurable standard to determine when a pet product poses unreasonable adverse effects, and update EPA‚Äôs 1998 Guideline for Companion Animal Safety to align with international standards.¬† The first OIG recommendation directs the EPA to revise and issue interim registration review decisions for flumethrin and imidacloprid, perform risk assessments for domestic animals and issue written determination of the Seresto pet collar’s safety. It also asks for an account of the decision-making process by the Office of Pesticide Programs and to enable public feedback by including these documents in the relevant review dockets.
Unsurprisingly, the EPA‚Äôs Office of Chemical Safety and Pollution Prevention (OCSPP) claimed they had satisfied this recommendation with actions taken on July 13, 2023, implying no further action was necessary. The OIG pointed out that the EPA’s response missed the recommendation intent. The OIG highlighted that the EPA did not use the formal process required for reviewing these products (interim pesticide registration and a domestic animal risk analysis), did not allow for public comments, and did not conclusively determine the safety of the Seresto collars as advised by issuing a determination on whether the Seresto pet collar poses unreasonable adverse effects in pets. This recommendation remains unresolved and the OIG directs EPA to submit “its responses concerning specific actions in process or alternative corrective actions proposed on the recommendation” within 60 days.
EPA‚Äôs other substantive response was to point to a February 2023 joint white paper by the EPA and Food and Drug Administration (FDA) titled ‚ÄúA Modern Approach to EPA and FDA Product Oversight,” which discusses moving regulatory jurisdiction over pet collars and roughly 600 other topical pet products from the EPA to the FDA. ¬†
In the absence of real regulatory reform, readers may ask what they can do to keep their pets safe. 
How to Keep Pets Safe: Use Principles of Ecological Pest Management 
For your pet: While keeping your pets and home free of fleas and ticks is important, Beyond Pesticides recommends talking to your veterinarian about treatment options and asking questions about poisoning incidents associated with any product they recommend. Pet owners should vacuum daily during flea season with a strong vacuum cleaner, changing the bag often; groom pets with a flea comb daily, using soapy water to dunk and clean the comb between strokes; bathe pets frequently with soap and water; and restrict pets to a single bed and wash bedding frequently to kill larvae. If you choose to use a flea and tick product on your pet, have it applied by your veterinarian and monitor pets for any signs of an adverse reaction after application. 
At home: Ecological Pest Management emphasizes the broader ecology of pest management and avoiding toxic chemicals unless there are no alternatives. Use Beyond Pesticides‚Äô ManageSafe™ page to find out how to take a least-toxic approach to issues in the home and garden!¬†
Grow Organic Lawns and Gardens!  
Create a pesticide-free space for your pet and encourage neighbors to do the same. There are plenty of resources to help! See Beyond Pesticides’ factsheets for information on how to manage a weed-free yard and lawn: Read Your “Weeds”: A Simple Guide to Creating a Healthy Lawn. Fall is the best time to intervene and make your yard free of toxic chemicals. Read our fall lawncare fact sheet, Organic Lawn Care 101, for specific information on how to prime your yard for next year! An organic lawn requires a holistic paradigm shift, not a product-for-product swap. However, if you‚Äôre looking for safe products, look at our Products Compatible with Organic Landscape Management, and our campaign, Parks for a Sustainable Future, for hands-on assistance to municipalities nationwide.¬†
Advocate for Policy Change 
Ultimately, the burden of keeping our pets safe from toxic chemicals should not fall on the public. Cities, counties, states, and the federal government should respond to the body of evidence showing that toxic pesticides are harmful through precautionary regulation and legislation. See our Tools for Change and contact us at [email protected] if you’re ready to join the movement to end the use of petrochemical pesticides and transition to organic! 
 
All unattributed positions and opinions in this piece are those of Beyond Pesticides. 
 
Sources:  
The EPA Needs to Determine Whether Seresto Pet Collars Pose an Unreasonable Risk to Pet Health, Office of Inspector General, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, February 29, 2024. 
Report finds EPA failing to do its job amid thousands of Seresto flea and tick collar complaints, New Lede, February 29, 2024. 
To flea or not to flea: survey of UK companion animal ectoparasiticide usage and activities affecting pathways to the environment.‚ÄĮPeerJ‚ÄĮ11:e15561, Perkins R, Goulson D.‚ÄĮ2023.¬†
Seresto Flea and Tick Collars: Examining Why A Product Linked to More Than 2,500 Pet Deaths Remains On The Market, U.S. House Committee on Oversight and Reform, Subcommittee Economic and Consumer Policy, June 2022.  
Posted in Bayer, behavioral and cognitive effects, Children, Elanco, Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), Fleas, Flumethrin, Food and Drug Administration (FDA), Groundwater, Imidacloprid, Mosquitoes, Pesticide Regulation, Pets, Repellent, Seresto, synergistic effects, Synthetic Pyrethroids, Ticks, Uncategorized by: Beyond Pesticides
2 Comments
05
Mar
(Beyond Pesticides, March 5, 2024) Buried in a court decision in February that determined that the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) violated the law in allowing harm associated with the herbicide dicamba‚Äôs registration is language that permits the damages to continue through this year‚Äôs growing season. The judge‚Äôs ruling, deferring to EPA‚Äôs interpretation of the existing stock provision in the federal pesticide law, continues a pattern of ‚Äúexisting stock‚ÄĚ allowances that permit hazards to continue well after a finding of harm or noncompliance. This process contrasts with the issuance of a product recall, which is typically done when pharmaceuticals are found to violate safety standards.
Despite the finding of dicamba’s harm and EPA’s failure to comply with standards, the continued use of the weed killer through the 2024 growing season is effectively authorized in a decision of the U.S. District Court of Arizona, which vacates the EPA’s 2021 authorization of the use of three over-the-top (OTT) uses of dicamba-based herbicide products. In response, EPA issued an existing stocks order.
EPA’s pattern of allowing the use of existing stocks has long been a concern for public health and environmental advocates, who have called for the discontinuance of use upon findings of elevated risk factors or illegal uses that do not comply with statutory standards. After EPA determined in 1999 that the toxic insecticide, chlorpyrifos, is highly neurotoxic to children, EPA announced in June 2000 an agreement it had reached with Dow AgroSciences that phased out most home uses, but permitted sales to continue through 2001 so that all existing stocks could be sold off. During the existing stock sell-off of chlorpyrifos labeled for home use, no warning was provided to the public and retailers offered discounts to help clear their shelves. Beyond Pesticides in the late 1980s (then the National Coalition Against the Misuse of Pesticides/NCAMP) sued EPA (see The Washington Post and The New York Times) when the agency negotiated an agreement with Velsicol to phase out the use of the insecticide chlordane and allow all existing stocks to be used up. Then the issue was cancer, and the judge in the case found that the additional cancers that would be caused by leaving the chemical in commerce for the phaseout period, including the cost to cancer victims, were unacceptable. On a regulatory level, the judge also found that EPA’s failure to evaluate the harm caused during the phase-out period was a violation of the agency’s responsibility under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA). The District Court’s finding was reversed on appeal, but by then, EPA had negotiated a shortened phaseout period and established a recall/buyback program, something the agency rarely does. For a history lesson on the failure of FIFRA, see National Coalition Against the Misuse of Pesticides, et al., Appellees, v. Environmental Protection Agency, et al., Appellants, 867 F.2d 636 (D.C. Cir. 1989).
The current situation with the continued use of dicamba under the existing stock allowance is described by EPA’s Office of Chemical Safety and Pollution Prevention: ‚ÄúThis Existing Stocks Order is limited in time and scope, allowing for certain sale, distribution, and use of existing stocks of these formerly-registered dicamba products for the 2024 growing season… EPA has received ample evidence that millions of gallons of OTT dicamba had already entered the channels of trade prior to February 6, 2024. Additionally, most growers have already placed orders for dicamba-tolerant seed for the 2024 growing season and, given the timing of these registrations being vacated, are not able to pivot to another herbicide-tolerant seed and herbicide system.‚ÄĚ
A report by AgWeek outlines how the existing stocks order will impact farmers differently depending on the state. “The products can be sold and used by different dates depending on the state, as follows:
- Iowa, Illinois and Indiana: Sales through May 13; use through June 12 or V4 growth stage in soybeans or first square growth stage in cotton, whichever comes first.
- Minnesota: Sales south of Interstate 94 through May 13 and north of I-94 through May 31; use south of I-94 through June 12 and use north of I-94 through June 30.
- South Dakota: Sales through May 21; use through June 20.
- Alabama, Arizona, Arkansas, Colorado, Delaware, Florida (excluding Palm Beach County), Georgia, Kansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Maryland, Michigan, Mississippi, Missouri, Nebraska, New Jersey, New Mexico, New York, North Carolina, North Dakota, Ohio, Oklahoma, Pennsylvania, South Caroline, Tennessee (excluding Wilson County), Texas, Virginia, West Virginia and Wisconsin: Sales for soybeans through May 31 and sales for cotton through June 30; use on soybeans through June 30 and use on cotton through July 30.‚ÄĚ
As Beyond Pesticides has mentioned in a previous Daily News, ‚ÄúDicamba and other types of herbicide have proven to pose stark adverse health risks to farmworkers and ecosystems. . . For example, there is a strong association between dicamba use and an increased risk of developing various cancers, including liver and intrahepatic bile duct cancer, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and acute myeloid leukemia. In the Gateway on Pesticide Hazards and Safe Pest Management entry for Dicamba, there is a slew of medical studies detailing adverse health and environmental effects, including neurotoxicity, kidney/liver damage, sensitization/irritation, birth/developmental defects, reproductive damage, and respiratory illnesses. Dicamba has also been proven to have adverse health impacts on wildlife habitats, including the spraying of approximately 1,328 pounds in the National Wildlife Refuge in 2016 alone, impacting bird populations and pollinator species in particular. Dicamba is a poster child of a failed regulatory system that creates ecosystem imbalances by attempting to correct them, considering that the herbicidal drift of this herbicide has proven to lead to antibiotic resistance after testing sublethal traces on bacteria.‚ÄĚ
The District of Arizona, in its ruling, provides leeway for the EPA to employ its powers pursuant to the FIFRA: ‚ÄúThe Court notes that in response to vacatur of the 2016, as amended in 2018, OTT dicamba registrations, the EPA cancelled the registrations but allowed use of existing stock. Vacating the registrations poses no greater risk to the environment than leaving it in place because other similar herbicide options are available to replace it in the interim. Threats of noncompliance or that growers will use more dangerous non-OTT dicamba products if these registrations are vacated are weakened by concerns reflected in the 2021 Report that such noncompliance already occurs.‚ÄĚ Indeed, Section 6 of FIFRA states, ‚ÄúThe [EPA] Administrator may permit the continued sale and use of existing stocks of a pesticide whose registration is suspended or cancelled under this section or section 136a [ ]11, to such extent, under such conditions, and for such uses as the Administrator determines that such sale or use is not inconsistent with the purposes of this subchapter.‚ÄĚ [7 U.S.C. ¬ß 136d(a)(1)]
As advocates witnessed with dimethyl tetrachloroterephthalate (DCPA), chlordane, methyl iodide, and chlorpyrifos, the use of existing stocks orders enables the continued use of toxic pesticides that the EPA has acknowledged are dangerous to farmworkers, farmers, ecosystems, wildlife, and the general public. Some of these existing stocks orders fail to include a sunset date in which these products are permanently phased out of both production and use.
The routine use of existing stock orders serve as an example of EPA‚Äôs commitment to facilitating access to toxic pesticides even after the unacceptable hazards and potential damage associated with their use has been determined. Advocates have challenged the continued marketing of pesticides after EPA has determined that risk criteria are exceeded and without any notice to the public and users. Beyond Pesticides takes the position that these hazards are not ‚Äúreasonable‚ÄĚ under FIFRA, given the availability and profitability of USDA certified organic practices that eliminate the need for toxic petrochemical pesticides like dicamba and chlorpyrifos. In collaboration with our partners, Natural Grocers, Stonyfield Organic, and other supporters, Beyond Pesticides has successfully trained parks and land managers for higher education institutions, cities, and municipalities to adopt organic principles as models for state and federal policy. Learn more by viewing Parks for a Sustainable Future.
All unattributed positions and opinions in this piece of those of Beyond Pesticides.
Sources: AgWeek, EPA
Posted in Dicamba, Drift, Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), Genetic Engineering, Herbicides, Litigation, Uncategorized by: Beyond Pesticides
No Comments
04
Mar
(Beyond Pesticides, March 4, 2024) With 14.7 million children and adolescents in the U.S. recognized as obese by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the established connection with endocrine disrupting contaminants, including many pesticides, Beyond Pesticides is calling on federal food assistance programs to go organic. The problem of childhood obesity is higher in people of color and, as a result, is an environmental justice issue. According to CDC, the prevalence of childhood obesity is ‚Äú26.2% among Hispanic children, 24.8% among non-Hispanic Black children, 16.6% among non-Hispanic White children, and 9.0% among non-Hispanic Asian children.‚ÄĚ
While childhood obesity is recognized as a serious problem, the National School Lunch Program of the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA)‚ÄĒalthough improved by the Healthy, Hunger-Free Kids Act of 2010‚ÄĒstill provides lunches laced with obesogenic pesticides. To take meaningful steps against childhood obesity, school lunches must be organic. The program served 4.9 billion meals in fiscal year 2022 in over 100,000 public and nonprofit schools, grades Pre-Kindergarten-12.
Contrary to popular opinion, the blame for the obesity epidemic cannot be attributed solely to diet and exercise broadly, but relates directly to pesticide and toxic chemical exposures, including residues in food, that may lead to Type 2 diabetes, heart disease, high blood pressure, kidney failure, a breakdown of cartilage and bone within joints, and other metabolic disorders. An increasing body of research shows that exposure to certain pesticides and environmental contaminants initiates various changes in metabolism leading to obesity‚ÄĒnot only in the exposed person, but also in offspring. According to medical researchers, obesity ‚Äúis a complex disease which has reached pandemic dimensions‚ÄĚ and multigenerational effects. The prevalence of obesity increased three-fold from 1980 to 2019.
While childhood obesity is recognized as a serious problem, the National School Lunch Program of the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA)‚ÄĒalthough improved by the Healthy, Hunger-Free Kids Act of 2010‚ÄĒstill provides lunches laced with obesogenic pesticides. To take meaningful steps against childhood obesity, school lunches must be organic.
>> Tell USDA’s Food and Nutrition Service to require organic school lunches. Tell EPA not to register pesticides that contain obesogens.
The failure of the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to prevent exposure to obesogens and carry out its statutory mandate to evaluate endocrine disrupting pesticides, puts the public, especially children, at risk. In addition, EPA does not consider and promote nontoxic and beneficial alternatives, such as organic food production‚ÄĒwhich the agency could do under its mandate to protect against ‚Äúunreasonable adverse effects‚ÄĚ to people and environment in the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA).
Environmental obesogens are endocrine-disrupting chemicals that ‚Äúmay increase adipose tissue deposition, expand adipocytic size, regulate appetite and satiety, and slow metabolism to induce the occurrence of obesity.‚ÄĚ A recent review of the literature finds, ‚ÄúEnvironmental obesogens have the potential to induce adipogenesis, increase energy storage, and interfere with appetite and homeostasis within the neuroendocrine system, thereby promoting the development of obesity. Since the obesogen hypothesis was proposed in 2006, more than 50 chemicals have been identified as environmental obesogens. Furthermore, the increasing usage of newly developed chemical products has led to the detection of increasing amounts of new contaminants in the environment, which may have obesogenic effects and cause potential risks to human health.‚ÄĚ
The current list of identified environmental obesogens includes pesticide active ingredients such as chlorpyrifos, atrazine, organotins, and triclosan, as well as contaminants and other ingredients that may be found in pesticide products such as dioxins, phthalates, per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), alkylphenols, and polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). In addition to the effects of a single obesogen, two or more obesogens may have a synergistic effect, as shown by the interaction of tributyltin (TBT) and perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS).
>> Tell USDA’s Food and Nutrition Service to require organic school lunches. Tell EPA not to register pesticides that contain obesogens.
Letter to Food and Nutrition Service Deputy Under Secretary Stacy Dean, USDA Secretary Vilsack, and Members of Congress:
Consistent with the mission of the Food and Nutrition Service to end hunger and obesity through the administration of 15 federal nutrition assistance programs including the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC), Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), and school meals, it is important that school lunches be free of chemical obesogens. The only way to ensure this is to require that school lunches be prepared with organic ingredients.
Contrary to popular opinion, the blame for the obesity epidemic cannot be attributed solely to diet broadly, but relates directly to pesticide and toxic chemical exposures, including residues in food, that are known as obesogens and associated with a number of related health conditions‚ÄĒ high blood pressure, high blood sugar, excess body fat around the waist, and abnormal cholesterol levels collectively known as the ‚Äúmetabolic syndrome.‚ÄĚ Metabolic syndrome increases risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. Avoiding pesticide exposure is a good way to avoid obesogens, so organic food should be part of every strategy‚ÄĒincluding school lunch programs‚ÄĒdesigned to provide healthy nutrition to children.
Childhood obesity is a serious problem in the U.S., leading to a host of health problems in childhood and later in life. Juvenile obesity is highest in Hispanic, African American, and lower income groups, which provides an opportunity for the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s (USDA) school lunch program to have a positive impact.
Environmental obesogens are endocrine-disrupting chemicals that ‚Äúmay increase adipose tissue deposition, expand adipocytic size, regulate appetite and satiety, and slow metabolism to induce the occurrence of obesity.‚ÄĚ A recent review of the literature finds, ‚ÄúEnvironmental obesogens have the potential to induce adipogenesis, increase energy storage, and interfere with appetite and homeostasis within the neuroendocrine system, thereby promoting the development of obesity. Since the obesogen hypothesis was proposed in 2006, more than 50 chemicals have been identified as environmental obesogens. Furthermore, the increasing usage of newly developed chemical products has led to the detection of increasing amounts of new contaminants in the environment, which may have obesogenic effects and cause potential risks to human health.‚ÄĚ
The current list of identified environmental obesogens includes pesticide active ingredients such as chlorpyrifos, atrazine, organotins, and triclosan, as well as contaminants and other ingredients that may be found in pesticide products such as dioxins, phthalates, per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), alkylphenols, and polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). In addition to the effects of a single obesogen, two or more obesogens may have a synergistic effect, as shown by the interaction of tributyltin (TBT) and perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS).
The National School Lunch Program (NSLP)‚ÄĒas a federally assisted meal program operating in public and nonprofit private schools and residential childcare institutions to provide ‚Äúnutritionally balanced, low-cost or free lunches to children each school day‚ÄĚ‚ÄĒmust play a leadership role in removing hazardous chemicals from the meals it feeds to children. In providing free or reduced cost lunches to qualified children, NSLP is an excellent way to ensure that children can receive obesogen-free meals. However, since many pesticides are obesogens, those school lunches must be organic.
Please initiate policy requiring organic school lunches.
Thank you.
Letter to EPA:
Contrary to popular opinion, the blame for the obesity epidemic cannot be attributed solely to diet broadly, but relates directly to pesticide and toxic chemical exposures, including residues in food, that may lead to Type 2 diabetes, heart disease, high blood pressure, kidney failure, a breakdown of cartilage and bone within joints, and other metabolic disorders. An increasing body of research shows that exposure to certain pesticides and environmental contaminants initiates various changes in metabolism leading to obesity‚ÄĒnot only in the exposed person, but also in offspring. According to medical researchers, obesity ‚Äúis a complex disease which has reached pandemic dimensions‚ÄĚ and multigenerational effects. The prevalence of obesity increased three-fold from 1980 to 2019.
Environmental obesogens are endocrine-disrupting chemicals that ‚Äúmay increase adipose tissue deposition, expand adipocytic size, regulate appetite and satiety, and slow metabolism to induce the occurrence of obesity.‚ÄĚ A recent review of the literature finds, ‚ÄúEnvironmental obesogens have the potential to induce adipogenesis, increase energy storage, and interfere with appetite and homeostasis within the neuroendocrine system, thereby promoting the development of obesity. Since the obesogen hypothesis was proposed in 2006, more than 50 chemicals have been identified as environmental obesogens. Furthermore, the increasing usage of newly developed chemical products has led to the detection of increasing amounts of new contaminants in the environment, which may have obesogenic effects and cause potential risks to human health.‚ÄĚ
The current list of identified environmental obesogens includes pesticide active ingredients such as chlorpyrifos, atrazine, organotins, and triclosan, as well as contaminants and other ingredients that may be found in pesticide products such as dioxins, phthalates, per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), alkylphenols, and polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). In addition to the effects of a single obesogen, two or more obesogens may have a synergistic effect, as shown by the interaction of tributyltin (TBT) and perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS).
The inability of the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to prevent exposure to obesogens through the use of pesticides is one more failure of the agency to carry out its mandated regulation of endocrine disrupting pesticides. It is evidence of a failed pesticide regulatory system that does not consider and promote nontoxic and beneficial alternatives, such as organic agriculture‚ÄĒwhich the agency could do under its mandate to protect against ‚Äúunreasonable adverse effects‚ÄĚ to people and environment in the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA).
Please ensure that pesticide risk assessments include the harms arising from exposure to obesogens. Please also ensure that the baseline against which ‚Äúbenefits‚ÄĚ of pesticides are measured is organic agriculture.
Thank you.
Posted in Agriculture, Alternatives/Organics, Children, Children/Schools, Diabetes, Endocrine Disruption, Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), metabolic syndrome, Take Action, Uncategorized, US Department of Agriculture (USDA) by: Beyond Pesticides
8 Comments
01
Mar
(Beyond Pesticides, March 1, 2024) A comprehensive research review published in Environment & Health analyzes existing research demonstrating the link between an increase in obesity and the proliferation of synthetic chemicals that ‚Äúinterfere with lipid metabolism.‚ÄĚ The study documents over 50 obesogens with high-level human exposure rates, including per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFASs), phthalates (PAEs), and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs), that can lead to lipid metabolism disruption including health impacts on the liver and insulin resistance, among other metabolic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and dyslipidemia. Authors in this study highlight the scientific research community‚Äôs focus on adipose tissue and the liver, and a need to further explore effects on cardiovascular and kidney health. This anthology of research demonstrates the complexity of the threats associated with toxic pesticides, the severe limitations of their regulatory review, and the failure to consider organic practice and product alternatives that eliminate their use.
Environmental obesogens are chemicals that are proven to have a health impact on metabolic systems relating to obesity. This review evaluates literature, going back to the 2006 obesogen hypothesis, on the metabolic impacts of environmental obesogens, including epidemiologic data, in vitro studies, and bioassays. Researchers scanned Web of Science, PubMed, Google Scholar, and Scopus for research studies with search terms including ‚Äúenvironmental obesogens,‚ÄĚ ‚Äúlipid metabolism,‚ÄĚ ‚Äúinfluencing factors,‚ÄĚ and ‚Äúresearch approaches.‚ÄĚ
The study dissects numerous influencing factors on long-term adverse health effects from obesogen exposure, including transgenerational effects, windows of susceptibility, gender differences, structure-effect relationships, and dietary habits. Researchers find that exposure to obesogens can ‚Äúalter the epigenetic programming of germ cells (sperm or egg),‚ÄĚ meaning that health impacts from these chemicals can be transferred forward through ‚Äúmultiple generations,‚ÄĚ vulnerabilities associated with ‚Äúwindows of susceptibility.‚ÄĚ In a multitude of animal studies, exposure to toxic chemicals, substances, and pesticides (e.g. chlorpyrifos, PAEs, dioxins, organotins, flame retardants, BPA and analogues, alkylphenols, PFASs, food additives, and heavy metals) in earlier stages of life can lead to health issues when their parent is exposed to chemicals. For example, bis(2-exthylexyl) phthalate (DEHP) ‚Äúwas found to cause long-term disturbance in the glucose homeostasis of [‚ÄėWistar rats‚Äô] offspring,‚ÄĚ leading to an increase in visceral fat and overall body weight. The review also finds distinctions in lipid metabolic impacts between men and women: ‚ÄúWomen typically exhibit a body fat percentage that is approximately 10% higher than that of men.‚ÄĚ Gender differences in obesogenic effects are important to track, given the distinction in regulatory pathways impacted by endocrine disruptors in lipid metabolism for men and women.
The molecular structure of the obesogens, be they isomers, stereoisomers, or analogues, can ‚Äúproduce significant variations in their [health] effects, requiring further experimental verification,‚ÄĚ however, much more research is needed to be done to increase understanding. Dietary habits, particularly high-fat diets of processed food products, represent the most significant source of exposure to obesogens. ‚ÄúThe gut microbiota plays a vital role in the development of obesity,‚ÄĚ the authors report. ‚ÄúThe composition of the gut microbiota is highly dynamic and can be rapidly and substantially altered by diet and other environmental factors.‚ÄĚ Beyond Pesticides tracks scientific studies that corroborate this finding, underscoring the health implications of switching to organic food, including the reduction of glyphosate residues and urinary organophosphate pesticide metabolites.
Obesity is an international health problem. Without intervention, more than half the global population will be living with overweight or obesity problems by 2035, according to the World Obesity Federation. The World Health Organization in 2021 estimated that worldwide obesity has tripled since 1975. Meanwhile, during this same period there has been the introduction of hundreds of petrochemical-based pesticides with the promise of increased food production and pest protection that can be achieved with nontoxic practices.
Beyond Pesticides has discussed extensively the impact of pesticides on public health, as well as opportunities to safeguard yourself and your loved ones from their health impacts. As a keynote speaker at Beyond Pesticides‚Äô 36th National Pesticide Forum, ‚ÄúOrganic Neighborhoods: For healthy children, families, and ecology,‚ÄĚ Bruce Blumberg, PhD broke down the impacts of prenatal obesogens in the session Cutting Edge Science. ‚ÄúIn the obesogen-exposed animals, this structure is disturbed, and that leads to heritable changes in which genes are expressed. This altered structure is inherited, and that leads us to get this leptin-resistant thrifty phenotype four generations later, as published in Ancestral perinatal obesogen exposure results in a transgenerational thrifty phenotype in mice.‚ÄĚ There are several aspects of obesogens that scientists are still determining, including the number of obesogens and the degree to which prenatal exposure alters adult phenotype from babies as they grow up from ancestors who have intergenerational interactions with obesogens. There is also a study that describes associations between type 2 diabetes, obesity, and pesticide exposure, specifically ő≤-Hexachlorocyclohexane (ő≤-BHC) and oxadiazon.
What scientists do know are the links between health impacts, toxic pesticide exposure, and healthy alternatives. In 2018, researchers presented the following recommendations on how to avoid exposure to obesogens to the European Society for Endocrinology in Barcelona:
- ‚ÄúChoosing fresh food over processed products with long lists of ingredients on the label ‚Äď the longer the list, the more likely the product is to contain obesogens
- Buying fruit and vegetables produced without pesticides, such as certified organic or local pesticide-free products.
- Reducing the use of plastic, especially when heating or storing food. Instead, use glass or aluminum containers for your food and drinks.
- Removing shoes when entering the house to avoid bringing in contaminants in the sole of shoes.
- Vacuuming often, using high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters and dust your house frequently using a damp cloth.
- Removing or minimizing carpet at home or work, as they tend to accumulate more dust.
- Avoiding cleaning products when possible or choose those that do not contain obesogens.‚ÄĚ
Beyond Pesticides has a variety of resources and information to empower consumers with the tools to protect their well-being and opportunities to advocate for the mission to eliminate petrochemical pesticides in the next decade. An effective way to avoid obesogen exposure is purchasing organic food. See Eating With A Conscience and Feeding Your Family Organic…Affordably on strategies for more information.
All unattributed positions and opinions in this piece are those of Beyond Pesticides.
Source: Environment & Health
Posted in Cardiovascular Disease, Disease/Health Effects, metabolic syndrome, metabolic syndrome, Uncategorized, World Health Organization by: Beyond Pesticides
No Comments
29
Feb
(Beyond Pesticides, February 29, 2024)  In the face of federal inaction, an Oregon regulation banning the agricultural uses of the highly toxic chlorpyrifos took effect on January 1, 2024. Chlorpyrifos was voluntarily withdrawn from the market in 2000 for most residential uses by its manufacturer, Dow Chemical, and has been the subject of extensive litigation. At that time, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) allowed most agricultural uses to continue. Oregon joins four other states that have acted to ban chlorpyrifos, including Hawai’i, New York, California, and Maryland.  
Central to state action are nervous system and brain effects in children, especially farmworker children. Chlorpyrifos is banned in 39 countries, including the European Union (see here for more Beyond Pesticides coverage). State action has become important since the November 2023 decision by the U.S. Court of Appeals for the 8th Circuit, which overturned the EPA rule revoking all food tolerances for chlorpyrifos, an effective ban on chlorpyrifos use. The final EPA rule, issued in August 2021, came in response to a 9th Circuit Court of Appeals ruling that found the agency’s inaction on chlorpyrifos unlawful. The case was filed by Earthjustice, on behalf of public health, labor, and disability organizations. 
The Oregon Department of Agriculture began phasing out chlorpyrifos use three years ago. As of January 1, the state rule bans all uses of chlorpyrifos, except when used for commercial pre-plant seed treatments, applied to Christmas tree crops between April 1 and June 15 in granular form annually to control soil-borne pests, and in cattle ear tags.  
EPA‚Äôs inaction on chlorpyrifos spans decades. Following a petition filed in 2007 by Natural Resources Defense Council (NRDC) and Pesticide Action Network North America (PAN), the issue of chlorpyrifos‚Äô safety moved through the courts‚ÄĒwith the 9th Circuit Court of Appeals compelling EPA to reevaluate chlorpyrifos in compliance with the review process in 2021, finding that the agency‚Äôs action has been arbitrary and capricious. Prior to this decision, EPA missed numerous deadlines in response to the original 2007 petition. In 2015, the EPA administrator in the Trump administration, Scott Pruitt, rejected‚ÄĮthe‚ÄĮconclusions of EPA scientists and independent scientific literature by reversing a‚ÄĮtentative decision to revoke food residue tolerances of chlorpyrifos due to the chemical‚Äôs neurotoxic impacts. This would have effectively banned chlorpyrifos from agriculture.¬†¬†
Poster child for pesticide regulatory failure 
As Jay Feldman, executive director of Beyond Pesticides observed, this disturbing pattern of regulatory failure by the EPA is not isolated. ‚ÄúEPA‚Äôs decision making, delay tactics, and contradictory policies are not confined to chlorpyrifos. Chlorpyrifos, glyphosate, 2,4-D, atrazine, and many others are poster children for a failed regulatory system that props up chemical-intensive agriculture despite the availability of alternative organic practices not reliant on these toxic chemicals,‚ÄĚ Mr. Feldman said. ‚ÄúWe have to end use of petrochemical pesticides and fertilizers and not just chase individual pesticides in an unending battle that allows the pesticide treadmill to continue destroying agriculture and harming farmworkers, farmers, and people generally.‚Ä̬†
As the New York Times noted after the August 2021 9th Circuit ruling, ‚ÄúIn an unusual move, the new chlorpyrifos policy will not be put in place via the standard regulatory process, under which the EPA first publishes a draft rule, then takes public comment before publishing a final rule. Rather, in compliance with the court order, which noted that the science linking chlorpyrifos to brain damage is over a decade old, the rule will be published in final form, without a draft or public comment period.” “It is very unusual,‚ÄĚ Michal Freedhoff, EPA assistant administrator for chemical safety and pollution prevention, said of the court‚Äôs directive. ‚ÄúIt speaks to the impatience and the frustration that the courts and environmental groups and farmworkers have with the agency.”¬†¬†
“The court basically said, ‚ÄėEnough is enough,'” Ms. Freedhoff said. ‚ÄúEither tell us that it‚Äôs safe, and show your work, and if you can‚Äôt, then revoke all tolerances.‚ÄĚ In a withering attack on EPA, Judge Jed S. Rakoff of the Ninth Circuit wrote on behalf of the court that, rather than ban the pesticide or impose restrictions, the agency ‚Äúsought to evade, through one delaying tactic after another, its plain statutory duties.‚ÄĚ
Dow Chemical‚Äôs decision in 2000 to stop residential uses of chlorpyrifos, taken after extensive research highlighted the adverse impact on children, left its agricultural use unfettered for over 20 years due to EPA‚Äôs sustained inaction in the face of strong science. As Beyond Pesticides has warned before, EPA sits in the background and watches the marketplace, then codifies voluntary decisions by manufacturers after years, even generations, of poisoning and contamination. As a result, the voluntary actions by the companies are highly compromised and do not include agency determinations or findings‚ÄĒallowing false claims of safety, offering a shield from liability, and permitting unencumbered international marketing.¬†
Fast forward to 2024 and the reversal of years of science and court findings calling for an end to chlorpyrifos use. What could be characterized as ‚Äúgoing back to square one,‚ÄĚ the most recent Appeals Court finding in 2023 allows the agricultural uses to return to the market, except in the case of state action, like Oregon, Hawai‚Äôi, New York, Maryland, and California. Advocates continue to call for stronger mandates and a national goal to eliminate petrochemical pesticides, given the availability of productive and profitable organic practices. Federal Insecticide, Fungicide and Rodenticide Act and the Federal Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act (including the Food Quality Protection Act), continuously fail to adequately regulate chlorpyrifos, glyphosate, atrazine, 2,4-D, aldicarb, dicamba, neonicotinoids, synthetic pyrethroid, antimicrobials, and numerous others, including 1,200 active and hundreds of toxic ‚Äúinert‚ÄĚ (non-disclosed) ingredients in over 16,800 pesticide products.
A note about environmental justice 
Disproportionate impacts on low-income African American and Latino families, including farmworker families, continue with exposure documented, especially for farmworkers and their families. The threats from chlorpyrifos exposure are dire. Farmworker families tend to live in communities adjacent to treated fields and within the buffer zones of agricultural fields. Farmworker studies routinely show high exposure injury and disease from pesticide drift in these communities and other forms of contamination. As Beyond Pesticides reported in 2021, ‚ÄúChlorpyrifos exposure lingers in the agricultural communities where farmworkers and their families reside. ‚ÄúWe have found it in the houses, we have found it in carpet, in upholstered furniture, we found it in a teddy bear, and we found it on the walls and surfaces,‚ÄĚ said Stuart Calwell, lead attorney for the plaintiffs in a 2021 lawsuit on behalf of some Californian farmworker families. ‚ÄúThen a little child picks up a teddy bear and holds on to it.‚ÄĚ Ultimately, according to the attorneys, 100,000 people in California‚Äôs farming regions may need to remove items in their homes that were contaminated by chlorpyrifos.¬†
Each of the four plaintiff families has children with developmental disabilities that they indicate were caused by chlorpyrifos exposure. This real-world occurrence is supported by scientific literature. Studies find that children exposed to high levels of chlorpyrifos experience mental development delays, attention problems, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder problems, and pervasive developmental disorders at three years of age. Concentrations of chlorpyrifos in umbilical cord blood were also found to correspond to a decrease in psychomotor development and a decrease in mental development in 3-year-olds.  Additional research reinforces these findings, with evidence that children with high exposure levels of chlorpyrifos have changes to the brain, including enlargement of the superior temporal, posterior middle temporal, and inferior postcentral gyri bilaterally, and enlarged superior frontal gyrus, gyrus rectus, cuneus, and precuneus along the mesial wall of the right hemisphere. 
This toxic treadmill is not the sustainable way forward. The progress on one chemical like chlorpyrifos at the federal level, now reversed, required nonprofits, public health advocates, scientists, and people of good conscience to devote extraordinary resources in time and money at a period when a systemic overhaul is needed to meet the existential health, biodiversity, and climate crises to which petrochemical pesticides and fertilizers contribute significantly. The good news is that the solutions are within reach to move us forward with organic practices that sustain, nurture, and regenerate life. 
See Beyond Pesticides’ Organic Agriculture webpage and join our campaign for Keeping Organic Strong. 
All unattributed positions and opinions in this piece are those of Beyond Pesticides. 
Source: Oregon‚Äôs Department of Agriculture began phasing out the use of chlorpyrifos in 2020. Now, the state will ban most of its uses this month ‚ÄĒ with some exceptions, Abandoning Science‚ÄĒA look back at the failure to regulate the neurotoxic insecticide chlorpyrifos¬†
Posted in Agriculture, Chlorpyrifos, Dow Chemical, Drift, Environmental Justice, Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), Farmworkers, Nervous System Effects, Oregon, Pesticide Regulation, Pesticide Residues, Uncategorized by: Beyond Pesticides
No Comments
28
Feb
(Beyond Pesticides, February 28, 2024) The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is putting on hold its Vulnerable Species Project (VSP) after vociferous comments from the petrochemical pesticide industry to instead, ‚Äúcreate a narrow, tailored policy rather than a sweeping, burdensome one,‚ÄĚ according to a recent op-ed in the Wall Street Journal. Upon heavy pushback from the petrochemical pesticide industry and agribusiness, EPA is hosting a variety of workshops and openings for the public to provide feedback not just on VSP, but the Endangered Species Act (ESA) Workplan the Biden Administration originally introduced in 2021 in its entirety. Advocates are calling for the strengthening of pesticide regulation given the impending decisions that may shape the fate of ESA-FIFRA (Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act) compliance for years to come.
As EPA continues through its pesticide registration program to advance continued dependency on pesticides through its interpretation of FIFRA, despite the availability of nontoxic alternatives, endangered species extinction and biodiversity collapse has never been a high priority. While EPA has¬†initiated¬†efforts to address a significant backlog of¬†pesticide¬†evaluations,¬†Civil Eats has reported that the agency faces¬†a task so extensive that it‚ÄĮmay require several additional decades to fully catch up. EPA officials¬†stated, ‚ÄúEven if EPA completed this work for all of the pesticides that are currently subject to court decisions and/or ongoing litigation, that work would take until the 2040s, and even then, would represent only 5 percent of EPA‚Äôs ESA obligations.‚Ä̬†¬†
In this context, the VSP‚Äôs primary goal, according to the EPA website, ‚Äúwill [be to] identify certain vulnerable listed species, identify mitigations to protect them from pesticide exposure, and then implement these mitigations across different types of pesticides (e.g., herbicides, insecticides).‚ÄĚ In response to widespread scrutiny from industry actors over the breadth of the pilot project, EPA issued a press release on February 7, ‚ÄúEPA Outlines Implementation Approach for Endangered Species Act Pesticide Policies.‚ÄĚ There are three key components to this press release: ‚ÄúImproved‚ÄĚ Species Map, Credit for using Voluntary USDA Conservation Practices, and Offsets for Endangered Species Protections.
The ‚ÄúSpecies Map,‚ÄĚ according to the ESA Work Plan guide, ‚Äú are a group of StoryMaps to raise public awareness about protecting endangered species from pesticides. These StoryMaps use an interactive format to describe the 27 pilot endangered and threatened (listed) species, their habitats, and why they are vulnerable from pesticide exposure.‚Ä̬†The press release says, ‚ÄúIn April, EPA plans to hold a workshop to facilitate and prioritize the development of [endangered species] maps, and EPA will also develop guidelines that the public can use to develop and submit refined maps for hundreds of other endangered species.‚ÄĚ According to the Wall Street Journal opinion editorial, pesticide trade groups project that the pilot project would encompass 107 million acres across the United States, while EPA did not set a specific acreage. In November 2023, after receiving over 10,000 comments ‚Äď many of which were from pesticide industry-aligned groups ‚ÄďEPA decided, among other changes, to ‚Äúnarrow the areas within the endangered species range map [for the Vulnerable Species Project] to only include locations that are important to conserving a species.‚ÄĚ Beyond Pesticides will share more information regarding this workshop in the coming months.
The ‚ÄúCredit for using Voluntary USDA Conservation Practices‚ÄĚ and ‚ÄúOffsets for Endangered Species Protections‚ÄĚ sections, meanwhile, intend to substitute certain pollinator-friendly practices on the books for the introduction of new programs. Regarding USDA conservation practices, the press release says, ‚Äú[On February 6], EPA signed an MOU (memorandum of understanding) with USDA describing how EPA can include NRCS (Natural Resource Conservation Service) conservation practices on pesticide labels as one way growers who voluntarily perform those practices can use them to help fulfill pesticide label requirements. EPA and USDA are planning meetings and workshops in the coming months to further discuss the MOU and gain input from producers about mitigation options that may count toward fulfilling pesticide label requirements.‚ÄĚ EPA‚Äôs insistence on focusing on labeling rather than more stringent regulation has led to adverse health impacts and the proliferation of environmental contaminants into not only the food supply chain but also endangered and non-endangered species. Regarding the Offsets for Endangered Species Protections, ‚ÄúEPA, other federal agencies, and stakeholders are participating in a workshop…this month to discuss how to bring offsets into EPA‚Äôs ESA-FIFRA work. This initiative should give pesticide registrants and users more flexibility to meet label requirements to protect endangered species, while directly contributing to recovering those species.‚ÄĚ Beyond Pesticides points out that the practical effect of the offset approach may allow continued toxic pesticide use in those very agricultural areas that are habitats to the most vulnerable species and the workplace of farmworkers and people of color communities. To the extent that chemical-intensive farming practices are curtailed to protect endangered species, straightforward enforcement of the law, as intended, may also protect those who suffer disproportionately from adverse health effects associated with pesticide exposure, including heightened risk to cancer for male farmworkers and anemia and blood disorders to female farmworkers and farmers.
Even before this pushback from industry, EPA’s ESA strategy has long missed the marked in terms of ensuring that pesticides do not move off the target site and threaten the health of wildlife, pollinators, and ecosystems. For example, EPA granted the use of nucleic acid, a form of genetically engineered pesticide, to eliminate the threat of Colorado Potato Beetles for potato farmers within the United States and abroad, without considering the inevitable drift from permitted aerial spraying on fields to unintendedly targeted wildlife. According to advocates, this move represents the legacy of agency indifference to pesticide resistance originating in 1952 with the discovery of Colorado Potato Beetle resistance to DDT. For advocates, this is seen as a lack of leadership by the EPA Office of Pesticide Regulations (OPR) over the past half-century that manifests in the continuous decline of biodiversity through adverse impacts to bird, insect (e.g. butterfly), marine, and aquatic life from pesticides such as paraquat and neonicotinoids, for example.
On the 50th anniversary of the passage of the Endangered Species Act, Beyond Pesticides, in partnership with multiple environmental organizations, highlights the historical successes of the ESA as well as areas of growth to further protect endangered species against the compounding tolls of the climate crisis on ecosystem balance, habitat fragmentation, and pollution resulting from petrochemical pesticides and fertilizers. The article points out, ‚ÄúThe ESA is celebrated as one of the most effective conservation laws globally, credited with preventing the extinction of¬†99 percent of listed species. Over the past five decades, ESA has played a pivotal role in preventing these extinctions by safeguarding the most critically endangered species within biological communities.‚ÄĚ However, OPR has not always kept biodiversity in mind regarding its rulemaking pursuant to ESA on ‚Äúdevelop[ing] strategies to reduce harm from various pesticides, including herbicides and insecticides, while focusing on protecting the most vulnerable species.‚ÄĚ
These are critical times. The UN Development Programme in announcing its COP15: The Biodiversity Conference in 2022¬†provided context: ‚ÄúDespite ongoing efforts, biodiversity is deteriorating worldwide, and this decline is projected to worsen with business-as-usual. The loss of biodiversity comes at a great cost for human well-being and the global economy.‚ÄĚ Advocates have told EPA that meeting ESA mandates will require a major shift away from pesticides, not mitigation that allows continued use despite the availability of certified organic practices.
There are numerous ways to take action to strengthen protections for endangered species against pesticides, including past Actions of the Week. See ‚ÄúGroup Says Broader Biological Evaluation of Rodenticides Needed to Protect Endangered Species‚Äú to learn more about biodiversity loss and the role that the Endangered Species Act is designed to play in protecting endangered species from rodenticides. See ‚ÄúTake Action Today: Tell EPA To End Pesticide Dependency, Endangered Species Plan Is Inadequate‚ÄĚ to learn about the Draft Herbicide Strategy Framework and our position in advocating for the elimination of petro-chemical pesticide use by 2032. Beyond Pesticides will track the developments and upcoming public comment periods in relation to the recent press release in order to inform advocates on potential actions to call for further strengthening of the ESA Workplan.
Two ways that you can combat the negative impacts of pesticides on wildlife are to (1) implement organic practices for your own lawn and garden, and (2) support organic agriculture, rather than conventional agriculture, which relies on pesticide use. Beyond Pesticides supports organic agriculture as effecting good land stewardship and reducing wildlife‚Äôs hazardous chemical exposures. The pesticide reform movement, citing pesticide problems associated with chemical agriculture ‚ÄĒ from groundwater contamination and runoff to drift ‚ÄĒ views organic as the solution to these serious environmental threats. You can transition your communities‚Äô public spaces to organic land management by becoming a¬†parks advocate.¬†Sign up today¬†to learn how to protect children, pets, and pollinators in your local parks, playing fields, and other public spaces.¬†
All unattributed positions and opinions in this piece are those of Beyond Pesticides.  
Source: Wall Street Journal
Posted in Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), Habitat Protection, Pesticide Drift, Pesticide Regulation, Uncategorized, Wildlife/Endangered Sp. by: Beyond Pesticides
No Comments
27
Feb
(Beyond Pesticides, February 27, 2024) Popular culture and official policy continue to ignore a blatant source of the rise in obesity: chemical exposures, including pesticides. A study, ‚ÄúAssociations of chronic exposure to a mixture of pesticides and type 2 diabetes mellitus in a Chinese elderly population,‚ÄĚ contributes to the now-massive trove of evidence linking pesticides to diseases and shows that by the time people reach retirement age they are suffering from a heavy burden of contamination that raises their risk of complex disease.
Since the 1960s, obesity in both adults and children has nearly tripled. More than half of U.S. adults were either obese or severely obese by 2018, according to data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Study. The 55-year trend line is decidedly upward. More women than men are obese, and black women suffer the most, but men are racing to catch up. Between 1999 and 2018, Mexican American men shot up from the lowest percentage of obesity to nearly the highest.
Obesity is a milestone on the road to Type 2 diabetes, heart disease, high blood pressure, kidney failure, joint replacement, and more. The causes of obesity are severely misunderstood. Most people believe that discipline and willpower are what keep a person from being fat, even if they have ‚Äúfat genes.‚ÄĚ The medical opinion is ‚Äúcalories in, calories out‚ÄĚ ‚ÄĒ obesity, genetic or not, can be staved off with diet and exercise. But despite decades of advice, sweat, tears, and billions of dollars spent on ineffective diet pills and menus, obesity is a global emergency. If popular attitudes and medical theories were correct, obesity would be far less common and more easily controlled. It is not. Therefore, beliefs and advice are incorrect‚ÄĒor at least incomplete.
The researchers from the Shanghai Municipal Center for Disease Control and Prevention identified 39 pesticides in the study population. Women had slightly higher levels and a stronger correlation between obesity, pesticide burden and type 2 diabetes than men. The most significant contributors were ő≤-Hexachlorocyclohexane (ő≤-BHC) and oxadiazon.
ő≤-BHC is a byproduct of technical grade lindane production and common near lindane factories. For example, in 2005 an Italian biomonitoring program found ő≤-BHC levels 20 times higher than the legal limit in cows‚Äô milk. The subject cows‚Äô water came from a river which had been polluted by waste from a lindane facility. Lindane is available in the U.S. only as a treatment for head lice and not for any agricultural uses. It has been listed as a Persistent Organic Pollutant under the Stockholm Convention since 2009. The International Agency for Research on Cancer classifies it as a possible human carcinogen; it has been linked to aplastic anemia and breast cancer and is an endocrine disruptor. Oxadiazon is a herbicide and likely human carcinogen used in the U.S. on golf courses, parks, athletic fields, playgrounds, cemeteries and some horticultural contexts but which is not registered for any food uses.
The ő≤-BHC and oxadiazon associations with type 2 diabetes in the Chinese senior study are ‚Äúpronounced among elderly women,‚ÄĚ according to the authors. They are also linear, meaning that for each increment of pesticide body burden, the risk of diabetes rises a comparable amount. These data, the authors write indicate ‚Äúthat it is an urgent need to take practical measures to control these harmful pesticides.‚ÄĚ
Although ő≤-BHC and oxadiazon now have limited uses in the U.S., the study found levels in the Chinese seniors of many pesticides that are still used in the U.S. in agricultural, horticultural, residential, and other applications. These include atrazine, acetochlor, metolachlor, and permethrin, to name a few, all of which have been reported to disturb lipid functions. A 2020 review of agrochemicals affecting obesity discusses more obesogenic pesticides registered in the U.S.
A concurrent publication by most of the same authors as the 2024 Chinese pesticide study reviewed evidence for environmental obesogens‚Äô disruption of lipid metabolism. This review notes that, ‚ÄúCurrently, more than 50 types of chemicals with high human exposure levels have been identified as environmental obesogens that can interfere with lipid metabolism and induce obesity. Experimental studies have shown that the lipid metabolism interference effects of obesogens have multiple targets, including nuclear receptors [thyroid, steroid, vitamin D3, and retinoid receptors], transcription factors [wide number of proteins that initiate and regulate the transcription of genes], cytokines [proteins important to cell signaling], and hormones. The interfering factors of environmental obesogen-induced obesity include transgenerational effects, susceptibility [developmental] windows, gender differences‚Ķand diet habits…‚ÄĚ
Lipids are fat-soluble compounds that are essential for cells’ structural integrity along with numerous other functions in organisms from bacteria to humans. But when fat consumption exceeds the body’s need for lipids, humans make more fat cells or expand existing cells. When these storage options are full, lipids begin leaking into other tissues such as the kidneys and pancreas, contributing to a wide variety of serious diseases.
Research on environmental contributions to obesity was pioneered by Bruce Blumberg, who recounts how he discovered the effects of tributyltin (TBT) in his 2018 book with Kristin Loberg, The Obesogen Effect: Why We Eat Less and Exercise More but Still Struggle to Lose Weight. TBT refers to a family of tin compounds used to keep marine snails off ship hulls (a use now banned), to prevent fungal growth in wood and textile production, as a stabilizer in polyvinyl chloride products, and other uses. It bioaccumulates and can take 30 years to break down. Blumberg’s presentation at Beyond Pesticides’ 2018 36th National Pesticide Forum, is available on YouTube.
Dr. Blumberg, a professor of developmental and cell biology at the University of California Irvine and a molecular biologist by training, was curious about Japanese research showing that TBT could change fish from female to male, so he looked for cellular receptors that TBT could bind to. He found that TBT did not activate sex hormone receptors as expected; instead, it activated the process that leads to fat cell development. He showed that frog embryos exposed to TBT converted their testes to fat, that mice exposed to TBT in the womb had larger fat deposits as adults, and that this predisposition affected later generations. Subsequent research into the term Blumberg coined, obesogens, has expanded knowledge of these phenomena.
One of the widely-studied culprits is the notorious organophosphate chlorpyrifos. It has a painful and ragged history of regulation by EPA, which itself has repeatedly opined that it is toxic to human health. Currently, as BP reported last November, chlorpyrifos residues are still permitted in food owing to a shoddy and biased court-ordered instruction by the Eighth Circuit Court of Appeals.
The organophosphate insecticide chlorpyrifos does its damage in varied ways. Beyond Pesticides covered a 2019 study finding that it promotes obesity development even at low doses. The study found that chlorpyrifos prevented ‚Äúdiet-induced thermogenesis‚ÄĚ in brown adipose tissue at concentrations ‚Äúas low as 1 part per million.‚ÄĚ Brown fat is considered better than white fat, and it burns calories to keep the body at an even temperature in cold conditions.
An earlier study by some of the same authors of the 2024 pesticide-diabetes research showed that chlorpyrifos also contributes to obesity by causing leaky gut and inflammation; when they transferred chlorpyrifos-altered microbes to unexposed mice, those mice added fat and lost insulin sensitivity ‚Äďmajor factors in type 2 diabetes induction.
Despite reduced usage, TBT keeps on giving ‚Äď and demonstrating that even at individually low doses, and even when a chemical has been banned or restricted, it can remain in the environment and combine with other toxic chemicals to cause harm. A 2019 study showed that ‚ÄúCombined exposure [to TBT and the ‚Äúforever chemical‚ÄĚ perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS)] significantly promoted the fat accumulation in newly hatched [fish] larvae, even when the doses of TBT and PFOS were both at the levels that did not show obesogenic effect. The interactive effect of TBT and PFOS could aggravate the total obesogenic effect of their mixtures, indicating a synergistic interaction.‚ÄĚ
There are ways to fight back against the onslaught:
- Eating organic food reduces risk of metabolic diseases including diabetes, which strongly suggests that pesticides have a direct link to diabetes. See Beyond Pesticides‚Äô 2020 blog post, ‚ÄúFood For Thought: Eating Organic Reduces Risk of Type 2 Diabetes.‚ÄĚ In a post last October, ‚ÄúOrganophosphate Pesticides and the Link to Respiratory, Metabolic, and Heart Disease,‚ÄĚ we noted that ‚ÄúReplacing dietary exposure to food grown in chemical-intensive agriculture with organic consistently reduces pesticide levels in one‚Äôs body‚Ķmaintaining lower levels of conventional, synthetic pesticides is likely to reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases like type 2 diabetes. In addition to positive impacts on the human microbiome, organically grown food (i.e., milk, meat, strawberries, tomatoes, and a range of other foods) contain a much more diverse bacterial community than their chemically grown counterparts.‚ÄĚ
- Schools should switch to organic foods. See our ‚ÄúCall on USDA to Provide Organic School Lunches to Fight Childhood Obesity.‚ÄĚ
- See our Pesticide-Induced Diseases: Diabetes for more information.
The body of research now available also supports the very recent admission by some health professionals that obesity is not caused by poor character, laziness or lack of willpower. The review of environmental obesogens and their role in metabolic diseases cites approximately 50 studies reporting specific obesogenic effects of more than 50 chemicals. Obesity has multiple determinants, but absent willpower is not one of them. Unfortunately, the medical establishment is still focused on mechanisms, such as brain activity, that cause people to eat too much, and suggest that high-calorie food is too easily available. These are probably factors, but the message that environmental obesogens are a dire emergency has not yet been received. The prevailing concept is that too much food is the problem, when it’s perhaps not the amount of food, but the pesticide load of the food, that is an essential cause of the slow-motion global pandemic of obesity and diabetes.
All unattributed positions and opinions in this piece are those of Beyond Pesticides
Sources:
Associations of chronic exposure to a mixture of pesticides and type 2 diabetes mellitus in a Chinese elderly population. Tian Chen, Xiaohua Liu, Jianghua Zhang, Lulu Wang, Jin Su, Tao Jing, Ping XiaoChemosphere, Volume 351, March 2024,  https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0045653524000870?via%3Dihub [Open Access]
Environmental Obesogens and Their Perturbations in Lipid Metabolism. Xiaoyun Wang, Zhendong Sun, Qian S. Liu, Qunfang Zhou, and Guibin Jiang Environ. Health, February 13, 2024, https://doi.org/10.1021/envhealth.3c00202 [Open Access]
Agrochemicals and obesity, Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, Volume 515, 15 September 2020, Xiao-Min Ren, Yun Kuo, Bruce Blumberg, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0303720720302264?via%3Dihub [Open Access]
Pesticide-Induced Diseases: Diabetes. https://www.beyondpesticides.org/resources/pesticide-induced-diseases-database/diabetes;¬†‚Äúa wealth of additional research on the link between toxic pesticide exposure and the development of diabetes. Replacing conventional food products with organic consistently leads to reduced levels of pesticide in one‚Äôs body.‚ÄĚ
Food For Thought: Eating Organic Reduces Risk of Type 2 Diabetes, https://beyondpesticides.org/dailynewsblog/2020/11/food-for-thought-eating-organic-reduces-risk-of-type-2-diabetes/
Study Finds Recently Banned, Common Insecticide Promotes Obesity Development, and Related Illnesses, https://beyondpesticides.org/dailynewsblog/2021/09/study-finds-recently-banned-common-u-s-insecticide-promotes-obesity-development-and-related-illnesses/
Grandmother’s Exposure to DDT Increases Granddaughters’ Breast Cancer and Cardiometabolic Disorder Risk, https://beyondpesticides.org/dailynewsblog/2021/04/grandmothers-exposure-to-banned-pesticide-ddt-increases-breast-cancer-and-cardiometabolic-disorder-risk-in-granddaughters/
Childhood Development Hurt By Preconception Exposure to Environmental Stressors, https://beyondpesticides.org/dailynewsblog/2015/08/childhood-development-hurt-by-preconception-exposure-to-environmental-stressors/
http://press.endocrine.org/doi/10.1210/en.2015-1350    
http://www.endocrine.org/news-room/current-press-releases/parents-preconception-exposure-to-environmental-stressors-can-disrupt-early-developmental-processes
Posted in Agriculture, Chlorpyrifos, Lindane, metabolic syndrome, Obesity, organochlorines, organophosphate, Uncategorized by: Beyond Pesticides
1 Comment
26
Feb
(Beyond Pesticides, February 26, 2024) Beyond Pesticides today launched an action to stop a nationwide campaign by chemical manufacturers to shield themselves from liability cases filed by those who have been harmed by pesticide products. As widely reported, Bayer/Monsanto has been hit with numerous jury awards and settlements totaling billions of dollars for adverse health effects associated with their weed killer glyphosate (RoundupTM). After unsuccessfully seeking U.S. Supreme Court review of two of these cases, the industry is now pushing legislation in state legislatures that will shield them from future liability litigation.
This is not the first time that the pesticide and toxic chemical industry has sought protection from the states after losing in the highest U.S. Court. After the Supreme Court upheld the right of localities to restrict pesticides more stringently than the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency and state regulatory agencies in Wisconsin Public Intervenor v. Mortier (501 U.S. 597, 1991), the industry went to every state legislature in the country to seek state preemption of their local jurisdictions’ authority to restrict pesticides. They were successful in putting state preemption laws in place in 43 states and have since added another.  
Having failed in the courts, history is repeating itself as pesticide and chemical manufacturers descend on state legislators, this time with legislation to shield them from liability lawsuits filed by people injured from exposure to their products. So far, the industry has been successful in getting their bill introduced in at least four states. This activity is spurred on by the thousands of cases involving Roundup/glyphosate that have resulted in large jury awards and settlements against Bayer/Monsanto in the billions of dollars. While sponsors of these bills claim that the labels on pesticide products provide sufficient warning of hazards, users have been misled by advertising that falsely touts product safety. Reminiscent of previous state legislative battles, the chemical industry is now leaning on elected officials, whether in state legislatures or the U.S. Congress, to do its bidding in blocking, or preempting, court action. 
As Beyond Pesticides previously reported, Bayer’s efforts in the last year have been rebuffed twice by the U.S. Supreme Court, letting stand two lower court rulings against the company. The company’s most recent loss, on February 5, 2024, came from the Eleventh Circuit Court of Appeals, which decided in favor of the plaintiff in Carson v. Monsanto on Bayer’s claim that FIFRA preempts a failure to warn claim.  
Tell your state legislators to protect the right of citizens to seek redress against pesticide manufacturers from harm caused by their products. 
Last week, the Idaho Senate rejected¬†SB¬†1245, which would have provided legal protection to pesticide manufacturers from ‚Äúfailure-to-warn” liability. This legal framework has been pivotal not only for pesticide users seeking redress from exposure to glyphosate-based herbicide products such as Roundup, but also applies to any toxic pesticide products. Proponents of SB 1245 argue, ‚Äú[This bill] protect[s] companies that produce safe pesticides critical to agriculture in Idaho and beyond.‚ÄĚ Idaho Press continues,‚ÄĚ Sen. Harris said the bill does not restrict lawsuits against pesticide manufacturers for a number of claims, including product defects, drift or misapplication, or if the manufacturer fraudulently conceals known facts about the product.‚ÄĚ ¬†
While other causes of action are often pursued, the overwhelming majority of successful cases for pesticide injury lawsuits fall under ‚Äúfailure-to-warn” claims. Brigit Rollins, a staff attorney at the National Agricultural Law Center, describes this liability framework as, ‚Äúa type of civil tort that is frequently raised in products liability cases. Unlike negligence and design defect…failure to warn does not argue that a product has physical faults. Instead, a plaintiff typically raises¬†failure to warn claims¬†to allege that a product manufacturer failed to provide adequate warnings or instructions about the safe use of a product.‚ÄĚ Under the new push in several state legislatures, this legal framework would be moot, rendering victims around the United States without effective legal recourse and releasing industry actors such as Bayer from billions of dollars in ongoing and future settlements.¬†As of 2022, Bayer settled over 1,000 lawsuits paying out approximately $11 billion and faces an additional 30,000 lawsuits pending.¬†
Glyphosate litigation is a notable example of why the dependence on EPA’s labels provides inadequate protection‚ÄĒin this case, for users of the pesticide, but also for¬†neighboring farms,¬†farmworkers and bystanders,¬†consumers¬†of contaminated food and water, and the¬†biosphere. Legislators who choose to restrict the right of injured parties to seek recompense from pesticide manufacturers are doing their constituents a tremendous disservice.
Tell your state legislators to protect the right of citizens to seek redress against pesticide manufacturers from harm caused by their products.
Letter to state legislators
I am writing to ask you to reject any legislation that may be introduced in the state legislature to shield pesticide and toxic chemical manufacturers from lawsuits when users of their products are injured from their exposure to the chemicals. Legislation like this is popping up around the country and is unfair to people who have been harmed, despite their compliance with product labels. As you may know, numerous cases against Bayer/Monsanto involving the weed killer glyphosate (RoundupTM) have resulted in large jury awards and settlements for those who have been harmed. The manufacturer has appealed verdicts to the U.S. Supreme Court twice and has been rebuffed each time, so they are now asking states to prevent victims from seeking compensation. Although sponsors of these bills claim that the pesticide label is sufficient warning, users have been misled by advertising touting the products’ safety.
As an example of such legislation, a bill recently rejected by the Idaho Senate would have provided legal protection to pesticide manufacturers from ‚Äúfailure-to-warn” liability. This legal approach has been pivotal for pesticide users seeking redress from exposure to glyphosate-based herbicide products such as Roundup as well as other toxic pesticide products. Proponents of SB 1245 argue, ‚Äú[This bill] protect[s] companies that produce safe pesticides critical to agriculture in Idaho and beyond.‚ÄĚ Idaho Press continues,‚ÄĚ Sen. Harris said the bill does not restrict lawsuits against pesticide manufacturers for a number of claims, including product defects, drift or misapplication, or if the manufacturer fraudulently conceals known facts about the product.‚Ä̬†
While other causes of action are often pursued, the overwhelming majority of successful cases for pesticide injury lawsuits fall under ‚Äúfailure-to-warn” claims. Brigit Rollins, a staff attorney at the National Agricultural Law Center, describes this liability framework as, ‚Äúa type of civil tort that is frequently raised in products liability cases. Unlike negligence and design defect…failure to warn does not argue that a product has physical faults. Instead, a plaintiff typically raises failure to warn claims to allege that a product manufacturer failed to provide adequate warnings or instructions about the safe use of a product.‚ÄĚ Under the new push in several state legislatures, this legal framework would be moot, rendering victims without effective legal recourse and releasing industry actors such as Bayer from billions of dollars in ongoing and future settlements. As of 2022, Bayer settled over 1,000 lawsuits paying out approximately $11 billion and faces an additional 30,000 lawsuits pending.
Glyphosate litigation is a notable example of why the dependence on EPA‚Äôs labels provides inadequate protection‚ÄĒin this case, for users of the pesticide, but also for neighboring farms, farmworkers and bystanders, consumers of contaminated food and water, and the biosphere. Legislators who choose to restrict the right of injured parties to seek recompense from pesticide manufacturers are doing their constituents a tremendous disservice.¬†
I urge you to reject such legislation restricting the rights of injured parties in our state‚ÄĒwhether they be users of the pesticide, neighboring farms, farmworkers, landscapers, bystanders, consumers of contaminated food and water, or defenders of nature‚ÄĒto recover damages from pesticide manufacturers.
Thank you.
Posted in Agriculture, Bayer, Cancer, Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), Failure to Warn, Glyphosate, Litigation, Monsanto, non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma, Preemption, State/Local, Take Action, Uncategorized by: Beyond Pesticides
9 Comments
23
Feb
(Beyond Pesticides, February 23, 2024) The latest string of billion-dollar plaintiff judgments against Bayer/Monsanto, the maker of Roundup™ with active ingredient glyphosate, does not yet signal a capitulation by Bayer or a win for public health or the environment in the United States. A jury award of $2.25 billion, the largest to-date, was handed down in Philadelphia in January. As Beyond Pesticides reported previously, Monsanto has a long history of challenging scientific findings on Roundup/glyphosate and evidence of harm to human health, the environment, and crops themselves (see resistant super weeds here and here), as it seeks to avoid liability claims by those suffering from cancer.¬†
Bayer Looking to State Legislatures for Protection from Lawsuits 
As result of its failure in quash lawsuits, Bayer has moved its case to state legislatures, where it is seeking the adoption of statutes that preempt liability claims by damaged parties. 
As reported by Beyond Pesticides, a rash of state legislation has been introduced in Idaho, Iowa, Missouri, and Florida, which would block plaintiff liability claims when pesticide products, like Roundup, cause harm. The chemical industry pushes the notion that the registration of its pesticide products with the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is a mark of safety that should shield it from liability. The industry want immunity from legal redress for the ‚Äúfailure to warn‚ÄĚ those harmed from exposure to its products.¬†¬†
Successful verdicts against Bayer/Monsanto are generally based on the ‚Äúfailure to warn‚ÄĚ principle and have withstood judicial appeals, including before the U.S. Supreme Court twice in the last couple of years. While Bayer¬†announced a reformulation of its residential Roundup product would remove glyphosate by January 2023, its widespread agricultural and public landscaping uses continue (ed. note: it is unclear whether Bayer has removed glyphosate from retail Roundup formulations).¬†Advocates point out that the proposed state legislation to limit liability, if passed into law, would release from liability all pesticide manufacturers responsibility for adverse effects associated with labeled product use. Tort liability claims rest on the manufacturers‚Äô ‚Äúfailure to warn‚ÄĚ consumers that when the company‚Äôs pesticide products are used as labeled and directed they may cause harm, such as non-Hodgkin lymphoma in the case of glyphosate-based Roundup.¬†¬†
Regulatory Failures Increase Need for Lawsuits Against Manufacturers 
In December, farmworker organizations and Beyond Pesticides, represented by the Center for Food Safety, filed a‚ÄĮpetition‚ÄĮwith EPA urging the agency to remove glyphosate from the market after having won a 2022 court decision forcing EPA to redo its science evaluation.¬†
That 2022 court decision in the‚ÄĮCourt of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit ruled‚ÄĮthat EPA‚Äôs 2020 approval of glyphosate was ‚ÄĮunlawful. The court voided EPA‚Äôs‚ÄĮ‚Äúinterim registration review‚ÄĚ decision approving the continued use of glyphosate, issued in early 2020. ‚ÄúEPA did not adequately consider whether glyphosate causes cancer and shirked its duties under the Endangered Species Act (ESA),‚ÄĚ the court wrote‚ÄĮin its opinion. At the time of the decision, Beyond Pesticides said: “EPA’s failure to act on the science, as detailed in the litigation, has real-world adverse health consequences for farmworkers, the public, and ecosystems. Because of this lawsuit, the agency’s obstruction of the regulatory process will not be allowed to stand, and EPA should start shifting food production to available alternative non- and less-toxic practices and materials that meet its statutory duty.” As reported by the Center for Food Safety, counsel in the case, ‚Äú[T]he court struck down, or vacated the human health assessment. The court also required that EPA redo and/or finish all remaining glyphosate determinations by an October 2022 deadline, or within four months. This includes a redone ecological toxicity assessment, a redone costs analysis of impacts to farmers from pesticide harms, as well as all Endangered Species analysis and mitigation.‚Ä̬†
Failure to Warn 
A Pesticides and You article (2005) by H. Bishop Dansby explains the U.S. Supreme Court decision on ‚Äúfailure to warn‚ÄĚ in Bates v. Dow Agrosciences (U.S. Supreme Court, No. 03-388, 2005), which includes the following:¬†
- Duty to Warn: Manufacturers have a legal duty to provide adequate warnings about the potential risks associated with their products, including pesticides. This duty arises from the recognition that manufacturers possess knowledge about the potential dangers of their products and have a responsibility to inform consumers about these risks. 
- Negligence and Design Defect: If a plaintiff alleges that a pesticide product caused harm even when used according to the label, they may argue that the product was negligently designed due to a failure to warn. In other words, they claim that the manufacturer did not adequately warn about the risks associated with the product’s design. The court may view this cause of action as a “failure to warn” disguised as a “design defect.”¬†
- Parallel Remedies: The court clarified that state common law tort actions, such as failure to warn claims, can run parallel to federal regulations under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA). This means that even though FIFRA regulates pesticide labeling, state actions can still be pursued if they do not conflict with federal regulations and are not preempted. 
Bates v. Dow cites an earlier case, Ferebee v. Chevron (Ferebee,‚ÄĮ736 F.‚ÄĮ2d, at 1541‚Äď1542), in which the court found: ‚ÄúBy encouraging plaintiffs to bring suit for injuries not previously recognized as traceable to pesticides such as [the pesticide there at issue], a state tort action of the kind under review may aid in the exposure of new dangers associated with pesticides. Successful actions of this sort may lead manufacturers to petition EPA to allow more detailed labelling of their products; alternatively, EPA itself may decide that revised labels are required in light of the new information that has been brought to its attention through common law suits. In addition, the specter of damage actions may provide manufacturers with added dynamic incentives to continue to keep abreast of all possible injuries stemming from use of their product so as to forestall such actions through product improvement.‚Ä̬†
As previously reported by Beyond Pesticides, the U.S. Supreme Court spoke with clarity in Bates: 
‚ÄúThe long history of tort litigation against manufacturers of poisonous substances adds force to the basic presumption against pre-emption. If Congress had intended to deprive injured parties of a long available form of compensation, it surely would have expressed that intent more clearly. See Silkwood v. Kerr-McGee Corp., 464 U. S. 238, 251 (1984).[Footnote 25] Moreover, this history emphasizes the importance of providing an incentive to manufacturers to use the utmost care in the business of distributing inherently dangerous items. See Mortier, 501 U. S., at 613 (stating that the 1972 amendments‚Äô goal was to ‚Äústrengthen existing labeling requirements and ensure that these requirements were followed in practice‚ÄĚ). Particularly given that Congress amended FIFRA to allow EPA to waive efficacy review of newly registered pesticides (and in the course of those amendments, made technical changes to ¬ß136v(b)), it seems unlikely that Congress considered a relatively obscure provision like ¬ß136v(b) to give pesticide manufacturers virtual immunity from certain forms of tort liability. Overenforcement of FIFRA‚Äôs misbranding prohibition creates a risk of imposing unnecessary financial burdens on manufacturers; under-enforcement creates not only financial risks for consumers but risks that affect their safety and the environment as well.‚Ä̬†
Lawsuits Not Slowing Down  
Beginning in October 2023, Bayer has racked up over $4 billion in verdicts and shareholders are punishing the company‚Äôs stock price. Bayer has slashed shareholder dividends by 95%, part of an ongoing effort to conserve cash in the wake of its 2018 merger with Monsanto. According to Reuters, ‚ÄúAround 165,000 claims have been made against the company for personal injuries allegedly caused by Roundup, which Bayer acquired as part of its $63 billion purchase of U.S. agrochemical company Monsanto in 2018.‚ÄĚ They report that in 2020, ‚Äú…Bayer settled most of the then-pending Roundup cases for up to $9.6 billion but failed to get a settlement covering future cases. More than 50,000 claims remain pending,‚ÄĚ as of December 2023. In addition, two new Roundup trials have started in Pennsylvania and Arkansas, with an ongoing trial in Delaware and a case coming up for trial in California. Court watchers note that Bayer‚Äôs previous streak of earlier victories over plaintiffs may reflect a Bayer strategy of bringing the weakest plaintiff cases to trial first to deter others from filing lawsuits. And this strategy worked until it did not.¬†¬†
Bayer Legal Strategy Failing  
Bayer has lost almost all of the cases filed against it for compensation and punitive damages associated with the plaintiffs‚Äô charge that its product¬† caused them harm. Its legal strategy, pursued through the court system up to the U.S. Supreme Court has failed to fend off ongoing litigation for harm associated with its glyphosate-based product. As Bayer‚Äôs website has touted in a five-point strategy to mitigate the company‚Äôs financial ‚Äúrisks‚ÄĚ from future litigation, ‚ÄúA favorable ruling by the U.S. Supreme Court on the federal preemption question could largely end the Roundup litigation. The main question here is whether state-based failure-to-warn claims are preempted by federal law since the EPA concluded glyphosate does not cause cancer and approved the Roundup™ label without a warning.‚Ä̬†¬†
Bayer is not giving up on the current U.S. Supreme Court to overturns current law, as established by previous court decisions, including  Bates v Dow. However, that strategy is not succeeding, at least not yet. As Beyond Pesticides previously reported, Bayer’s efforts in the last year have been rebuffed twice by the U.S. Supreme Court, letting stand two lower court rulings against the company. The company’s most recent loss, on February 5, 2024, came from the Eleventh Circuit Court of Appeals, which decided in favor of the plaintiff in Carson v. Monsanto on Bayer’s claim that FIFRA preempts a failure to warn claim.  
Bayer Monsanto ‚ÄúHistory of Disinformation, Corrupted Science and Manufactured Doubt about glyphosate‚Ä̬†
Beyond Pesticides reported in December 2022 on the release of ‚ÄėMerchants of Poison, a report was issued by U.S. Right to Know (USRTK, a nonprofit investigative research group focused on promoting transparency for public health), Friends of the Earth (FOE), and Real Food Media. It carries the pithy subtitle, ‚ÄúA case study in disinformation, corrupted science, and manufactured doubt about glyphosate,‚ÄĚ a description cited by the Friends of the Earth press release as ‚Äúat the core of the pesticide industry‚Äôs public relations playbook.‚ÄĚ The report comports with Beyond Pesticides‚Äô coverage of the pesticide industry‚Äôs egregious misbehavior, and of glyphosate, the world‚Äôs most widely used herbicide.¬†
Organic Land Care is a Viable Solution Now  
While the agrichemical industry continues to argue that chemical-intensive farming and land management is needed for higher yields, the data says that is not the case. Please see ‚ÄĮResearch on organic agriculture shows it can provide quadruple the performance, synergizing financial, human health, ecological, and socio-economic well-being. See Beyond Pesticides‚Äô webpage on ‚ÄĮOrganic Agriculture‚ÄĮfor more information. Additionally, toxic herbicides are not needed for beautiful turf systems, whether playing fields, parks, school yards, or open spaces. Please see Parks for a Sustainable Future and join with Beyond Pesticides to convert community parks and playing fields to organic land management.¬†¬†
See this recent Beyond Pesticides summary of the health risks of pesticide exposures, and a deeper dive on glyphosate’s and pesticides’ broad environmental harms, pp. 9 and 17, respectively, and 2017 Beyond Pesticides’ glyphosate fact sheet and updated glyphosate news and litigation coverage here.  
All unattributed positions and opinions in this piece are those of Beyond Pesticides.    
Sources:  
Philadelphia jury awards $2.25 billion to man who claimed Roundup weed killer gave him cancer; US Supreme Court case Bates v. Dow Agrosciences LLC, 544 U.S. 431 (2005)  
Postscript: 
Primer on Federal Preemption, Pesticide Regulation, and U.S. Supreme Court, Bates v. Dow 2005 
As H.Bishop Dansby, Esq. wrote in Beyond Pesticides‚Äô 2005 Pesticides and You, ‚ÄúFederal pre-emption has the potential for effecting the aims of conservative tort reformers because it transfers responsibility for safety of products from the courts to administrative agencies… the legal concept of federal pre-emption means that federal law and regulation takes the place of state law‚Ķthe bottom line of this double talk is that state tort actions are once again allowed against pesticide manufacturers. FIFRA pre-emption is to be interpreted narrowly as affecting only the regulation by states of the wording of the label. Even failure to warn causes of action are allowed, on the theory that state actions can run in parallel with FIFRA regulation‚Ķ If a plaintiff alleged that a pesticide product was negligently designed because it harmed a person even when applied according to the label, the court would rule that such a cause of action was really a ‚Äúfailure to warn‚ÄĚ disguised as ‚Äúdesign defect.‚ÄĚ In other words, if the EPA had decreed that the product was a good product when used according to the label, the judgment about whether it was properly designed had already been made. This created the anomalous situation that products could be legal and harmful even when used as directed. Indeed, this is exactly the situation with cigarettes. But, after Bates, this is not the law as to pesticides. The Bates court was clear that it intended to allow state common law torts to be a parallel remedy to FIFRA regulation: Private remedies that enforce federal misbranding requirements would seem to aid, rather than hinder, the functioning of FIFRA. ‚ĶFIFRA contemplates that pesticide labels will evolve over time, as manufacturers gain more information about their products‚Äô performance in diverse settings. As one court explained, tort suits can serve as a catalyst in this process: ‚ÄúBy encouraging plaintiffs to bring suit for injuries not previously recognized as traceable to pesticides such as [the pesticide there at issue], a state tort action of the kind under review may aid in the exposure of new dangers associated with pesticides. Successful actions of this sort may lead manufacturers to petition EPA to allow more detailed labeling of their products; alternatively, EPA itself may decide that revised labels are required in light of the new information that has been brought to its attention through common law suits. In addition, the specter of damage actions may provide manufacturers with added dynamic incentives to continue to keep abreast of all possible injuries stemming from use of their product so as to forestall such actions through product improvement.‚ÄĚ Ferebee, 736¬†¬†US Supreme Court clearly indicated that the pesticide manufacturers remain responsible for harm their products may cause when used as labeled in Bates v Dow:¬†
‚ÄúBecause it is unlawful under the statute to sell a pesticide that is registered but nevertheless misbranded, manufacturers have a continuing obligation to adhere to FIFRA‚Äôs labeling requirements. ¬ß136j(a)(1)(E); see also ¬ß136a(f)(2) (registration is prima facie evidence that the pesticide and its labeling comply with the statute‚Äôs requirements, but registration does not provide a defense to the violation of the statute); ¬ß136a(f)(1) (a manufacturer may seek approval to amend its label). Additionally, manufacturers have a duty to report incidents involving a pesticide‚Äôs toxic effects that may not be adequately reflected in its label‚Äôs warnings, 40 CFR ¬ß¬ß159.184(a), (b) (2004), and EPA may institute cancellation proceedings, 7 U. S. C. ¬ß136d(b), and take other enforcement action if it determines that a registered pesticide is misbranded.‚Ä̬†
From Bates v. Dow:  reference to EPA general waiver of efficacy review 
In 1978, Congress once again amended FIFRA, 92 Stat. 819, this time in response to EPA‚Äôs concern that its evaluation of pesticide efficacy during the registration process diverted too many resources from its task of assessing the environmental and health dangers posed by pesticides. Congress addressed this problem by authorizing EPA to waive data requirements pertaining to efficacy, thus permitting the agency to register a pesticide without confirming the efficacy claims made on its label. ¬ß136aTM(5). In 1979, EPA invoked this grant of permission and issued a general waiver of efficacy review, with only limited qualifications not applicable here. See 44 Fed. Reg. 27932 (1979); 40 CFR ¬ß158.640(b) (2004). In a notice published years later in 1996, EPA confirmed that it had ‚Äústopped evaluating pesticide efficacy for routine label approvals almost two decades ago,‚ÄĚ Pesticide Registration Notice 96‚Äď4, p. 3 (June 3, 1996), available at www.epa.gov/opppmsd1/PR_Notices/pr96-4.html, App. 232, and clarified that ‚ÄúEPA‚Äôs approval of a pesticide label does not reflect any determination on the part of EPA that the pesticide will be efficacious or will not damage crops or cause other property damage.‚ÄĚ Id., at 5, App. 235.¬†¬†
Posted in Bayer, Failure to Warn, Florida, Glyphosate, Idaho, Iowa, Missouri, Monsanto, Pesticide Regulation, Preemption, State/Local by: Beyond Pesticides
1 Comment
22
Feb
(Beyond Pesticides, Feb 22, 2024) The Idaho Senate failed to pass SB 1245 last week which would have provided legal protection to pesticide manufacturers from ‚Äúfailure-to-warn” liability. This legal framework has been pivotal not only for plaintiffs, who are typically users of a toxic product, seeking redress from exposure to glyphosate-based herbicide products such as Roundup, but can also potentially extend to any toxic pesticide products. Similar bills have recently been introduced in the Iowa, Florida, and Missouri state legislatures as petrochemical pesticide industry actors such as Bayer face billions of dollars in legal settlements from victims of pesticide injury. While the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA) registration process permits the labeling of products with pesticidal claims based on compliance with testing requirements, the state legislation would establish EPA-authorized pesticide labels as definitive evidence that cannot be challenged in a court of law.
The Idaho legislation, SB 1245, was introduced in January in the state Senate by Senator Mark Harris, who represents Soda Springs County, which has North America’s largest elemental phosphorus mine (phosphorus is a critical ingredient in developing glyphosate). Proponents of SB 1245 argue, ‚Äú[This bill] protect[s] companies that produce safe pesticides critical to agriculture in Idaho and beyond.‚ÄĚ Idaho Press continues,‚ÄĚ Sen. Harris said the bill does not restrict lawsuits against pesticide manufacturers for a number of claims, including product defects, drift or misapplication, or if the manufacturer fraudulently conceals known facts about the product.‚ÄĚ While these other legal avenues are possible, the overwhelming majority of successful cases for pesticide injury lawsuits fall under ‚Äúfailure-to-warn” claims. Brigit Rollins, a staff attorney at the National Agricultural Law Center, describes this liability framework as, ‚Äúa type of civil tort that is frequently raised in products liability cases. Unlike negligence and design defect…failure to warn does not argue that a product has physical faults. Instead, a plaintiff typically raises failure to warn claims to allege that a product manufacturer failed to provide adequate warnings or instructions about the safe use of a product.‚ÄĚ
Under this new industry push in different state legislatures, the product liability legal framework would be undermined, rendering victims around the United States without effective legal recourse and shielding industry actors such as Bayer from billions of dollars in ongoing and future judgments and settlements. As of 2022, Bayer settled over 100,000 lawsuits on glyphosate/Roundup, paying out approximately $11 billion. The company faces an additional 30,000 lawsuits pending, according to reporting by Forbes.
Meanwhile, a bill, SF 2392, similar to the bill in Idaho has been introduced in the Iowa Senate. Prior to opting to introduce the legislation, two study bills had been considered by both the Senate and House Agriculture Committees without much notice. Another kindred bill, SB 1416, was introduced in the Missouri Senate last Tuesday and will establish the following, ‚ÄúUnder the act, a pesticide registered by certain federal agencies or consistent with certain federal pesticide labeling requirements or health assessments shall satisfy any warning label requirement regarding health or safety or any other provision of current law.‚ÄĚ As of this publication, it is currently unclear whether this bill will move forward or if a companion bill will be filed in the House. A similar bill, SB 1252, introduced in the Florida Senate, explicitly states, ‚ÄúA products liability action, including a failure to warn, may not be brought or maintained against any distributor, dealer, or applicator,‚ÄĚ barring several exemptions. This bill was introduced in January and still must be voted out of two more committees (Agriculture and Rules) after passing through the Judiciary committee on February 5. A similar version in the Florida House, HB 347, passed both the Civil Justice subcommittee and Judiciary committee earlier this month and was introduced to the House on February 15.
Beyond Pesticides has covered the history of products liability litigation against petrochemical companies such as Bayer, including a 2004 U.S. Supreme Court ruling (Bates v. Dow AgroSciences LLC). In the past, the Supreme Court has protected the rights of pesticide injury victims to seek legal recourse: In this case, ‚Äúthe court found, ¬†‚ÄėThe long history of tort litigation against manufacturers of poisonous substances adds force to the basic presumption against preemption. If Congress had intended to deprive injured parties of a long available form of compensation, it surely would have expressed that intent more clearly. See Silkwood v. Kerr-McGee Corp., 464 U. S. 238, 251 (1984). Moreover, this history emphasizes the importance of providing an incentive to manufacturers to use the utmost care in the business of distributing inherently dangerous items.‚Äô‚ÄĚ
More recently in 2022, ‚Äúthe Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals voided EPA‚Äôs ‚Äėinterim registration review‚Äô decision approving continued use of glyphosate, issued in early 2020 saying, ‚ÄôEPA did not adequately consider whether glyphosate causes cancer and shirked its duties under the Endangered Species Act (ESA),‚Äô and the U.S. Supreme Court refused to consider (deny certiorari) a Bayer petition to save the company from being held accountable to those diagnosed with cancer after using glyphosate herbicides.‚ÄĚ
As Beyond Pesticides previously reported, there are numerous adverse health effects associated with glyphosate-based Roundup exposure, including documented studies outlining adverse health effects on the nervous system. A study by Arizona State University found that, ‚Äúglyphosate can infiltrate the brain through the blood (blood-brain barrier), increasing neurological disease risk.‚ÄĚ This finding is alarming given that the rate of Alzheimer‚Äôs disease amongst the U.S. population is projected to double by 2050. In 2015, the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) determined that glyphosate is probably carcinogenic, potentially leading to cancers such as non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. Glyphosate, alongside other herbicides such as dicamba and glufosinate, have also been found to lead to higher populations of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in soil, according to a 2021 article in the journal, Molecular Biology and Evolution. For more information on glyphosate and its potential health impacts, see the Pesticide-Induced Diseases Database.
For information on how to protect yourself and your loved ones from petrochemical pesticide exposure, see Gateway on Pesticide Hazards and Safe Pest Management and Non-Toxic Lawns and Landscapes to find alternative land management systems rooted in organic principles. For more information on the health benefits of organic food products relative to conventionally grown, see Eating With a Conscience. If you believe that you may have been exposed to pesticides, see Pesticides Emergencies to find contact information for lab testing, lawyers, or other information.
All unattributed positions and opinions in this piece are those of Beyond Pesticides.  
Source: Idaho Press
Posted in Bayer, Blood Disorders, Failure to Warn, Florida, Glyphosate, Idaho, Iowa, Label Claims, Missouri, Nervous System Effects, Preemption, Uncategorized by: Beyond Pesticides
3 Comments
21
Feb
(Beyond Pesticides, February 21, 2024) In addition to its effects including cancer, and reproductive, immune or nervous system disruption, according to international findings, a review published in Toxics finds that the the widely used weed killer 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) causes significant changes in liver structure and function. 2,4-D can damage liver cells, tissue, and inflammatory responses through the induction of oxidative stress. The liver, the largest solid organ in the human body, is an essential part of the digestive system responsible for blood detoxification, nutrient metabolization, and immune function regulation. However, rates of chronic liver diseases are increasing, representing the second leading cause of mortality among all digestive diseases in the U.S. In fact, researchers warn of the rise in liver disorders and metabolic syndrome among young people. Therefore, reviews like this highlight the research available to make decisions on safeguarding human health from chemical exposure to mitigate further disease outcomes and complications.
2,4-D is used on turf, lawns, and rights-of-way, as well as in forestry and aquatic systems. 2,4-D products are available as liquid, dust, and granule fields, as well as fruit and vegetable crops, including in genetically engineered crop production. The chemical is widely used in ‚Äúweed and feed‚ÄĚ lawn products. It is critical to note that EPA allows residues of 2,4-D in virtually all food commodities widely consumed; in drinking, surface, and groundwater; on playing fields; and in parks and schoolyards.
The review primarily focuses on structural damage and chemical biomarkers indicating toxicity to the liver and its function. Assessing studies from PubMed, Web of Science and Scopus, researchers found 83 articles on liver effects and exposure to 2,4-D, ranging from in vivo (in living organisms) models (~70%) to in vitro (in test tube) models (~30%). Most studies focused on the 2,4-D as an active ingredient, while the remainder focused on commercial formulations of 2,4-D. However, the review did make a note of studies evaluating mixtures of pesticides that include 2,4-D. The biomarkers of concern include a decrease in antioxidant capacity (oxidative stress) and changes in lipids, liver function, and xenobiotic metabolism. Despite the studies finding an association between 2,4-D exposure and liver toxicity, the researchers highlight the need for future studies to investigate the mechanisms involved in liver toxicity.
Analysis: A multitude of research describes a range of unacceptable hazards from 2,4-D exposure, including the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) finding that the chemical is a possibly human carcinogen (e.g., soft tissue sarcoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma). Moreover, exposure to 2,4-D can cause adverse neurological effects like the development of ALS and loss of smell and hormone deficiencies like endocrine disruption. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) finds babies born near areas of high 2,4-D use, such as farming communities, have higher rates of birth abnormalities, respiratory and cardiovascular issues, and developmental defects. Although glyphosate replaced a lot of 2,4-D herbicide use during the late 1990s and early 2000s, increasing glyphosate resistance is shifting the market back to heavy 2,4-D use and the chemical’s potential contribution to the growth of antibiotic resistance in human pathogenic bacteria. Considering the agricultural industry is now speeding toward multi-herbicide-tolerant (genetically engineered) cropping systems, public and environmental health is at greater risk from chemical input threats from this cropping system.
Comparative: From 1974 up to the present day, studies in this review highlight what many studies have previously: 2,4-D has a negative impact on the liver both structurally and biochemically. The review highlights that oxidative stress increases the progression of 2,4-D-induced liver damage. Yet, the lack of studies on the mechanism of action, targets, and molecular pathways involved in liver toxicity needs further understanding. Further understanding will allow government and health officials to make informed decisions that reduce and/or eliminate human and environmental health risks. However, this review notes that using in silico and chemico tools can be a viable and efficient alternative for predicting the toxicity mechanisms of pesticides to understand the interactions between molecules and toxic chemicals.¬† Thus, the researchers in the review advocate for ‚Äú[‚Ķ]the use of predictive methodologies in investigating the mechanism of action of 2,4-D [to] offer a promising perspective for advancing our knowledge of its toxicity and contributes to the development of more effective strategies for environmental safety and public health.‚ÄĚ
Health officials estimate about 100 million individuals in the U.S. have some liver disease, with cases of specific liver diseases, like nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), having doubled over the past 20 years. Therefore, it is essential to mitigate preventable exposure to disease-inducing pesticides. For more information about pesticides’ effects on human and animal health, see Beyond Pesticides’ Pesticide-Induced Diseases Database, including pages on immune system disorders (e.g., hepatitis [liver condition], cancer (including lymphoma), and more.
One meaningful way to reduce human and environmental contamination from pesticides is to buy, grow, and support organic. Numerous studies find that levels of pesticides in urine significantly drop when switching to an all-organic diet. Furthermore, given the wide availability of non-pesticidal alternative strategies, families, from rural to urban, can apply these methods to promote a safe and healthy environment, especially among chemically vulnerable individuals or those with health conditions. For more information on why organic is the right choice for consumers and the farmworkers that grow our food, see the Beyond Pesticides webpage, Health Benefits of Organic Agriculture.
All unattributed positions and opinions in this piece are those of Beyond Pesticides.
Source: Toxics
Posted in 2,4-D, Agriculture, Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), Lawns/Landscapes, Liver Damage, Oxidative Stress by: Beyond Pesticides
3 Comments
20
Feb
(Beyond Pesticides, February 20, 2024) With health risks including developmental, metabolic, cardiovascular, and reproductive harm, cancer, damage to the liver, kidneys, and respiratory system, as well as the potential to increase the chance of disease infection and severity, per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) and their toxic trail of contamination in the environment is wreaking havoc with all life. The use of PFAS in industrial and commercial applications has led to widespread contamination of water and biosolids used for fertilizer, poisoning tens of millions of acres of land and posing a significant threat to the biosphere, public health, gardens, parks, and agricultural systems. Farmers and rural communities, in particular, bear the brunt of this contamination, as it affects their drinking water, soil quality, and livestock health.  
Tell Congress that the Farm Bill must include the Relief for Farmers Hit with PFAS Act and the Healthy H2O Act to protect farmers and rural communities from PFAS contamination. 
Led by Chellie Pingree (D-ME), U.S. Senators Tammy Baldwin (D-WI), and Susan Collins (R-ME),¬†a bipartisan and bicameral bill‚ÄĒthe¬†Relief for Farmers Hit with PFAS Act‚ÄĒhas been introduced to provide assistance and relief to those affected by PFAS. A second bill, the¬†Healthy H2O Act,‚ÄĮintroduced‚ÄĮby‚ÄĮRepresentatives Pingree and David Rouzer (R-NC)‚ÄĮand‚ÄĮSenators Baldwin and Collins, provides grants for water testing and treatment technology directly to individuals and non-profits in rural communities.¬†
There are more than 9,000 synthetic (human-made) chemical compounds in the PFAS family, which includes the most well-known subcategories, PFOS (perfluorooctane sulfonate) and‚ÄĮPFOA (perfluorooctanoic acid). These PFAS compounds have been dubbed ‚Äúforever chemicals‚ÄĚ for their persistence in the environment (largely because they comprise chains of bonded fluorine‚Äďcarbon atoms, those bonds being among the strongest ever created). PFAS contamination of drinking water, surface and groundwater, waterways, soils, and the food supply, among other sources, is a ubiquitous and concerning contaminant across the globe. PFAS contamination of drinking water resources is a serious and growing issue for virtually all U.S. states, as¬†Environmental Working Group (EWG) demonstrates via its interactive map, and¬†for hydrologic ecosystems around the world.¬†
The widespread exposure to these compounds arises from multiple sources: 
- Contamination of drinking water and wastewater treatment resulting in fertilizers produced from biosolids (processed output from treatment plants), as well as residues in food packaging some pesticides; 
- extensive ‚Äúlegacy‚ÄĚ (historic) use in fabric and leather coatings, household cleaning products, firefighting foams, stain-resistant carpeting, and other products;¬†
- historic and current industrial uses in the aerospace, automotive, construction, and electronics sectors; and 
- current uses in many personal care products (e.g., shampoo, dental flosses, makeup, nail polish, some hand sanitizers, sunscreens); water-and-stain-proof and -resistant fabrics and carpeting; food packaging; and non-stick cookware, among others. 
Although some of these uses and resulting contamination have been phased out, many persist, including several related to food processing and packaging. The flooding of the materials stream with thousands of persistent synthetic PFAS compounds since their first uses in the 1950s allows them to remain widespread in the environment and in human bodies. People can be exposed to PFAS compounds in a variety of ways, including occupationally, through food sources, via drinking contaminated water (another enormous emerging issue; see below), ingesting contaminated dust or soil, breathing contaminated air, and using products that contain, or are packaged in materials that use, the chemicals. 
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) notes, ‚Äú[B]ecause of their widespread use and their persistence in the environment, many PFAS are found in the blood of people and animals all over the world and are present at low levels in a variety of food products and in the environment. PFAS are found in water, air, fish, and soil at locations across the nation and the globe. Scientific studies have shown that exposure to some PFAS in the environment may be linked to harmful health effects in humans and animals.‚ÄĚ
Among the potential health risks of some PFAS compounds for humans are: 
- impacts on the immune system (including decreased vaccine responses); 
- endocrine disruption; 
- reproductive impacts, including lowered infant birth weight; 
- developmental delays in children; 
- increased risk of hypertension, including in pregnant people (eclampsia); 
- alterations to liver enzymes; 
- increased risk of some cancers, including prostate, kidney, and testicular; 
- increase in circulatory cholesterol levels; 
- increased risk of cardiometabolic diseases (via exposure during pregnancy); and 
- possible‚ÄĮincreased risk of COVID-19 infection and severity.¬†
Tell Congress that the Farm Bill must include the Relief for Farmers Hit with PFAS Act and the Healthy H2O Act to protect farmers and rural communities from PFAS contamination. 
After years of advocate pressure, EPA has begun to take action under its¬†PFAS Strategic Roadmap‚ÄĒincluding ‚Äúdesignat[ing] two of the most widely used‚ÄĮper- and polyfluoroalkyl substances [PFOA and PFOS]‚ÄĮas hazardous substances under the¬†Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act¬†(CERCLA), also known as ‘Superfund;’‚Ä̬†issuing interim updated drinking water health advisories¬†for PFOA and PFOS); issuing final health advisories on two others that had been considered ‚Äúreplacement‚ÄĚ chemicals for manufacturing uses‚ÄĒperfluorobutane sulfonic acid and its potassium salt (PFBS) and hexafluoropropylene oxide (HFPO) dimer acid and its ammonium salt (the so-called ‚ÄúGenX chemicals‚ÄĚ).¬†
PFAS compounds have been found to contaminate water and irrigation sources, and soils themselves ‚ÄĒ often through the use of fertilizers made from so-called ‚Äúbiosludge‚ÄĚ (biosolids) from local waste treatment plants. In addition, these plants may discharge millions of gallons of wastewater into waterways, contaminating them; current waste and water treatment generally does not eliminate PFAS compounds from the treated effluent water.¬†Biosolids¬†and¬†wastewater‚ÄĮhave long been sources of exposure concerns related to pesticides, industrial chemicals, pharmaceuticals, personal care products, and household chemicals; PFAS contamination is now rising as a specific and concerning addition to that nasty list.¬†
These forever (and perhaps ‚Äúeverywhere‚ÄĚ) compounds¬†may be contaminating¬†nearly 20 million acres of productive agricultural land in the U.S. A significant portion of farmers, perhaps 5%, is using biosludge from local treatment plants as fertilizer on their acreage. The use of biosludge was thought by many, a decade ago, to be a sensible use of the waste products from treatment; it was even encouraged by many state agricultural department programs, but now¬†it is recognized¬†that these products present threats when spread on fields that produce food‚ÄĒor anywhere that presents the possibility of human, organism, or environmental exposures to potentially toxic PFAS compounds. Notably, there are currently¬†no federal requirements¬†to¬†test¬†such sludge ‚Äúfertilizers‚ÄĚ for the presence of PFAS.¬†
Recognizing the impacts on the agricultural sector from PFAS, the state of Maine has taken the lead in both state and federal efforts to support farmers who have been affected by PFAS contamination, including the Relief for Farmers Hit with PFAS Act and the Healthy H2O Act.
In short, these bills would achieve the following: 
- The¬†Healthy H2O Act¬†addresses PFAS contamination in water supplies by providing funding for water testing, treatment, and remediation. By allocating resources to support the implementation of effective PFAS filtration systems, it can ensure that farmers and rural communities have access to clean and safe water, protecting‚ÄĮboth human health and agricultural productivity.¬†
- The¬†Relief for Farmers Hit with PFAS Act¬†provides financial assistance and support to farmers affected by PFAS contamination. By establishing a comprehensive assistance program, we can help farmers mitigate the economic burdens resulting from PFAS-related disruptions and implement necessary remediation efforts. Additionally, this act supports research and education initiatives to enhance farmers’ awareness and understanding of PFAS risks and best management practices.¬†
Meanwhile, we must not lose sight of the fact that PFAS chemicals are not the only legacy contaminants. Others include wood preservatives, DDT, dioxins, and the termiticide chlordane. Unfortunately, some of these continue to be added to the environment, sometimes inadvertently, but also intentionally, particularly through pesticide use. 
Tell Congress that the Farm Bill must include the Relief for Farmers Hit with PFAS Act and the Healthy H2O Act to protect farmers and rural communities from PFAS contamination. 
Letter to Congress
I am writing to urge you to cosponsor S.747, the Relief for Farmers Hit with PFAS Act, and S. 806, the Healthy H2O Act‚ÄĒand push for their inclusion in the Farm Bill‚ÄĒin order to help farmers who have been impacted by PFAS (perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances) contamination. As indicated by the title of the bill, farmers have often been ‚Äúhit with‚ÄĚ legacy contaminants through no fault of their own, and the bill will authorize $500 million over FY 2023-2027 to the U.S Department of Agriculture to help farmers, including: more capacity for PFAS testing for soil or water sources; blood monitoring for individuals to make informed decisions about their health; equipment to ensure a farm remains profitable during or after known PFAS contamination; relocation of a commercial farm if the land is no longer viable; alternative cropping systems or remediation strategies; educational programs for farmers experiencing PFAS contamination; research on soil and water remediation systems, and the viability of those systems for farms; and improving rural drinking water. This money, if appropriated, comes from taxpayers, not those responsible for the contamination.
PFAS chemicals, also known as ‚Äúforever chemicals,‚ÄĚ are legacy contaminants whose historical use, including many decades ago in some instances, has led to their toxic persistence in the environment and in organisms. However, PFAS chemicals are not the only legacy contaminants. Others include wood preservatives, DDT, dioxins, and the termiticide chlordane. Unfortunately, some of these continue to be added to the environment, sometimes inadvertently, but also intentionally, particularly through pesticide use.
Since these legacy ‚Äúforever chemicals‚ÄĚ continue to be added to the environment, it is particularly important to stop their use. Many of them, like PFAS, are endocrine-disrupting chemicals that have not been adequately restricted. Thus, while I urge you to pass these bills offering relief to farmers harmed by PFAS, we must also do all that we can to prevent further contamination.
I urge you to use your oversight of EPA to ensure that persistent toxic pesticides and other chemicals are no longer allowed to be released into the environment. Ensure that EPA carries out its responsibility to ensure that PFAS and other endocrine disruptors are not released into the environment.
Thank you.
Posted in Agriculture, Biosolids, Biosolids/Sewage Sludge, Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), PFAS, Sewage Sludge, Take Action, Uncategorized, Water by: Beyond Pesticides
8 Comments











