
01
Mar
(Beyond Pesticides, March 1, 2018)  A comprehensive review of notorious, bee-killing neonicotinoid insecticides finds that crop yields  and on-farm profit can be maintained and improved by replacing these toxic chemicals with alternative pest management strategies. The new study is part of an ongoing update to the 2014 Worldwide Integrated Assessment undertaken by an international team of scientists called the Task Force on Systemic Pesticides. The results of this review point to the need for strong action against these chemicals by all levels of government.
and on-farm profit can be maintained and improved by replacing these toxic chemicals with alternative pest management strategies. The new study is part of an ongoing update to the 2014 Worldwide Integrated Assessment undertaken by an international team of scientists called the Task Force on Systemic Pesticides. The results of this review point to the need for strong action against these chemicals by all levels of government.
“Regulators need to realize that if we want sustainable agricultural practices, we need a more restrictive regulatory framework and programs to support farmers making the switch,” said Task Force co-chair and scientist at France’s National Scientific Research Centre Jean-Marc Bonmatin, PhD, in a press release. “Our findings on the availability of alternatives will be particularly relevant where new restrictions on neonics are being considered.”
The Task Force reviewed 200 studies on systemic insecticides, looking at their use and pest resistance in annual and perennial crops, the viability of alternative pest management techniques, and the potential to implement alternative forms of crop insurance to cover risks, rather than spray expensive insecticides.
For perennial crops, researchers focus on the use of neonicotinoids to manage pests in fruit orchards and vineyards. Given mixed reports on the efficacy of neonicotinoids to control problem pests, the Task Force established strong evidence for the viability of alternative pest management techniques. Common moth pests, for instance, could be managed effectively by disrupting mating patterns through the use of pheromones. Exclusion netting with insect-proof screens could control both moths and increasingly problematic pests such as the brown marmorated stink bug. The use of biological control agents, such as parasitoids, insect-killing fungi, and other pest predators, could eliminate neonicotinoid use to control aphids and certain moth species. Likewise, ecological engineering, by planting habitat suitable to pest predators, can effectively knock down a range of pests, including aphids, mealybugs, thrips, and moths.
In annual crops, the main use of neonicotinoids is prophylactic, as the chemicals are usually applied to the seed of corn, soy, canola, and other row crops. Researchers found in the literature that a significant amount of neonicotinoid use could be abated by more thorough pest level evaluations. For example, major developments in modeling the prevalence of wireworm, a major pest in corn, enables a low-cost and reliable method to address the pest through less toxic means before their population gets out of hand. The literature on ecological engineering also appeared promising, with studies indicating that by incorporating flowers strips into rice fields, insecticide use could be reduced by 70% while increasing yields 5%.
Given the focus on less toxic, low cost management methods, the Task Force reviewed the practicality of a mutual fund risk insurance model to pay farmers when pest outbreaks do occur. Such an approach was piloted for corn farmers in Italy, with the results analyzed by researchers. As opposed to private crop insurance, a mutual fund insurance model is managed by a collective of farmers, who may a nominal fee per hectare (a hectare is ~2.5 acres) into the fund. As part of the collective, farmers are encouraged to follow strict integrated pest management principles and only use insecticides as a last resort. They are allowed to withdraw from the fund not only for pest damage, but also flooding, freezing, cold, drought, or loss from wildlife. The results of a two-year pilot saw 47,000 hectares covered under the fund, with the cost to buy in at ~3.3 euros ($4) per hectare, a tenth the price of an insecticide treatment to the same fields. The fund sat at 160,335 euros (~$200,000), and paid out roughly 84,000 euro (~$103,000), a little over 50% of the revolving fund.
“Crop insurance programs can be tailored to reduce the financial risk to farmers from potential pest infestations without the environmental costs of insecticide use,” Dr. Bonmatin said. “And on a cost-recovery basis, insurance premiums are far cheaper than insecticides, so farmers’ net incomes rise, too. It’s a win-win approach for farmers and the environment.”
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) determined as far back as 2014 that neonicotinoid seed treatments provide little to no benefit to farmers. However, in contrast to the European Union, which is currently considering whether to make a ban on these chemicals permanent, EPA continues to acknowledge the risks of these chemicals, yet do very little to encourage even a reduction in their use. To date, all the agency has done is add new label language widely criticized as inadequate and disproportionate to the risk these chemicals present pollinators.
The Task Force on Systemic Pesticides’ update to the Worldwide Integrated Assessment should put lawmakers and regulators at ease when determining whether to ban these hazardous insecticides. Not only are there a range of alternative pest management strategies available to address the pests neonicotinoids target, but the success of the mutual fund insurance model provides an economic replacement to the use of toxic neonicotinoids to avert the risk of crop loss.
Further research from the comprehensive Worldwide Integrated Assessment can be viewed on the Task Force’s webpage. And for more information about what you can do to stop neonicotinoids from harming pollinators, wildlife, and ecosystems, visit Beyond Pesticides’ Bee Protective webpage.
All unattributed positions and opinions in this piece are those of Beyond Pesticides.
Source: EurekAlert Press Release, Environmental Science and Pollution
Posted in neonicotinoids, Pesticide Regulation, Pollinators, Uncategorized by: Beyond Pesticides
No Comments
28
Feb
(Beyond Pesticides, February 27, 2018) As stricter regulations and technological changes begin to  decrease air pollution from cars and other vehicles, scientists are finding that the use of pesticides and other household chemicals represent an increasing proportion of smog-forming pollution in the U.S. Research published in the journal Science this month indicates that personal care products, cleaning agents, perfumes, paints, printing ink, and pesticides warrant greater attention from regulators for their ability to form toxic fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and tropospheric ozone (O3). ‚ÄúThe things I use in the morning to get ready for work are comparable to emissions that come out of the tailpipe of my car,‚ÄĚ said Brian McDonald, PhD, the study‚Äôs lead author and air-pollution researcher at the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) in Boulder, Colorado to Nature. ‚ÄúI think that‚Äôs what surprises a lot of people.‚ÄĚ
decrease air pollution from cars and other vehicles, scientists are finding that the use of pesticides and other household chemicals represent an increasing proportion of smog-forming pollution in the U.S. Research published in the journal Science this month indicates that personal care products, cleaning agents, perfumes, paints, printing ink, and pesticides warrant greater attention from regulators for their ability to form toxic fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and tropospheric ozone (O3). ‚ÄúThe things I use in the morning to get ready for work are comparable to emissions that come out of the tailpipe of my car,‚ÄĚ said Brian McDonald, PhD, the study‚Äôs lead author and air-pollution researcher at the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) in Boulder, Colorado to Nature. ‚ÄúI think that‚Äôs what surprises a lot of people.‚ÄĚ
Recognizing a gap in emission data as pollution from cars and other mobile sources of fossil fuel has waned over the past several decades, researchers set out to determine what chemicals were contributing to smog that continues to plague cities throughout the U.S. Using data from energy and chemical manufacturing, combined with roadway pollution and laboratory measurements, scientists created a ‚Äúmass balance‚ÄĚ of all compounds produced by the fossil fuel industry in the U.S. Through this process, it was discovered that emissions of volatile organic chemicals (VOCs), which eventually turn into pollution once released into the air, from household products are ‚Äúone to two orders of magnitude higher than from vehicle exhaust,‚ÄĚ according to the study.
When broken down, scientists attributed between 15 to 42% of VOC emissions to vehicle use, and 39 to 62% to the use of household products, with the remainder being associated with the production of fossil fuels.
The study authors then hypothesize that these chemicals must also be showing up in high concentrations in indoor air. Using a model that took data from measurements of indoor air in commercial and residential buildings, compounds associated with personal care products are roughly seven times higher indoors than amounts found in ambient air.
However, it is when these chemicals make their way outside that they become a significant pollution problem, as they oxidize in the presence of nitrogen oxides to form ozone or nuclearize in the presence of sunlight to form PM2.5. ‚ÄúSay somebody is inside using perfume, cologne,‚ÄĚ explains Chris Cappa, PhD, a co-author of the study and researcher at the University of California¬†at Davis to The Washington Post. ‚ÄúThat smell eventually dissipates. And the question is, where did it go. And there‚Äôs air exchange with the outside. Those odors dissipate because it‚Äôs basically getting moved outside. It‚Äôs just taking that indoor air and exchanging it with the outdoor air. It‚Äôs not that hard to get things from the indoor environment outside.‚ÄĚ
To confirm their emissions estimates based on the mass balance data, observed VOC emissions from Los Angeles were compared to their model, and when personal care products were accounted for, authors found the results in line with their assessment.
Chemical dependency in agriculture is also contributing to air pollution. A study published earlier this year in Science Advances by researchers at University of California, Davis finds that California regulators may be drastically underestimating chemical-intensive agriculture’s contribution to nitrogen oxide (NOx) caused air pollution, acid rain, and respiratory illness in the state. While NOx  pollution is usually associated with energy production and vehicle emissions, fertilizer use on crop fields is contributing to significant air pollution problems. Advocates say that the study is an urgent call for farmers to eliminate dependency on soluble, synthetic, nitrogen-based fertilizers and adopt the use of insoluble soil amendments that support soil biology that provide plants with nutrients. See Daily News on this.
Beyond Pesticides has long warned consumers about the volatility of pesticides used in and outside the home. Many insect baiting stations are labeled ‚Äúnonvolatile‚ÄĚ but may still off-gas noxious poisons into one‚Äôs home. The propensity for herbicides such as dicamba to volatilize after use has led to a rash of nontarget drift and damage to neighboring crop fields. The present study adds another layer of concern to these already toxic products, and indicates that the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency must more seriously consider secondary effects like volatilization-caused air pollution when considering whether to continue allowed uses of a pesticide.
All unattributed positions and opinions in this piece are those of Beyond Pesticides.
Source: Nature, Washington Post, Science
Posted in Uncategorized by: Beyond Pesticides
No Comments
27
Feb
(Beyond Pesticides, February 26, 2018) It is no secret that large organic dairy herds of 15,000 to  20,000 cows or more dot the Western US in California, Colorado and Texas in particular. They have repeatedly come under fire from watchdog groups, journalists and farmers who have observed and documented the absence of cows on pasture during grazing season, as required by the Organic Foods Production Act (OFPA). This circumventing of the law could soon change with the commercialization of the fluorescene spectroscopy (FS), which detects the amount of forage a dairy herd is eating by measuring the luminescence of metabolized grass in milk. The law requires that herds graze daily during a given region’s growing season, at least 120 days per year, and consume a minimum of 30% grass in their daily diet.
20,000 cows or more dot the Western US in California, Colorado and Texas in particular. They have repeatedly come under fire from watchdog groups, journalists and farmers who have observed and documented the absence of cows on pasture during grazing season, as required by the Organic Foods Production Act (OFPA). This circumventing of the law could soon change with the commercialization of the fluorescene spectroscopy (FS), which detects the amount of forage a dairy herd is eating by measuring the luminescence of metabolized grass in milk. The law requires that herds graze daily during a given region’s growing season, at least 120 days per year, and consume a minimum of 30% grass in their daily diet.
Until now, there has been no technology to scientifically verify that organic milk comes from grass-fed dairy cows. . The organic dairy certification system relies on visual inspections by certifiers during the grazing season and an evaluation of the dairy’s herd management plan.. While most organic dairies are in compliance, there are questions about the ability of the super-large dairies to meet stringent organic pasture regulations. The FS testing system could revolutionize organic diary production transparency with a scientific tool that reassures consumers that the organic milk and dairy products they consume meet the strict, minimum requirements of OFPA.
When cows regularly graze on pasture, traces of chlorophyll from the grasses they eat and metabolize remain in their milk. When exposed to the light frequency of the FS, a bright and measurable fluorescent marker can be seen. Scientists at Iowa State University’s (ISU) Center for Sustainable Agriculture recently published a peer-reviewed study in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry that concludes that the FS reliably measures the amount of grass a herd has eaten. They explain how the results from using FS are instantaneous, the tests are inexpensive, involve only light and not chemistry, and they could be administered at the site of a dairy pick-up.
According to ISU‚Äôs study co-author, Jacob Petrich, ‚ÄúYou just need to shine light on the sample, and there are signatures in the milk that you can see. There‚Äôs very little preparation to be done, and you get the answer almost immediately.‚ÄĚ
Several expos√©s have uncovered how USDA has failed to enforce the National Organic Program‚Äôs pasture regulations on large dairies. A 2017 Washington Post article documents an eight day investigation of Aurora Organic Dairy‚Äôs Greeley, Colorado, plant where ‚Äúsigns of grazing were sparse. . .the number of cows seen on pasture numbered only in the hundreds. . .At no point was any more than 10 percent of the herd out.‚ÄĚ To confirm the author‚Äôs observations, the Post sent milk samples to the Virginia Tech for lab testing, which confirmed that the ‚Äúkey indicators‚ÄĚ of grass-feeding matched those of conventional milk. During that same year, organic inspectors arrived at the dairy in November, after the grazing season, so they had no way of verifying Aurora‚Äôs compliance with OFPA grazing requirements.
Back in 2007, the Cornucopia Institute, an organic agriculture watchdog group, filed a complaint with USDA against the same company, arguing that it violated organic grazing rules. While USDA admitted that Aurora was in ‚Äúwillful violation‚ÄĚ of OFPA rules, the agency agreed to a settlement and the dairy continued its operations. According to the Post article, little has changed at Aurora. Still, the government remains silent in the face of such flagrant violations.
A former National Organic Standards Board (NOSB) member and owner of organic Radiance Dairy in Fairfield, Iowa, Frances Thicke, PhD, does not see how large herds such as those that supply milk to big box stores can meet USDA‚Äôs organic grazing requirements. ‚ÄúI don‚Äôt think that you can possibly graze 15,000 cow and milk them twice a day. It‚Äôs biologically, physically impossible to do that ‚Äď for the cows to go out far enough to get grass and come back. That just can‚Äôt be done, because it‚Äôd be too far to walk. Besides, they‚Äôre on a desert.‚ÄĚ Milk samples from his grass-fed cows wereused in the ISU study and they showed a high level of chlorophyll metabolites, which verify that the cows are pastured.
Consumers expect that the organic milk they drink comes from cows that roam on pasture because it is good for the cows and for the people who drink their milk. Organically produced milk contains significantly higher levels of beneficial fatty acids than conventionally produced milk because organic farmers pasture their cows when grasses and legumes are growing. A 2014 study tested 220 organic and 164 conventional whole-milk samples from producers in 7 regions across the U.S. and compared their fatty acid content over an 18 month period. Their research demonstrated that organic milk contains 62% more omega-3 fatty acids and 25% less omega-6 fatty acids then conventional milk. Although omega-3 fatty acids are essential to human health, they are not naturally produced in the human body, so they must be obtained through food consumption. Omega-3s are also integral to healthy cell function and they have been shown to prevent heart disease and stroke. Conversely, excessive levels of omega-6 fatty acids, like those predominant in conventional milk, promote cardiovascular disease, autoimmune diseases, inflammation, blood clotting, and tumor growth.
Clearly, from a health perspective, it is important to eat whole fat milk products made with milk sourced from grass-fed organic dairies. But, how can you be sure? While FS is still in the early stages of development because more testing on different breeds and cow diets is needed, researchers agree that a hand-held and consumer-friendly devise would not be difficult to develop, but they are not there yet.
In the meantime, it is critical for you to educate yourself about the most authentic and trusted organic dairy producers at the grocery stores where you shop. Buy local from a dairy farmer you get to know and trust. If you aren’t sure, ask your neighbors and colleagues who are their go-to dairy companies. Investigate the plant codes on milk containers so you can avoid mega-organic dairies like Aurora (08-29). Choose a recognized name brand over generic brands and store brands from mega stores like Walmart, Target and Costco, who tend to source their milk from large organic dairies to accommodate the large volumes they sell. Don’t buy the cheapest brands because they don’t pay farmers a fair price and they are likely stretch the rules for compliance with OFPA. Most importantly, don’t give up on the organic label. Organic’s system of regulation, inspection, and third party certification is still the most transparent food system we have and the most beneficial for human health and the environment.
Check-out Beyond Pesticides’ Eating with a Conscience website to learn more about the many benefits of organic food production for consumers, workers, and rural families. To advocate for organic integrity and the protection and strengthening of organic standards, see Beyond Pesticides’ Keeping Organic Strong webpage.
All unattributed positions and opinions in this piece are those of Beyond Pesticides.
Sources: The Washington Post, The New Food Economy, Organic Advocacy, The Cornucopia Institute
Posted in Agriculture, Alternatives/Organics, National Organic Standards Board/National Organic Program, Uncategorized by: Beyond Pesticides
No Comments
26
Feb

U.S. Rep. Earl Blumenauer (D-OR) discussing Saving America’s Pollinators Act.
(Beyond Pesticides, February 26, 2017) U.S. Representatives Earl Blumenauer (D-OR) and Jim McGovern (D-MA) reintroduced the Saving America’s Pollinators Act (H.R. 5015), which suspends the registration of certain neonicotinoid insecticides until the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency conducts a full scientific review that ensures these chemicals do not harm pollinators. Last week, Beyond Pesticides joined Rep. Blumenauer and other experts from environmental, conservation, whistleblower, and farmworker health groups on Capitol Hill to urge Congress to take action to protect pollinators in the face of ongoing obstruction by an increasingly industry-influenced EPA.
Tell your Representative to cosponsor the Save America’s Pollinators Act!“
Pollinators are the backbone of America‚Äôs agriculture system. Acting now to protect them and stop their decline is essential to the sustainability of our nation‚Äôs food supply,‚ÄĚ Rep. McGovern said. ‚ÄúSimply taking the word of the manufacturers that their products are safe is not an option. Consumers need strong oversight. That is why I am proud to join Congressman Blumenauer in demanding the EPA fully investigate the effect that certain harmful pesticides may have on the vitality of our pollinators.‚ÄĚ
Numerous scientific studies implicate neonicotinoid pesticides as key contributors to the global decline of pollinator populations. EPA’s own scientists have found that neonicotinoids pose far-reaching risks to birds and aquatic invertebrates. For example, they find deadly impacts to birds from neonicotinoid-treated seeds, poisoned insect prey, and contaminated grasses.
‚ÄúEPA‚Äôs recent assessment confirms what the science has already shown: that neonicotinoids are highly toxic not just to bees, but to aquatic species and birds. To protect our waterways and pollinators it is imperative that action be taken to ban these chemicals,‚ÄĚ said Nichelle Harriott, science and regulatory director at Beyond Pesticides.
University researchers have found that tiny amounts of neonicotinoids are enough to cause migrating songbirds to lose their sense of direction and become emaciated. A recent study by U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) researchers found neonics widespread in the Great Lakes at levels that harm aquatic insects, or the aquatic food web‚ÄĒthe foundation of healthy aquatic ecosystems.
‚ÄúThe health of our food system depends on the health of our pollinators. The status quo is like flying blind ‚Äď we shouldn‚Äôt be using these pesticides when we don‚Äôt know their full impact,‚ÄĚ said Rep. Blumenauer. ‚ÄúThe EPA has a responsibility to get to the bottom of this issue and protect pollinators.‚ÄĚ
Canada’s pesticide regulatory agency has recommended banning the most widely used neonicotinoid, imidacloprid, based on harms to aquatic ecosystems. Europe has instituted a temporary ban on neonicotinoids based on their harms to pollinators, and the European Commission recently proposed extending the ban indefinitely and eliminating all agricultural uses of the chemicals.
Given the ongoing obstruction by EPA leadership, however, Representatives Blumenauer and McGovern are offering a legislative remedy to address the national pollinator crisis. But Congress won’t act unless members hear from their constituents. Help push EPA to take substantive action on neonicotinoids by urging your Representative to cosponsor the Saving America’s Pollinators Act.
Letter to Congress:
Please cosponsor the Save America’s Pollinators Act (H.R. 5015) introduced by Representatives Earl Blumenauer and Jim McGovern. Our nation’s pollinators are suffering, which poses a huge threat to our food system. A third of the food we eat depends on pollination by insects and birds.
Over the past decade, documented incidents of honey bee colony collapse disorder and other bee losses have reached a record high. In some cases, beekeepers  have repeatedly lost 100 percent of their operations. Thousands of scientific studies have implicated neonicotinoids as key contributors to declining pollinator populations.
Although Canada and the European Union are taking action to ban neonicotinoids, EPA fails to act. Given the ongoing obstruction by EPA leadership, however, Representatives Blumenauer and McGovern are offering a legislative remedy to address the national pollinator crisis. Please help protect pollinators by cosponsoring the Save America’s Pollinators Act.
Thank you.
Posted in Bayer, Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), National Politics, neonicotinoids, Pollinators, Take Action, Uncategorized by: Beyond Pesticides
No Comments
23
Feb
(Beyond Pesticides, February 23, 2018) Agrichemical corporation Monsanto has lost its bid to halt a 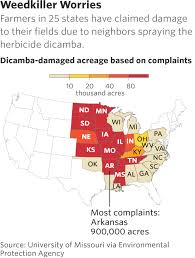 statewide ban on the use of its specialty dicamba herbicide in Arkansas. Despite a lengthy process of evaluation and public comment that led to a prohibition on the use of drift-prone dicamba herbicides during the growing season on Arkansas farms, Monsanto made one last-ditch attempt to stop the law from going into effect by suing the entire state. With the industry’s loss, Arkansas is on track to implement the toughest restrictions against dicamba in the U.S.
statewide ban on the use of its specialty dicamba herbicide in Arkansas. Despite a lengthy process of evaluation and public comment that led to a prohibition on the use of drift-prone dicamba herbicides during the growing season on Arkansas farms, Monsanto made one last-ditch attempt to stop the law from going into effect by suing the entire state. With the industry’s loss, Arkansas is on track to implement the toughest restrictions against dicamba in the U.S.
State Circuit Court Judge Chris Piazza dismissed the lawsuit last week based on a recent Arkansas Supreme Court ruling, which held that the state cannot be made a defendant in court. Monsanto’s lawsuit argued against the makeup of the state‚Äôs Plant Board, which voted to prohibit the company‚Äôs product last November. Monsanto also made claims that the state did not consider the economic damage a ban on the herbicide would cause, despite not seeking monetary restitution in court. Beyond Pesticides led a nationwide campaign to urge action by the Arkansas Plant Board to ban dicamba.
Dicamba is an herbicide originally registered for use in 1967 to control broadleaf weeds. The chemical is notoriously drift-prone, but Monsanto (with its XTEND herbicide) as well as the companies BASF (Engenia herbicide) and DowDupont (FeXapan herbicide), attempted to produce formulations that did not volatilize as much as older formulations. Their move was hastened by the increasing failure of another herbicide, glyphosate, to control herbicide-tolerant weeds in fields of genetically engineered crops.
The development of glyphosate-tolerant row crops (corn, cotton, soybeans) enabled the chemical industry to vertically integrate their seed and pesticide divisions, requiring farmers contracting with these companies to plant the company’s seed as well as spray its specific herbicide products on their crops to manage weeds. However, repeated and extensive use of the same herbicide, glyphosate, predictably resulted in weeds in these fields developing their own tolerance to the herbicide. Genes able to confer resistance to the older herbicide dicamba were discovered just as glyphosate was becoming less effective. Companies like Monsanto needed to solve the issue of drift to make sure that surrounding farms not using dicamba-tolerant crops were not affected, but as state action by not only Arkansas, but also Missouri, North Dakota, and Minnesota, show, the new product formulations have not been not successful.
Monsanto rushed its XTEND cropping system to market. The company allowed seeds of dicamba-tolerant soybeans to be put on the market without U.S. Environmental Protection Agency approval of its companion herbicide. Shortly after, reports started to roll in indicating that the many farmers were, unsurprisingly, using older dicamba formulations on their crops, leading to widespread damage of neighboring farms. However, even when the XTEND herbicide was eventually put on the market, damage reports did not slow, and research by weed scientists found that the product does volatize enough to cause drift damage.
Bader Farms, which grows over 110,00 peach trees on over 1,000 acres in Missouri, sued Monsanto after its insurance company issued a refusal to pay for damages caused by off-label dicamba drift from surrounding farms. In June of this year, University of Arkansas’ agricultural research station had over 100 acres of soybeans ruined from nearby dicamba use. And most shockingly, NPR reports that last October a dispute over dicamba drift led to the murder of one Arkansas farmer.
Monsanto’s current push to pay farmers to use the XTEND cropping system by covering half of the cost of the herbicide per acre is yet another irresponsible move by a company constantly under fire for its indecent business practices. With Arkansas’ dicamba ban held up by state courts, advocates say that other states must move quickly to follow suit.
If you are concerned about the use of dicamba-based herbicides in agricultural areas where you live, contact your state department of agriculture and voice your concerns. Find their contact information through Beyond Pesticides’ state pages. For more information about the hazards associated with GE agriculture, see our program page on genetic engineering.
All unattributed positions and opinions in this piece are those of Beyond Pesticides.
Source: Associated Press
Posted in Agriculture, Arkansas, Dicamba, Glyphosate, Litigation, Monsanto, Pesticide Drift, Uncategorized by: Beyond Pesticides
No Comments
22
Feb
(Beyond Pesticides, February 22, 2018) Online retailer Amazon will pay $1.2 million in penalties  to settle violations to U.S. regulations for selling illegal and misbranded pesticides in its online store. Under the terms of the settlement, Amazon will monitor and remove illegal pesticide products from its website. These products, mostly imported, were not registered for use and sale in the U.S. and can pose hazards to unsuspecting consumers.
to settle violations to U.S. regulations for selling illegal and misbranded pesticides in its online store. Under the terms of the settlement, Amazon will monitor and remove illegal pesticide products from its website. These products, mostly imported, were not registered for use and sale in the U.S. and can pose hazards to unsuspecting consumers.
As part of an agreement with the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Amazon has agreed to pay $1.2 million in administrative penalties for nearly 4,000 violations of the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA) by allowing third-party distributors to sell imported pesticide products on Amazon even though the products were not registered in the U.S. While agreeing to the settlement, Amazon neither admitted nor denied the specific facts alleged by the EPA.
‚ÄúThis agreement will dramatically reduce the online sale of illegal pesticides, which pose serious threats to public health in communities across America,‚ÄĚ EPA Region 10 Administrator Chris Hladick said in a news statement.
The most concerning illegal products being sold are insecticide chalk products imported from Chinese manufacturers (3 pcs Cockroaches Bugs Ants Roach Kills chalk; Miraculous Insecticide Chalk; HUA Highly Effective Cockroach Killer Bait Powder; RBTZ Safe Highly Effective Roach Killer Bait Powder Indoor (2pcs); HUA Highly Effective Fly by Killing Bait Powder (3 packs); Ars Mat 60pcs Refil for ARS Electric Mosquito Killer Convenient, Clean & Smokeless). These products contain false and misleading statements of safety on their labels and contain active ingredients such as pyrethroids, propoxur, and azamethiphos. Azamethiphos is not registered in the U.S. and propoxur has limited uses. The chalk products are used by drawing a pesticide-laden barrier on a surface the user does not want an insect to cross and survive. They are often packaged in bright colors making the products look like sidewalk chalk, toys or even candy. Children can easily open and play with the products, or even put them in their mouths.
According to EPA officials, because of the enormous shift from brick-and-mortar retailers to online commerce, ‚ÄúThis is a very difficult avenue of pesticides sales to get our hands around,‚ÄĚ said Chad Schulze, EPA Region 10 Pesticide Enforcement Team Lead.
Amazon has removed the products from its website, banned foreign sellers from selling pesticides and stepped up the monitoring of its website for illegal pesticides. The company also asked customers who purchased the products in 2013-2016 to communicate safety concerns, urged them to dispose of the items and refunded customers the cost of the products, about $130,000. Under the terms of the agreement, Amazon said it will develop an online training course about pesticide regulations and policies in an effort to reduce the number of illegal pesticides available through the online marketplace, the EPA said. The training, which will be mandatory for all entities planning to sell pesticides on Amazon, will be available to the public and online marketers in English, Spanish and Chinese.
According to reports, EPA began investigating the sale and distribution of online pesticides at the end of 2014 by searching the internet for unregistered pesticides offered by online retailers. The following year, the EPA inspected an Amazon facility in Lexington, Kentucky, and inspectors in EPA‚Äôs Region 10 office successfully ordered illegal pesticides from Amazon. In August 2015, EPA issued an order to Amazon to prohibit the sale of the illegal pesticide products, including some that the regulatory agency said could be mistaken for blackboard or sidewalk chalk by children. Another ‚ÄúStop Sale Order‚ÄĚ against Amazon was issued in January 2016 after the agency discovered that unregistered or misbranded insecticide bait products were also being offered for sale.
Last year, EPA’s Office of the Inspector General (OIG) released a report finding the agency can better reduce risks from illegal pesticides by effectively identifying imports for inspection and sampling. The report finds low rates of inspection and sampling across the U.S. to stop the importation of pesticide products that violate federal laws and recommends increased training and coordination between U.S. Customs and Border Protection to deter the import of harmful pesticides. Illegal imports of pesticides can present significant human health and environmental risks and have been linked to poisonings of children and pets. Illegal imports include high-hazard pesticides that can be counterfeit, produced at unregistered establishments, or produced using unauthorized ingredients.
With inspection guidelines being voluntary and set at only two percent ‚ÄĒwhich is still not being met‚ÄĒ advocates say that there will continue to be pesticide products being sold illegally to unsuspecting U.S. customers. These pesticides may contain ingredients banned in the U.S. or applied in ways that can pose risks to human health.
In March 2017, over 30 environmental and public health groups, joined by several environmentally responsible businesses, sent a letter to Amazon CEO Jeff Bezos, urging him to remove products linked to pollinator declines from the retailer‚Äôs website. Citing federal inertia that has allowed pollinator declines to continue at alarming rates, the groups pointed to the need for action from private companies to combat known threats to pollinators, in this case a class of pesticides known as neonicotinoids. Neonicotinoid pesticides are found in many home and garden products, and have been determined by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency to be highly toxic to bees. According to the letter,¬†‚Äúindependent scientific literature associates the use of bee-toxic pesticides, particularly neonicotinoids, with impaired pollinator health and decline, including reduced populations of native bees, butterflies and other beneficial organisms.‚ÄĚ The groups call on Amazon ‚Äúto use its influence as the largest online retailer in the U.S. to lead marketplace change and protect pollinators by prohibiting the sale of pollinator-toxic neonicotinoid pesticide products, educating consumers on the availability of safer, ‚Äúpollinator friendly‚ÄĚ alternatives.‚Ä̬†The letter to Amazon was accompanied by¬†a product list¬†identifying over 100 products sold on Amazon‚Äôs website that contain bee-toxic neonicotinoid pesticides.
To ensure that you are not buying or have not bought an illegal pesticide product, check the label for an EPA registration number or visit the website information provided. If you are still unsure, contact Beyond Pesticides for assistance.
All unattributed positions and opinions in this piece are those of Beyond Pesticides.
Source: Reuters
Posted in Announcements, Corporations, Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), Label Claims, Pesticide Regulation by: Beyond Pesticides
No Comments
21
Feb
(Beyond Pesticides, February 21, 2018) Officials in Quebec announced this week that the  Canadian province will implement new restrictions on the use of five highly toxic pesticides. As part of efforts to fulfill the vision of the Quebec Pesticide Strategy, a progressive, forward-thinking framework for pesticide regulation announced in 2015, atrazine, chlorpyrifos, and the neonicotinoids imidacloprid, clothianidin, and thiamethoxam will have new limits placed on their use. ‚ÄúTogether with the groups involved, we have found a balanced regulatory solution to protect the health of our farmers, aquatic ecosystems and pollinators,‚ÄĚ Isabelle Melancon, Quebec‚Äôs Minister of Sustainable Development, Environment, and the Fight Against Climate Change (Environment Ministry) said in a press release. ‚ÄúWe hope to obtain in this way a significant reduction in the use of the most at-risk pesticides in Quebec, in a framework of transparency and integrity.‚ÄĚ
Canadian province will implement new restrictions on the use of five highly toxic pesticides. As part of efforts to fulfill the vision of the Quebec Pesticide Strategy, a progressive, forward-thinking framework for pesticide regulation announced in 2015, atrazine, chlorpyrifos, and the neonicotinoids imidacloprid, clothianidin, and thiamethoxam will have new limits placed on their use. ‚ÄúTogether with the groups involved, we have found a balanced regulatory solution to protect the health of our farmers, aquatic ecosystems and pollinators,‚ÄĚ Isabelle Melancon, Quebec‚Äôs Minister of Sustainable Development, Environment, and the Fight Against Climate Change (Environment Ministry) said in a press release. ‚ÄúWe hope to obtain in this way a significant reduction in the use of the most at-risk pesticides in Quebec, in a framework of transparency and integrity.‚ÄĚ
Quebec’s new rules offer a range of positive developments for human health and wildlife. The changes will require the following:
- Prior to any application of atrazine, chlorpyrifos, or neonicotinoid class insecticide, farmers will need the approval of a certified agronomist from the Ordre des agronomes du Quebec (OAQ).
- Agricultural producers will be required to keep a record of all pesticides applied, as well as declare their annual sales of pesticides. The Quebec Environment Ministry will publish a report on retail sales.
- Seeds coated in neonicotinoid insecticides will be considered pesticides and subject to the same requirements therein.
- Residential and commercial use of neonicotinoids on lawns will be prohibited.
To ensure the implementation of these new regulations goes smoothly, the Environment Ministry will establish a monitoring committee to oversee the process. The province has already allocated $14 million over five years to assist farmers in reducing pesticide risks and adapting to the new measures.
Prior approval requirements at such a large scale represent a novel approach to pesticide regulation that has only otherwise been seen in local policies, such as Portland, ME‚Äôs recent pesticide restrictions, which require a waiver approval by a committee in order to apply toxic pesticides. Michel Duval, President of OAQ, is confident that the system will be successful. ‚ÄúProtecting the health of the population, pollinators and the environment is paramount,‚ÄĚ he said in press release. ‚ÄúAs stakeholders who play an important role in the implementation of integrated pest management in agricultural enterprises, agronomists are happy to put their knowledge and skills to work for the preservation of quality of the environment and the welfare of bees. Agronomic justification, as well as the support and training of farmers, seem to us to be a winning formula for establishing better agri-environmental practices.‚ÄĚ
The imposition of record-keeping is basic measure to protect public health. Publicly accessible reports on pesticide use can provide critical information, particularly in agricultural regions, that physicians and those that suspect they were poisoned by pesticides can use to treat possible pesticide-related illnesses. Recordkeeping can also increase accountability for pesticide incidents when they occur to non-target species or are found at concerning levels in waterways.
The reclassification of neonicotinoid-coated seeds as regular pesticides is an important development, because at the federal level in the U.S. and Canada, regulatory loopholes have allowed the chemical industry to categorize neonicotinoid coated seeds as ‚Äútreated articles,‚ÄĚ exempt from the safety requirements other registered pesticides must follow. Prior approval of neonicotinoid coated seeds should never occur under a smart pest management strategy, as peer-reviewed research finds these coatings, while presenting a significant risk to pollinators and birds, increase pesticide dependency, and do little to improve yields. Neighboring Ontario province took action against neonicotinoid coated seeds in 2014, aiming to reduce the use of these products by 80% to improve the health of its beekeeping industry. In the U.S., the state of Vermont passed a law in 2016 providing the state authority to regulate treated seeds as registered pesticides.
To further protect pollinators, restrictions on the use of neonicotinoids in turf will significantly impact urban areas. The range of scientific data on neonicotinoids‚Äô harm to pollinators, coupled with reports on the contamination of ‚Äúbee-friendly plants‚ÄĚ with these chemicals has led many retailers throughout the world, including Lowes, Home Depot, Walmart, Tru Value, Woolworths, to stop their sale. Scotts Miracle-Gro began phasing neonicotinoids out of their Ortho brand in mid-2016. ¬†These actions have followed increasing activity in U.S. states to restrict their use in residential settings, as Maryland and Connecticut have done. In this regard, Quebec‚Äôs move follows actions by their largest city, Montreal, which completely banned neonicotinoid use within the city in 2015.
Quebec’s new rules on toxic pesticides represent a compromise for both farmers and health advocates. These chemicals may continue to be used, but inserting agronomic experts with an eye for both the economic and health concerns surrounding the use of highly toxic pesticides into the process may be a strategy to significantly reduce pesticide use. The good news is that by also improving record-keeping, Quebec’s strategy can be closely evaluated to ensure the approval process is not simply a rubber stamp for pesticide use.
See Beyond Pesticides’ Pesticide Gateway for more information on the health and environmental effects of the pesticides targeted by Quebec’s Environment Ministry. And take action to restrict bee-toxic chemicals in the U.S. by asking your member of Congress to join in support of the Saving America’s Pollinators Act, which would suspend the use of neonicotinoids until EPA shows that they do not harm pollinators.
All unattributed positions and opinions in this piece are those of Beyond Pesticides.
Source: Quebec Environment Ministry Press Release (google translate)
Posted in Uncategorized by: Beyond Pesticides
No Comments
20
Feb
(Beyond Pesticides, February 20, 2018)¬†The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) finds that the U.S.  Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) label restrictions on total release foggers, otherwise known as ‚Äúbug bombs,‚ÄĚ are a public health failure. Bug bombs pose a significant risk of acute illness to individuals even when they attempt to follow new label instructions. Beyond Pesticides has long called for bug bombs to be banned, as there are a myriad of non-toxic alternative strategies to successfully manage household pests.
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) label restrictions on total release foggers, otherwise known as ‚Äúbug bombs,‚ÄĚ are a public health failure. Bug bombs pose a significant risk of acute illness to individuals even when they attempt to follow new label instructions. Beyond Pesticides has long called for bug bombs to be banned, as there are a myriad of non-toxic alternative strategies to successfully manage household pests.
Urge your Governor to ban bug bombs in your state!
Bug bombs are small cans primarily comprised of an insecticide, often a synthetic pyrethroid, a synergist such as piperonyl butoxide (PBO), and an aerosol propellant. In addition to the explosion/fire risk if the aerosol product is used in an unattended home near a pilot light or other spark-producing appliance, both synthetic pyrethroids and PBO pose acute and chronic human health risks. PBO is added to pesticide formulations to increase the toxicity of synthetic pyrethroids, and has been linked to childhood cough. Peer-reviewed research associates synthetic pyrethroids with behavioral disorders, ADHD, and delayed cognitive and motor development, and premature puberty in boys. Not only can bug bombs acutely poison, but once applied these chemicals can persist in the home for over a year, putting individuals and families at risk of chronic exposure and subsequent health issues.
CDC‚Äôs report, Acute Illnesses and Injuries Related to Total Release Foggers, updates a previous study released in 2008 with new data reveals that EPA‚Äôs attempt to reduce bug bomb illness and injury through label changes was unsuccessful. Looking at records from 2007-2015, a total of 3,222 unique cases of illness and injury were reported. The report indicates, ‚ÄúNo statistically significant reduction in overall incidence of TRF [total release fogger]-associated injuries and illnesses was observed in the first 3 years after the label revisions took effect.‚ÄĚ Incidents ranged from failing to leave an area after releasing the bug bomb, reentering the premises too early, use of too many products for the space provided, and even explosions related to the ignition of aerosols released from the product.
Urge your Governor to ban bug bombs in your state!
With EPA‚Äôs failure to protect people from the aptly named ‚Äúbombs,‚ÄĚ it is important for states to take action to protect citizens. If you have had problems with these products, please add your own experience to the suggested letter below.
Letter to Governor:
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) finds that EPA label restrictions on total release foggers, otherwise known as ‚Äúbug bombs,‚ÄĚ are a public health failure. Bug bombs pose a significant risk of acute illness to individuals even when attempting to follow new label instructions. There are a myriad of non-toxic alternative strategies to successfully manage household pests. Most common pest problems can be successfully dealt with by eliminating pest entryways into the home (i.e. caulking cracks/crevices, door sweeps, repairs, etc.), and sealing off access to food, water, and shelter (i.e. clean often, remove clutter, seal food in airtight containers, tight lid on trash can). Remaining pests can be dealt with through least-toxic products such as boric acid bait stations and desiccating dusts. (Use a mask when using these products.) Many pests, such as bed bugs, display widespread resistance to the pyrethroid insecticides contained in most bug bombs.
Several high profile incidents, including a 10-month-old boy in Williamston, SC who died after his mother used several bug bombs in their home, prompted EPA to conduct an evaluation of total release foggers, resulting in the ineffective label changes. The New York City Department of Health asked EPA to make these products restricted use, and the state of New York began moving toward similar actions at the state level, but to date no substantive restrictions have been placed on bug bombs by EPA.
Ventilation, as recommended by EPA, is not sufficient. The CDC report notes, ‚ÄúSome users ventilated treated premises for the recommended length of time or longer, but still became ill, suggesting that ventilation might be inadequate or the recommended period might be insufficient to fully eliminate TRF [total release fogger] residuals before occupancy.‚ÄĚ
Please protect our citizens from these dangerous ‚Äúbombs.‚ÄĚ Thank you.
Urge your Governor to ban bug bombs in your state!
Posted in ADHD, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Chemicals, Fumigants, Nervous System Effects, PBO, Piperonyl butoxide (PBO), Synthetic Pyrethroid, Take Action, Uncategorized by: Beyond Pesticides
No Comments
16
Feb

U.S. Rep. Earl Blumenauer (D-OR) discussing Saving America’s Pollinators Act.
(Beyond Pesticides, February 16, 2018) U.S. Representatives Blumenauer (D-OR) and Jim McGovern (D-MA) this week announced plans to reintroduce the Saving America’s Pollinators Act, (previously H.R. 3040) which suspends the registration of certain neonicotinoid insecticides until the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency conducts a full scientific review that ensures these chemicals do not harm pollinators. Beyond Pesticides joined Rep. Blumenauer and other experts from environmental, conservation, whistleblower and farmworker health groups on Capitol Hill to urge Congress to take action to protect pollinators in the face of ongoing obstruction by an increasingly industry-influenced EPA.
‚ÄúPollinators are the backbone of America‚Äôs agriculture system. Acting now to protect them and stop their decline is essential to the sustainability of our nation‚Äôs food supply,‚ÄĚ Rep. McGovern said. ‚ÄúSimply taking the word of the manufacturers that their products are safe is not an option. Consumers need strong oversight. That is why I am proud to join Congressman Blumenauer in demanding the EPA fully investigate the effect that certain harmful pesticides may have on the vitality of our pollinators.‚ÄĚ
Numerous scientific studies implicate neonicotinoid pesticides as key contributors to the global decline of pollinator populations. EPA’s own scientists have found that neonicotinoids pose far-reaching risks to birds and aquatic invertebrates. Last week, at the request of industry, EPA extended its comment period on preliminary ecological and human health risk assessments for the neonicotinoids clothianidin, thiamethoxam and dinotefuran, and a preliminary ecological risk assessment for the neonicotinoid imidacloprid. EPA’s risk assessments find deadly impacts to birds from neonicotinoid-treated seeds, poisoned insect prey, and contaminated grasses.
‚ÄúEPA‚Äôs recent assessment confirms what the science has already shown: that neonicotinoids are highly toxic not just to bees, but to aquatic species and birds. To protect our waterways and pollinators it is imperative that action be taken to ban these chemicals,‚ÄĚ said Nichelle Harriott, science and regulatory director at Beyond Pesticides.
University researchers have found that tiny amounts of neonicotinoids are enough to cause migrating songbirds to lose their sense of direction and become emaciated. A recent study by U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) researchers found neonics widespread in the Great Lakes at levels that harm aquatic insects, or the aquatic food web‚ÄĒthe foundation of healthy aquatic ecosystems.
‚ÄúThe health of our food system depends on the health of our pollinators. The status quo is like flying blind ‚Äď we shouldn‚Äôt be using these pesticides when we don‚Äôt know their full impact,‚ÄĚ said Rep. Blumenauer. ‚ÄúThe EPA has a responsibility to get to the bottom of this issue and protect pollinators.‚ÄĚ
Canada’s pesticide regulatory agency has recommended banning the most widely used neonicotinoid, imidacloprid, based on harms to aquatic ecosystems. Europe has instituted a temporary ban on neonicotinoids based on their harms to pollinators, and the European Commission recently proposed extending the ban indefinitely and eliminating all agricultural uses of the chemicals.
Given the ongoing obstruction by EPA leadership, however, Representatives Blumenauer and McGovern are offering a legislative remedy to address the national pollinator crisis. But Congress won’t act unless members hear from their constituents. Help push EPA to take substantive action on neonicotinoids by urging your Representative to support the Saving America’s Pollinators Act. With managed honey bee losses remaining at unsustainable levels and many wild pollinators at risk of extinction (1, 2, 3), it’s time, for the future of food and our environment, for the U.S. to finally protect pollinators.
Source: Representative Blumenauer Press Release
All unattributed positions and opinions in this piece are those of Beyond Pesticides.
Posted in Bayer, Clothianidin, dinotefuron, Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), Imidacloprid, neonicotinoids, Pesticide Regulation, Pollinators, Take Action, Thiamethoxam, Uncategorized by: Beyond Pesticides
No Comments
15
Feb
(Beyond Pesticides, February 15, 2018) The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) settled  claims against pesticide giant, Syngenta, after dozens of workers in Kuai, Hawaii were exposed to the neurotoxic pesticide chlorpyrifos in 2016 and 2017. EPA backed away from the $4.8 million settlement that it was initially seeking from Syngenta and negotiated a civil penalty of $150,000.
claims against pesticide giant, Syngenta, after dozens of workers in Kuai, Hawaii were exposed to the neurotoxic pesticide chlorpyrifos in 2016 and 2017. EPA backed away from the $4.8 million settlement that it was initially seeking from Syngenta and negotiated a civil penalty of $150,000.
Nineteen workers were exposed to chlorpyrifos after Syngenta sprayed the insecticide on a field of genetically engineered (GE) corn at its Kekaha farm. According to the complaint, the workers were allowed to reenter the field before the reentry period expired and without protective equipment. Ten workers were taken to the hospital and three were held overnight. This incident occurred in 2016, however a second incident occurred in 2017 when Syngenta failed to post warnings for worker crews containing 42 employees after applying chlorpyrifos. At the time of the incident, an inspector from the Hawaii Department of Agriculture (HDOA) was present on the Syngenta farm, which triggered an immediate investigation from the state. Consequently, a civil administrative enforcement action was brought against Syngenta seeking $4.8 million for violating multiple federal statues including worker protection standards, allegedly affecting as many as 77 workers and leading to the 388-count complaint. With maximum penalties as high as $19,000 per violation.
According to reports, the settlement, finalized last week, now amounts to about $387 per count. This is about three percent of the $4.8 million the EPA initially was seeking for the 2016 incident alone. Alexis Strauss, acting regional administrator for the EPA’s Region 9, acknowledged that the settlement was far less than the maximum allowed under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA) and its regulations designed to protect workers. In addition, EPA found that Syngenta failed to provide both adequate decontamination supplies on-site and prompt transportation to a medical facility for exposed workers.
Ms. Strauss said it ‚Äúwould be lovely‚ÄĚ if the EPA had been able to impose a higher penalty, but she added, ‚ÄúYou don‚Äôt get to settle with a company by getting the maximum amount for every violation.‚ÄĚ
In addition to the $150,000 penalty, Syngenta will also spend $400,000 on worker protection training sessions for growers under the agreement, and the company will develop a curriculum and training materials tailored to local growers who face pesticide compliance challenges related to language, literacy, geographic, and cultural factors.
Ms. Strauss, who has been with the EPA for 39 years, said the decision to back down from the stiff fine for Syngenta was not the product of politics, but rather a desire to reach a conclusion and help communities. But EPA‚Äôs new Administrator Scott Pruitt has made it clear he intends to severely limit the agency ability to protect the environment and people from pesticides and other contaminants. One of his first acts in office was to¬†rescind the proposal to ban chlorpyrifos in agriculture. This, despite findings and recommendations of¬†EPA‚Äôs own scientists and a 2016 Scientific Advisory Panel (SAP), claiming more evidence was needed. Mr. Pruitt and his team are aiming to reduce the staff of what was nearly 15,000 to below 8,000. Without adequate staff, thorough vetting and oversight of pesticides products and their impacts under FIFRA for their impact on human health and the environment is likely to suffer, while giving a free pass to the industry. Administrator Pruitt has also¬†issued a directive¬†banning scientists who receive grant funding from the EPA from serving on its advisory board. This leads an EPA to be more beholden to industry ‚Äúscience‚ÄĚ and its priorities of profit and unlimited pollution.
Chlorpyrifos is highly neurotoxic, organophosphate pesticide and the scientific literature is filled with evidence of chlorpyrifos’ impact on children’s developing brains and long-term impact on cognitive function, IQs and neurological disorders like ADHD and autism. Epidemiological data also points to subpopulations that are disproportionately affected by chlorpyrifos exposures. Low-income African-American and Latino families, including farmworker families, continue to suffer the most, and this disproportionate impact creates an environmental justice issue that the agency has ignored. A 2014 study conducted by the UC Davis Mind Institute also found that pregnant women who lived within a mile of fields where chlorpyrifos was sprayed more than tripled their chances of giving birth to a child with autism. Recently, researchers at the University of California, Santa Barbara, analyzing 500,000 birth observations, report that exposure to pesticides as a result of living in the agriculturally dominated San Joaquin Valley increases the risk of giving birth to a baby with abnormalities.
Native Hawaiian communities have spent nearly a decade long battle against multinational pesticide corporations on the islands. Data released in 2014 reveal that high levels of restricted use pesticides, in some cases almost double the pounds per acre average of other states, are being used in Kauai County. According to the Center for Food Safety, in 2014 alone, there were 1,381 field test sites in Hawaii, compared to only 178 sites in California, a large agricultural state. Most of these field test sites are used for crops genetically engineered to be herbicide-tolerant. Testing these crops means repeated spraying of dangerous chemicals in Native Hawaiian communities. Chemical companies continue to advocate for the status quo, which allows them to maintain current levels of pesticide use with little oversight.
Hawaii is now considering bills in the state House and Senate to ban chlorpyrifos, as well as a proposal to require farmers to notify the public when they use certain pesticides and to create buffer zones around some schools.
For more information on the history and background of the fight for sensible pesticide protections in Hawaii, see Beyond Pesticides’ Daily News Blog entries on the state.
Source: Civil Beat
Posted in Agriculture, Chlorpyrifos, contamination, Farmworkers, Syngenta by: Beyond Pesticides
No Comments
14
Feb
(Beyond Pesticides, February 14, 2018) Total release foggers, otherwise known as bug bombs,  received updated labels from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in 2011 as part of efforts to reduce accidental poisonings, but a new report from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) finds that EPA restrictions are a public health failure. Bug bombs pose a significant risk of acute illness to individuals even when attempting to follow new label instructions. Beyond Pesticides has long called for bug bombs to be banned, as there are a myriad of non-toxic alternative strategies to successfully manage household pests.
received updated labels from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in 2011 as part of efforts to reduce accidental poisonings, but a new report from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) finds that EPA restrictions are a public health failure. Bug bombs pose a significant risk of acute illness to individuals even when attempting to follow new label instructions. Beyond Pesticides has long called for bug bombs to be banned, as there are a myriad of non-toxic alternative strategies to successfully manage household pests.
CDC’s report, Acute Illnesses and Injuries Related to Total Release Foggers, updates a previous study released in 2008 which found significant safety concerns about bug bombs and ultimately prompted EPA to revise the labels of these products. At the time, CDC found a total of 466 illnesses or injuries associated with the use of total release foggers between 2001-2006. Incidents ranged from failing to leave an area after releasing the bug bomb, reentering the premises too early, use of too many products for the space provided, and even explosions related to the ignition of aerosols released from the product.
Bug bombs are small cans primarily comprised of an insecticide, often a synthetic pyrethroid, a synergist such as piperonyl butoxide (PBO), and an aerosol propellant. In addition to the explosion/fire risk, if the aerosol product is used in an unattended home near a pilot light or other spark-producing appliance, both synthetic pyrethroids and PBO pose acute and chronic human health risks. PBO is added to pesticide formulations to increase the toxicity of synthetic pyrethroids, and has been linked to childhood cough. Peer-reviewed research associates synthetic pyrethroids with externalizing and internalizing disorders, ADHD, and delayed cognitive and motor development, and premature puberty in boys. Not only can bug bombs acutely poison, but once applied these chemicals can persist in the home for over a year, putting individuals and families at risk of chronic exposure and subsequent health issues.
In response to the report and several high profile incidents, including a 10 month old boy in Williamston, SC who died after his mother used several bug bombs in their home, EPA conducted an evaluation of total release foggers. The agency determined at the time that incidents were ‚Äúoverwhelmingly minor in nature,‚ÄĚ resulting from ‚Äúa few basic errors‚ÄĚ and concluded that ‚Äúlabel improvements can mitigate these risks.‚ÄĚ This response was strongly criticized by Beyond Pesticides and other health groups, who called for increased education on alternative pest management strategies, and bans on the residential use of bug bombs by the general public. The New York City Department of Health asked EPA to make these products restricted use, and the state of New York began moving towards similar actions at the state level, but to date no substantive restrictions have been placed on bug bombs by EPA or any particular state.
CDC‚Äôs new data reveals that EPA‚Äôs attempt to reduce bug bomb illness and injury through label changes was unsuccessful. Looking at records from 2007-2015, a total of 3,222 unique cases of illness and injury were reported. The report indicates, ‚ÄúNo statistically significant reduction in overall incidence of TRF [total release fogger]-associated injuries and illnesses was observed in the first 3 years after the label revisions took effect.‚ÄĚ Reasons why changed little from the previous report, with CDC indicating the most reported causes were failure to vacate a treated premise, and early reentry.
Rather than clarify, EPA‚Äôs new labels may have caused more problems. For instance, EPA added pictures to the labels to show required steps. One step indicates that, after fogging, individuals should allow the premises to air out. However, the labels do not provide guidance on how to minimize exposure when ventilating, so many are injured during that process. And. as is too often the case, even following EPA‚Äôs new product labels did not eliminate illnesses. The CDC report notes, ‚ÄúSome users ventilated treated premises for the recommended length of time or longer, but still became ill, suggesting that ventilation might be inadequate or the recommended period might be insufficient to fully eliminate TRF [total release fogger] residuals before occupancy.‚ÄĚ
The continued poisoning and injury of individuals from bug bombs due to insufficient protections is a regulatory failure that EPA has repeated in numerous arenas. How has the agency attempted to address the pollinator crisis? New labels. Problems with Monsanto’s dicamba herbicide drifting onto other farm fields and damaging crops? New labels. Beyond Pesticides is calling for the establishment of an alternatives assessment within EPA. Under an alternatives assessment, when pesticides are found to have adverse effects on human health or the environment, focus shifts to employing less-toxic alternatives to their use, rather than attempting to mitigate risk by revising labels that very few read or adequately comprehend.
Before reaching for a bug bomb to manage household pests, consider the factors that led the pest into the building in the first place. Most common pest problems can be successfully dealt with by eliminating pest entryways into the home (i.e. caulking cracks/crevices, doorsweeps, repairs, etc.), and sealing off access to food, water, and shelter (i.e. clean often, remove clutter, seal food in airtight containers, tight lid on trash can). Remaining pests can be dealt with through least toxic products such as boric acid bait stations and desiccating dusts. Also remember that many pests, such as bed bugs, display widespread resistance to the pyrethroid insecticides contained in most bug bombs.
Beyond Pesticides ManageSafe webpage can assist with many common household and landscape pest problems to prevent the need to use toxic pesticides. For detailed information and specific pest questions individuals can call 202-543-5450 or email [email protected].
All unattributed positions and opinions in this piece are those of Beyond Pesticides.
Source: Morbidity and Mortality Weekly (CDC)
Posted in Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), PBO, Synthetic Pyrethroids, Uncategorized by: Beyond Pesticides
No Comments
13
Feb
 (Beyond Pesticides, February 13, 2018) Arguments by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to withhold from public and court review key documents revealing how it approved the first genetically engineered (GE) salmon were rejected by the Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals. Now, documents detailing how the agency reviewed and approved the GE animal will have to be produced for court review in the ongoing case challenging its controversial approval.
(Beyond Pesticides, February 13, 2018) Arguments by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to withhold from public and court review key documents revealing how it approved the first genetically engineered (GE) salmon were rejected by the Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals. Now, documents detailing how the agency reviewed and approved the GE animal will have to be produced for court review in the ongoing case challenging its controversial approval.
Thousands of pages of government documents pertaining to the 2015 approval of GE salmon for human consumption were being withheld even after plaintiffs challenging the approval demanded that FDA provide all the information the agency considered in its decision. The case, Institute for Fisheries Resources v. Burwell, Case No. 3:16-cv-01574-VC, brought by the Center for Food Safety (CFS) and Earthjustice on behalf the Institute for Fisheries Resources, Pacific Coast Federation of Fishermen’s Associations, Golden Gate Salmon Association, Kennebec Reborn, Friends of Merrymeeting Bay, Cascadia Wildlands, Ecology Action Center, Friends of the Earth, Center for Biological Diversity, Food and Water Watch, and the Quinault Indian Nation, was filed in 2016 after FDA approved its first-ever GE food animal, an Atlantic salmon engineered to grow quickly.
The lawsuit challenges FDA‚Äôs claim that it has authority to approve and regulate GE animals as ‚Äúanimal drugs‚ÄĚ under the 1938 Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. Those provisions were meant to ensure the safety of veterinary drugs administered to treat disease in livestock and were not intended to address entirely new GE animals that can pass along their altered genes to the next generation. Many are concerned that the approval of GE salmon opens the door to other GE animals like chickens, cows, sheep, goats, rabbits,¬† and pigs that are reportedly in development.
The plaintiffs demanded that FDA provide all of the documents the agency considered in its decision and last January, the lower court agreed. Several months later, FDA sought to overturn that decision by seeking a writ of mandamus from the appeals court, an extraordinary mechanism that is hardly ever used for routine document disputes. In its mandamus petition, the Trump Administration raised a dangerous argument, with severe ramifications for effective court review of government actions‚ÄĒthat defendant agencies can determine unilaterally what information to give to courts reviewing their decisions, and do not have to disclose any internal materials, even if the agency considered those materials in its decision. If adopted, this view would cause far-reaching damage to public review of agency decisions that have major impacts on everyday life.
‚ÄúOur courts provide a level playing field where not even the federal government is above the law,‚ÄĚ said Steve Mashuda, managing attorney for Oceans at Earthjustice and counsel in the case. ‚ÄúFederal agencies cannot avoid accountability by omitting inconvenient facts and presenting a fictional account of their decisions.‚ÄĚ
Last month, the Ninth Circuit agreed, issuing a short order denying the appeal. FDA will now have to produce the rest of the GE salmon documents. Last summer, the plaintiffs opposed FDA’s appeal, as did two dozen law professors who are experts on administrative and environmental law.
‚ÄúDictatorial secrecy is antithetical to democracy. This is a safeguarding win for government transparency, accountability, and meaningful judicial review of government decisions,‚Ä̬†said George Kimbrell, of CFS and counsel in the case.¬†‚ÄúWe look forward to the next stages of this case.‚ÄĚ
In approving the GE salmon, FDA determined it would not require labeling of the GE fish to let consumers know what they are buying. FDA’s approval also ignored comments from nearly 2 million people opposed to the approval because the agency failed to analyze and prevent risks to wild salmon and the environment, as well as fishing communities.
CFS notes that the lawsuit also highlights FDA’s failure to protect the environment and consult wildlife agencies in its review process, as required by federal law. U.S. Atlantic salmon and many populations of Pacific salmon are protected by the Endangered Species Act and in danger of extinction. Of concern is the risk of GE salmon escaping or accidental release into the environment. The new species could threaten wild populations by mating with endangered salmon species, outcompeting them for scarce resources and habitat, and/or introducing new diseases. There is a high risk for GE organisms to escape into the natural environment, and that GE salmon can crossbreed with native fish.
For more information on the human environmental hazards associated with GE technology, and national and local efforts to label GE food, visit Beyond Pesticides’ Genetic Engineering webpage.
All unattributed positions and opinions in this piece are those of Beyond Pesticides.
Source: Center for Food Safety
Posted in Federal Agencies, Genetic Engineering, Litigation by: Beyond Pesticides
No Comments
12
Feb
(Beyond Pesticides, February 12, 2018)¬† The most recent findings on the development of Parkinson‚Äôs disease after  exposure to the highly toxic paraquat add to the well-established body of scientific literature linking the herbicide to Parkinson‚Äôs ‚ÄĒ which should lead to finally eliminating the use of the herbicide in the U.S. The chemical was banned in the European Union in 2007, and many health groups, including Beyond Pesticides and The Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson‚Äôs Research, are calling on the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to stop the use of paraquat by denying its upcoming reregistration.
exposure to the highly toxic paraquat add to the well-established body of scientific literature linking the herbicide to Parkinson‚Äôs ‚ÄĒ which should lead to finally eliminating the use of the herbicide in the U.S. The chemical was banned in the European Union in 2007, and many health groups, including Beyond Pesticides and The Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson‚Äôs Research, are calling on the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to stop the use of paraquat by denying its upcoming reregistration.
In addition to its connection with Parkinson‚Äôs disease, paraquat is known to be highly acutely toxic. By generating free radicals, it essentially burns its way through the body, targeting the lungs ‚ÄĒcausing lung fibrosis‚ÄĒ and other organs. Most acutely toxic exposures result in death, sometimes delayed by as much as three weeks.
Although paraquat is a restricted use pesticide (RUP), EPA is proposing to eliminate the minimum age for applying RUPs, which would permit teenagers to use it.
Tell EPA and Congress to ban paraquat! This link will send the following message to EPA and your Congressional delegation:
I urge EPA to join other countries in banning the use of paraquat.
Recent research confirms paraquat’s link to Parkinson’s disease. Parkinson’s disease, which affects an estimated 750,000 to one million Americans, is a chronic and progressive neurodegenerative brain disorder caused by a loss of neurons and dopamine, the neurotransmitter they produce. There is currently no cure or therapy to slow, stop, or reverse the progression of the disease.
Research linking Parkinson’s disease with exposure to paraquat has been mounting for years. Last month, in the journal Cell Reports (Chinta, et al.) reported that exposure to paraquat induces senescence of cells (loss of the cells’ power), which may account for paraquat’s neurotoxicity. Other recent studies show:
- exposure to paraquat increases the likelihood of Parkinson’s disease;
- the effect is dose dependent; and
- the risk increases when combined with other factors, such as genetic disposition and exposure to other pesticides.
The economic ‚ÄĒ and emotional ‚ÄĒ costs of living with Parkinson‚Äôs are too high to allow the continued use of a chemical so strongly linked to the disease. The cost of providing care in the U.S. for a person with Parkinson‚Äôs is conservatively $26,400 per year, resulting in an annual economic burden of $19.8 to $26.4 billion.
In addition, paraquat’s acute toxicity has long been a concern. There is no antidote, and paraquat causes thousands of deaths annually, mostly by pulmonary fibrosis. By generating free radicals, it essentially burns its way through the body, targeting the lungs and other organs. Most acutely toxic exposures result in death, sometimes delayed as much as three weeks.
Please join with 32 other countries in banning the use of this dangerous pesticide.
Thank you.
Tell EPA and Congress to ban paraquat!
All unattributed positions and opinions in this piece are those of Beyond Pesticides.
Posted in Agriculture, Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), Paraquat, Take Action, Uncategorized by: Beyond Pesticides
No Comments
09
Feb
(Beyond Pesticides, February 9, 2018) Attorneys General in eleven states join Monsanto and the  National Wheat Growers Association last month in challenging California’s listing of glyphosate as a carcinogen under the state’s Proposition 65 law. California added glyphosate to the list of cancer-causing chemicals in July 2017, but has since been attacked by Monsanto and its allies for carrying out state law that requires carcinogens to be labeled and monitored.
National Wheat Growers Association last month in challenging California’s listing of glyphosate as a carcinogen under the state’s Proposition 65 law. California added glyphosate to the list of cancer-causing chemicals in July 2017, but has since been attacked by Monsanto and its allies for carrying out state law that requires carcinogens to be labeled and monitored.
The plaintiffs, led by the National Association of Wheat Growers, argue that listing glyphosate as a carcinogen under Prop 65 will irreparably harm the agriculture industry, adversely affecting farmers and consumers throughout the U.S. The case, seeking a stay of the listing, was filed in the in Federal Court in the Eastern District of California in November, 2017. Earlier last year, Monsanto lost its case before a state Superior Court in which it sought to stay the Prop 65 listing.
Idaho, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Louisiana, Michigan, Missouri, North Dakota, Oklahoma, South Dakota and Wisconsin have filed an amicus brief in support of the preliminary injunction sought by agriculture groups against California’s Prop 65 regulation. The U.S. Chamber of Commerce and the California Chamber of Commerce filed their own amicus brief in support of the preliminary injunction to halt the regulation. (Nat‚Äôl Ass‚Äôn of Wheat Growers, et al. v. Zeise, et al., No. 2:17-cv-02401WBS). In their amicus brief, states point out that California‚Äôs Prop 65 mandates impede the duty of states to protect their own citizen-consumers as well as states‚Äô economic freedoms to stimulate growth, and ‚Äúencroaches on the equal sovereignty of other States‚ÄĚ
According to Lexology, the plaintiffs are arguing (1) that the First Amendment prohibits the government from compelling individuals or entities to engage in speech; and (2) that the Supremacy Clause requires state laws that conflict with federal laws to be preempted. Labeling for glyphosate is governed by certain federal regulations implemented and enforced by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). They have requested that the federal court declare California’s action to be improper and enjoin the state from continuing to list glyphosate as a chemical that requires a Prop 65 warning.
Further, Monsanto and the agricultural interests allege that they are already being adversely affected by the decision, but state officials maintain that there is no need to issue a preliminary injunction on the listing, rejecting the allegation that they are already being adversely impacted by the decision. Monsanto, the chemical giant that makes glyphosate (Roundup), requested the state reconsider its listing but was rejected last summer.
Under the Labor Code listing mechanism of Proposition 65, substances identified by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) must be listed in the state of California as known to cause cancer. This listing requires warning labels on products and the listed substances are subject to limits on discharges into surface waters. In March 2015, IARC found that there was sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity in experimental organisms to classify glyphosate as ‚Äúprobably carcinogenic to humans‚ÄĚ (Group 2A).
Industry has since challenged IARC‚Äôs finding, arguing that it is an outlier as an “overwhelming majority of government regulators and other experts” have found glyphosate is not carcinogenic and have “flatly rejected” IARC’s conclusion. In its request for a preliminary injunction, industry argues that they are facing “imminent harm” from the warning label requirements. The state rejects that claim, noting that the requirements will not enter into effect until July 2018 and that it has yet to determine which products will have to be labeled. The plaintiffs may speculate that a Prop 65 warning requirement will cause “an array of harm, from loss of reputation to disruption of food supply and private enforcement litigation” but their “sky-is-falling speculations” do not justify a preliminary injunction. The state agency adds that¬†Prop 65 does not “dictate the text of the warning,” providing companies the right to “tailor to its individual situation” and to “place the cancer risk in context” for the public.
Monsanto has been trying to undermine findings that show its flagship product, glyphosate, is anything other than ‚Äúsafe.‚ÄĚ However, its attempts to unduly influence and undermine scientific research and government review of its product has been disclosed widely in the press. This has prompted the European Parliament to set up a special committee to look into the¬†European Union‚Äôs (EU) authorization procedure for pesticides, in light of their recent controversial review of glyphosate. It was reported that the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA)¬†copied dozens of pages from a Monsanto¬†study in¬†reaching its conclusion that glyphosate is ‚Äúunlikely to pose a carcinogenic hazard to humans.‚Ä̬†EFSA‚Äôs recommendation was supposed to provide an independent analysis for EU member states when deciding to renew the chemical. Last year, the¬†European Parliament banned Monsanto lobbyists¬†from committee¬†meetings and digital resources, as well as prohibiting Monsanto lobbyists from meeting with any Member of the European Parliament.¬†This was an attempt to limit Monsanto‚Äôs influence on the EU review process amid mounting public pressure. Similarly, The¬†New York Times¬†reported on Monsanto‚Äôs internal emails¬†and email traffic between the company and U.S. federal regulators that suggested that Monsanto had ghostwritten research on glyphosate, which was later attributed to academics.¬†In December 2017, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA),¬†declared that glyphosate is likely not carcinogenic, conflicting with IARC‚Äôs 2015 classification. Some charge that EPA‚Äôs assessment relied heavily on industry studies to arrive at its conclusion, and ignored its own guidelines for assessing cancer risks.
In California, the Court is set to hear arguments on the motion on February 20th.
Fight back against Monsanto’s attempt to undermine the scientific and democratic process by getting involved at the local level. Work to pass policies that restrict not only glyphosate, but the entire range of toxic synthetic pesticides registered by EPA. Beyond Pesticides has resources to help you get started, including an organizing guide, model policy, and list of less toxic, organic compatible products. For more information on IARC’s glyphosate cancer classification and the IARC review process, see Beyond Pesticides’ article in our journal Pesticides and You.
Source: The Fence Post, Legal Scoops
Posted in Agriculture, California, Cancer, Glyphosate, Uncategorized by: Beyond Pesticides
No Comments
08
Feb
 (Beyond Pesticides, February 8, 2018) New trials are being launched in the United Kingdom (UK) to monitor fields that have long strips of wildflowers planted through croplands to boost natural predators and potentially reduce pesticide spraying. The large-scale trials are meant to determine how effective these strips can be as a tool for practitioners wishing to enhance biological pest control in the field.
(Beyond Pesticides, February 8, 2018) New trials are being launched in the United Kingdom (UK) to monitor fields that have long strips of wildflowers planted through croplands to boost natural predators and potentially reduce pesticide spraying. The large-scale trials are meant to determine how effective these strips can be as a tool for practitioners wishing to enhance biological pest control in the field.
The field trials, carried out by the Centre for Ecology and Hydrology (CEH), are being conducted on 15 large arable farms in central and eastern England and would be monitored for five years. Until now, wildflower strips have been placed at the edge of fields as refuges. However, natural predators in these strips would be unable to access the center of large planted fields, and thereby unable to effectively target pests that are in the fields. In the new trials, six-meter wide strips of annual wild and cultivated plants – with 13 to 16 species – will be planted 100 meters apart so that predators will be able to attack aphids and other pests typically found in fields.
The researchers at CEH’s ASSIST program (Achieving Sustainable Agricultural Systems) will determine whether in-field strips are feasible tools for practitioners wishing to enhance biological pest control in the field. The most important focus is on supporting diverse communities of predatory and parasitic insects that kill pests. Research increasingly suggests that complex communities of predators and parasitoids are the most effective at controlling pests. Researchers will also be looking out for any sign that drawing the wild insects into the center of fields, and therefore closer to where pesticides are sprayed does more harm than good.
Resources provided by in-field strips and normal field margins benefit the greatest diversity of important predators. According to Ben Woodcock, PhD, ecological entomologist at CEH, sowing specific grasses and wildflowers in the field can support predators in the crop canopy or those that target internal pests living in stems or seed pods. Many parasitic wasps, for instance, need access to open flowers so that they can feed on pollen and nectar. Without this resource, the number of eggs they can lay is dramatically reduced and with it pest control.
Concern over the environmental damage caused by pesticides has grown rapidly in recent years, especially with the drastic decline in pollinator populations. Using wildflower margins to support insects including hoverflies, parasitic wasps and ground beetles have been shown to slash pest numbers in crops and even increase yields. Similar fields are underway in other parts of Europe where flowers such as cornflowers, coriander, buckwheat, poppy and dill are planted in strips. According to reports, densities of leaf beetle pests in fields of winter wheat were 40 to 53% lower than when no flower strips were sown. This low pest pressure even resulted in a 61% reduction in damage to the wheat plants.
Strips of flowering plants, especially with plants attractive to beneficial insects like pollinators, have been used to increased biodiversity on farms and provide refuge for these insects. Flower strips are also designed to provide early season pollen and nectar resources for important crop pollinators, such as bumblebees and solitary bees. In this respect, they provide dual benefits ‚Äď enhanced natural pest control and crop pollination. In order for annual flower strips for beneficials to be fully maximized, it is important for them to be well integrated into linked perennial habitats with hedgerows, low-input meadows and wildflower strips, and secondly, for them to be combined with a management approach that protects beneficials. This also means protecting them from harmful pesticides. Previous research has shown that hedgerows improve a farm‚Äôs ecology and reduce the need for pesticides. Read Beyond Pesticides‚Äô Hedgerows for Biodiversity: Habitat is needed to protect pollinators, other beneficial organisms, and healthy ecosystems.
Dr. Woodcock notes that strips can be easy to manage and readily re-established in another field or location in the same field. With GPS-linked farm machinery allowing the exact location of these strips to be known, this can reduce the chances of accidental spraying of the strips.
To attract beneficial insects and protect their habitats in your own backyard, there are several steps you can take. Like any other living organism, pollinators need food, water, and shelter in order to thrive. For more information, see Managing Landscapes with Pollinators in Mind
Source: The Guardian, CEH Blog
Posted in Agriculture, Beneficials, Biodiversity, Biological Control by: Beyond Pesticides
No Comments
07
Feb
(Beyond Pesticides, February 7, 2018) New data from the California monarch butterfly count indicate that the western  population of the species is continuing to decline at an alarming rate, with scientists and conservation groups pointing to man-made factors like logging, climate change, and herbicide use on genetically engineered (GE) crop fields as primary drivers. The annual California count of western monarch butterflies stationed volunteers at 262 sites, more than ever before, yet at 200,000 butterflies counted, the numbers nearly matched the lowest level recorded this decade, when only 145,000 butterflies were seen in 2012. The decline of these iconic butterflies demands swift action from lawmakers and regulators to protect their dwindling numbers.
population of the species is continuing to decline at an alarming rate, with scientists and conservation groups pointing to man-made factors like logging, climate change, and herbicide use on genetically engineered (GE) crop fields as primary drivers. The annual California count of western monarch butterflies stationed volunteers at 262 sites, more than ever before, yet at 200,000 butterflies counted, the numbers nearly matched the lowest level recorded this decade, when only 145,000 butterflies were seen in 2012. The decline of these iconic butterflies demands swift action from lawmakers and regulators to protect their dwindling numbers.
Dramatic declines in monarch populations mirror continuing declines in honey bees and other wild pollinator species. Species declines may be even broader than pollinators, affecting all insects in general. Research from Germany recently found that insect abundance declined 75% over the last 30 years, owing the results primarily to agricultural intensification.
The western population of monarch butterflies ‚Äď those found west of the Rocky Mountains ‚Äď overwinter in coastal California forests. Throughout the warmer months, female butterflies will lay eggs only on milkweed, making these plants critical to the survival of the species. Adults forage on nectar from a range of flowers in Arizona, California, Idaho, Nevada, Oregon, Washington, and Utah, before returning back to their forest groves for the winter.
According to past data from the Xerces Society, which began its annual monarch count in 1997, at that time over 1.2 million monarch butterflies were found to overwinter in California’s central coast. When compared to the count that took place just one year before in 2016, western monarch numbers are down by 100,000 butterflies.  In the 1980s, over 10 million monarchs spent the winter in California forestland.
A study conducted by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service last year on the butterfly‚Äôs dwindling population indicates that western monarchs have an extinction risk of 86% within the next 50 years. Within only 20 years, the risk is still 72%. ‚ÄúThis study doesn‚Äôt just show that there are fewer monarchs now than 35 years ago,‚ÄĚ said study author Cheryl Schultz, PhD, an associate professor at Washington State University Vancouver. ‚ÄúIt also tells us that, if things stay the same, western monarchs probably won‚Äôt be around as we know them in another 35 years.‚ÄĚ
Eastern monarch populations have also been declining over the past several decades. A 2017 study by the World Wildlife Fund and other conservation groups determined that the population has decreased by 80% since the 1990s, further warning that within 20 years eastern monarch’s iconic migration route from Canada to Mexico could completely, and likely irreversibly, collapse.
A range of factors have been linked to monarch declines. Natural events such as extreme weather, wildfires and smoke have been discussed, but a greater emphasis has been placed on manmade impacts. Climate change can alter the migration patterns. Legal and illegal logging and development in Mexico and coastal California has eliminated significant habitat for monarch overwintering. And milkweed, the sole source for female monarchs to lay eggs and perpetuate the species, once abundant throughout the entirety of the United States, is now nearly eradicated around farmland through which the species makes its annual migration.
Those wishing to support their local monarch populations can find sources of milkweed for their particular climate by visiting the Xerces Society milkweed seed finder.  Individual residents taking action is a critical part of the long-term solution for monarchs, but broader changes in land-use and agriculture are needed to ensure that these species will still be around for another 50 years.
GE crops, able to tolerate repeated sprayings of a particular herbicide, whether glyphosate, dicamba, or 2,4-D, are making the edges and roadsides around farm fields where milkweed often grows desolate, lifeless areas. Further compounding a lack of milkweed is the additional use of insecticides on these fields. Chemical company encourage farmers to use systemic neonicotinoids to coat the outer layer of their GE seeds in an unnecessary attempt to protect it from pests. Unfortunately, both herbicides and insecticides don’t stay where they’re originally applied. Herbicide use on GE-tolerant crops drift and kill milkweed and other plants pollinators rely on. Coated seeds will often drift during planting, or run-off into soil and groundwater afterwards, contaminating these same pollinator-friendly plants.  Research published in 2015 found that milkweed contamination from drifting neonicotinoids made the plants toxic to larvae which rely on it as its sole source of food once hatched.
Changing the way we farm can make an immense difference for the protection of monarchs and other pollinators. Help pollinators by only purchasing products that don’t allow GE crops or toxic systemic insecticides. Certified organic agricultural practices successfully produce profitable yields while managing to not poison the air, water, soil, vegetation, and other wildlife around their farm.
But changing agriculture also requires additional authority to institute protections for these important pollinators. Take action today! Tell the National Resource Conservation Service to significantly increase the amount of funding spent on monarch conservation and the habitat restoration, and ensure that restored habitat is not poisoned with hazardous pesticides.
All unattributed positions and opinions in this piece are those of Beyond Pesticides.
Source: Xerces Society, Reuters
Posted in Uncategorized by: Beyond Pesticides
No Comments
06
Feb
(Beyond Pesticides, February, 6, 2018) Scientists, doctors, and environmental groups are pushing back against the  Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) efforts to purge academic scientists who had previously received EPA grants from sitting on the agency’s advisory committees. Last October, EPA issued a new policy that changes the makeup of its advisory boards by limiting the participation of scientists from academia and nonpartisan nonprofit organizations. Critics say the change attempts to fill these advisory committees with more industry-friendly officials whose belief systems are anti-environmental protection. On January 23, 2018, a group of scientists filed suit against EPA, citing the directive as arbitrary, without any factual or legal grounding and in violation of the Federal Advisory Committee Act, which requires advisory committees to be fairly balanced and protected from inappropriate influence by the appointing authority.
Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) efforts to purge academic scientists who had previously received EPA grants from sitting on the agency’s advisory committees. Last October, EPA issued a new policy that changes the makeup of its advisory boards by limiting the participation of scientists from academia and nonpartisan nonprofit organizations. Critics say the change attempts to fill these advisory committees with more industry-friendly officials whose belief systems are anti-environmental protection. On January 23, 2018, a group of scientists filed suit against EPA, citing the directive as arbitrary, without any factual or legal grounding and in violation of the Federal Advisory Committee Act, which requires advisory committees to be fairly balanced and protected from inappropriate influence by the appointing authority.
In 1978, Congress directed the EPA to establish the Science Advisory Board, which today is a 47-member panel, to provide scientific advice to the Administrator. EPA Administrator Scott Pruitt announced in October that he would exclude anyone from serving on any of the 23 EPA scientific advisory boards if they had received EPA grants to fund any of their research. Administrator Pruitt claims the policy change will prevent conflicts of interest. But, his decree means that the agency’s decision makers will not receive input from top scientific experts, many of whom rely on public grants to conduct independent studies.
The lawsuit explains that open exchange of accurate scientific information is a touchstone of a functioning¬†democracy, and contends that the Administrator failed to explain why scientists and experts who receive similar funding from other sources ‚ÄĒ scientists affiliated with private industry or local governments ‚ÄĒ fall outside the scope of the purge. In singling out academic members of the scientific community who are receiving EPA grants, EPA‚Äôs directive ‚Äúlays bare its real function: to stack the deck against scientific integrity.‚ÄĚ The lawsuit asks the court to overturn Pruitt‚Äôs directive and prevent EPA staff from implementing the directive.
‚ÄúThis is an abuse of power and an affront to the scientific integrity of the EPA and the federal government,‚ÄĚ said Joshua Goldman, senior legal analyst for the Union of Concerned Scientists.¬†‚ÄúThis directive singles out scientists from the nonprofit and academic sector‚ÄĒrecognized experts in their field who want to serve the public‚ÄĒand asks them to choose between public service and their scientific work. It‚Äôs another example of this administration‚Äôs hostility to independent scientific input and basing policy on impartial and balanced scientific evidence. The directive inherently prevents the agency from receiving independent scientific advice, and erects unnecessary barriers to scientists who want to use their expertise to serve the public.‚ÄĚ
The lawsuit was filed in the U.S. Court for the District of Massachusetts by Protect Democracy, a nonpartisan nonprofit organization, and the law firm Jenner & Block, representing the Union of Concerned Scientists and Dr. Elizabeth A. (Lianne) Sheppard, professor at the University of Washington, School of Public Health.
This lawsuit comes one month after Earthjustice¬†filed a similar complaint¬†on behalf of Physicians for Social Responsibility, National Hispanic Medical Association, and the International Society for Children‚Äôs Health and Environment, challenging EPA‚Äôs attempt to remove scientists from the agency‚Äôs advisory committees. Earthjustice‚Äôs suit argues that the policy illegally overrides federal ethics rules and that it is arbitrarily biased in favor of corporate interests. Advisors picked by Administrator Pruitt to join the advisory boards, like Robert Phalen, once claimed that ‚Äúmodern air is a little too clean for optimum health.‚ÄĚ Such advisors will inevitably tilt EPA decisions and programs in favor of polluters. Another Science Advisory Board appointees include a new chair, Michael Honeycutt, who has claimed that more smog would be a ‚Äúhealth benefit.‚ÄĚ As the lead toxicologist on Texas‚Äô state environmental agency, he has opposed stricter limits on mercury and arsenic releases and undermined protections for benzene, a common and powerful carcinogen
The EPA‚Äôs Science Advisory Board now¬†includes¬†14 new members who¬†consult or work¬†for the fossil fuel or chemical industries, which gave sizeable campaign contributions to Administrator Pruitt when he was an Oklahoma state senator and attorney general, according to the Union of Concerned Scientists.¬† Science advisory boards also play a crucial watchdog role. Scientists from across the country from diverse backgrounds are relied on the review and provide council to EPA programs and decision-making, ensuring the science is robust, transparent and sufficiently assessed to provide adequate protections for the environment. According to Earthjustice, since 2012, industry allies in Congress have¬†repeatedly proposed legislation¬†that would prohibit scientists from serving on the boards if they receive EPA grants. Industry understands that academic experts rely upon these grants to a much greater extent than industry consultants do. Much of the grant money goes to support graduate students who conduct academic research while earning paltry stipends‚ÄĒ$24,000 per year¬†is typical. If academics must choose between receiving EPA grants and continuing to serve on science advisory boards, the choice they really face is whether to continue funding students. Unsurprisingly, many teachers are committed to their students and will choose to leave the boards rather than decline funding. Pruitt then can replace them with industry allies.
These changes to EPA’s science advisory boards in just one of a host of measures aimed at dismantling the agency and opening the gates for an industry take over. While environmentalists and public health experts have criticized EPA for lax or inadequate regulation, the administrator has been getting rid of EPA scientists and staff and attacking public health and the environment through proposed budget cuts by the Trump administration.
Source: Earthjustice, Think Progress
All unattributed positions and opinions in this piece are those of Beyond Pesticides.
Posted in Uncategorized by: Beyond Pesticides
No Comments
05
Feb
(Beyond Pesticides, February 5, 2018)¬†We are all concerned about the workers  who grow and harvest our food. A sustainable food system must protect the land and the people who work the land, including the children and families of farmworkers. In two related actions, EPA is proposing to remove age requirements for application of pesticides. The actions involve changes to the Agricultural Worker Protection Standard (WPS), which went into effect this January and covers farmworkers hired to apply pesticides, and the Certification of Applicators (CA) rule, which will go into effect May 22 and covers those allowed to apply highly toxic restricted use pesticides (RUPs), the most toxic pesticides. The proposals to remove the age requirements present unacceptable risks to teenagers, who ‚Äúare still developing in critical physical and emotional areas, with particular regard to their brains and reproductive systems,‚ÄĚ according to the American Academy of Pediatricians (AAP).
who grow and harvest our food. A sustainable food system must protect the land and the people who work the land, including the children and families of farmworkers. In two related actions, EPA is proposing to remove age requirements for application of pesticides. The actions involve changes to the Agricultural Worker Protection Standard (WPS), which went into effect this January and covers farmworkers hired to apply pesticides, and the Certification of Applicators (CA) rule, which will go into effect May 22 and covers those allowed to apply highly toxic restricted use pesticides (RUPs), the most toxic pesticides. The proposals to remove the age requirements present unacceptable risks to teenagers, who ‚Äúare still developing in critical physical and emotional areas, with particular regard to their brains and reproductive systems,‚ÄĚ according to the American Academy of Pediatricians (AAP).
Tell your Congressional delegation that EPA must not eliminate the minimum age requirement.
Under the Obama administration, EPA added a minimum age requirement of 18 to both rules. A 16-year-old may apply RUPs under the supervision of a certified applicator under the CA rule. Reportedly, the reason for removing the age requirement is that ‚Äúteenagers often work for less money than older employees.‚ÄĚ
The removal of the age requirement is opposed by farmworker and children’s health advocates. Farmworker Justice applauded the new rule, including the age requirement, then sued EPA to implement the rule earlier this year. AAP points out that dangers of pesticide exposures to teens include long-term damage to nervous and reproductive systems. It also points out that 16 to 17-year-old workers in other industries are prohibited from working with hazardous chemicals.
At a U.S. Senate oversight hearing last week, New Jersey Senator Cory Booker blasted EPA Administrator Scott Pruitt for his lack of concern over environmental justice issues. In particular, Sen. Booker noted the proposal to drop the minimum age requirement for agricultural workers who can use pesticides. Many of these workers, Sen. Booker noted, come from “communities of color, indigenous communities and low income communities.” When Sen. Booker asked, “Do you think that children handling dangerous pesticides is a good idea?” Mr. Pruitt responded ‚Äďas he had to other Senators‚Äô questions‚ÄĒby changing the subject.
Tell your Congressional delegation that EPA must not eliminate the minimum age requirement.
All unattributed positions and opinions in this piece are those of Beyond Pesticides.
Posted in Agriculture, Environmental Justice, Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), Farmworkers, Uncategorized by: Beyond Pesticides
No Comments
02
Feb
(Beyond Pesticides, February 2, 2018) California regulators may be  drastically underestimating chemical-intensive agriculture’s contribution to nitrogen oxide (NOx) caused air pollution, acid rain, and respiratory illness in the state, according to a new study published in Science Advances by researchers at University of California, Davis. While NOx  pollution is usually associated with energy production and vehicle emissions, fertilizer use on crop fields is contributing to significant air pollution problems. Advocates say that the study is an urgent call for farmers to eliminate dependency on soluble, synthetic, nitrogen-based fertilizers and adopt the use of insoluble soil amendments that support soil biology that provide plants with nutrients.
drastically underestimating chemical-intensive agriculture’s contribution to nitrogen oxide (NOx) caused air pollution, acid rain, and respiratory illness in the state, according to a new study published in Science Advances by researchers at University of California, Davis. While NOx  pollution is usually associated with energy production and vehicle emissions, fertilizer use on crop fields is contributing to significant air pollution problems. Advocates say that the study is an urgent call for farmers to eliminate dependency on soluble, synthetic, nitrogen-based fertilizers and adopt the use of insoluble soil amendments that support soil biology that provide plants with nutrients.
NOx gasses are major sources of pollution in the U.S. and throughout the world, and include the compounds nitrogen oxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2). Chemical-intensive, synthetic nitrogen fertilizers are applied in a form that is readily available to plants, while organic nitrogen fertilizers require the biological life in the soil to break down the fertilizer into a form that plants can use. These nitrogen fertilizers that are not immediately taken up by plants can cause pollution problems. Natural nitrogen in the atmosphere must be transformed to be able to be used by organisms as a source of nutrients through a range of biological factors in the soil. However, the pollution associated with the production of synthetic fertilizers that requires petroleum or natural gas, increasingly from fracking, and the introduction of synthetic nitrogen and other pollutants into the atmosphere contributes to environmental degradation, asthma, and other public health problems..
While some fertilizer not taken up by crops will eventually turn into harmless nitrogen (N2), other amounts can become hazardous nitrogen oxide gasses. Once out of soil and into the atmosphere, NOx gasses react with moisture, sunlight, and other chemicals to form pollution. The gasses can combine with other chemicals in the air to form particulate matter able to deeply penetrate and harm human lungs, create acid rain when interacting with water, and form haze that decreases visibility. A 2014 report from the World Health Organization indicates that 1 in 8 total global deaths, around 7 million people each year, die prematurely as a result of exposure to air pollution.
The results of this study stand in stark contrast to the state’s current estimation of NOx  emissions from farmland soil. While the California Air Resources Board (CARB) indicates only 3.8% of NOx air pollution comes from croplands, researchers determined that the contribution may in fact be between as much as 20 to 51%.
The study suggests that the state’s methodology for recording cropland emissions may be at fault. CARB measures emissions using data obtained from farms only within 125 miles of Sacramento, thus failing to record higher NOx levels that emanate from areas with more intense agricultural production, such as California’s Central Valley.
Researchers took both a ‚Äútop-down‚ÄĚ and ‚Äúbottom-up‚ÄĚ approach to measuring NOx emissions. As part of the ‚Äútop-down‚ÄĚ approach, planes outfitted with scientific equipment took measurements of NOx emissions over California‚Äôs San Joaquin Valley, between Fresno and Visalia, a hotbed for agriculture and an area where some of the highest amounts of nitrogen fertilizer is applied. As part of the ‚Äúbottom-up‚ÄĚ approach, researchers compared results seen from direct measurements over the San Joaquin Valley to a model developed for the same region. The model created by researchers produced estimates only slightly higher than those discovered via plane measurements. Researchers then looked at NOx emissions compared to nitrogen application rates recorded by the state of California and the U.S. Department of Agriculture, finding that high rates of nitrogen fertilizer use in lined up neatly with high levels of NOx emissions.
Researchers determined that temperature, soil moisture, and the amount of nitrogen applied are the most significant factors in whether a soil will release NOx or inert forms of N2. Higher temperatures, more arid soil, and higher nitrogen fertilizer application rates act as the greatest risk factors for NOx emissions. However, the UC Davis scientists provided a range of suggested practices that farmers can implement to reduce harmful emissions. Lower application rates and precision fertilization, rather than broadcast applications, can help reduce excess nitrogen input into soils. Cover crops, and the creation of riparian areas around farmlands can help absorb residual nitrogen. Greater attention to irrigation practices can also ensure that inorganic nitrogen in the soil is not converted into nitrogen oxides. In organic farming systems, the nurturing of microbial activity in the soil food web (a feed-the-soil system) produces slow release nutrients including nitrogen that is taken up by he plants.
With population continuing to increase lock-step with demand for food, unless measures are taken to conserve nitrogen use, this trend is likely to accelerate. The good news is that many of these practices that support the soil food web are already being used on certified organic farms. And given the significance of this study, conventional farmers have a greater incentive to implement them as well. Speaking with the Fresno Bee, Jim Houston of the California Farm Bureau Federation said, ‚ÄúFarmers have a long history of adjusting their practices in response to emerging science, and we will watch to see if further studies verify the results reported here. It‚Äôs important to note that most of the steps the study suggests are already underway. Farmers want to use the appropriate amounts of fertilizer and have long relied on expertise from the University of California in making those applications.‚ÄĚ
While the study focused on agricultural applications of nitrogen, imprudent use of the fertilizer on garden, lawns, and landscapes also can represent a significant source of non-point nitrogen pollution. For these areas, focus first on cultural practices, and if fertilizer is needed based on a soil test, use Beyond Pesticides list of organic certified fertilizers to choose a soil amendment that, in an organic system, is not likely to result in pollution problems. And to support a healthier future for farming and safer, cleaner air for those living in and around agricultural communities, support organic practices by buying organic.
All unattributed positions and opinions in this piece are those of Beyond Pesticides.
Source: Science Advances, Fresno Bee, ScienceNews,
Posted in Agriculture, Alternatives/Organics, Fracking, Respiratory Problems, Uncategorized by: Beyond Pesticides
No Comments
01
Feb
(Beyond Pesticides, February 1, 2018) Scientists at the European Institute  for the Biology of Aging are finding new information about how Parkinson’s disease manifests itself after exposure to the herbicide paraquat, in hopes of finding ways to prevent the progression of the disease. Despite a well-established body of scientific literature linking the paraquat to Parkinson’s, and a ban on the use of the chemical in the European Union that dates back to 2007, its use is still permitted in the U.S. Many health groups, including Beyond Pesticides and organizations like the Michael J Fox Foundation are calling on the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency stop the use of paraquat by denying its upcoming reregistration.
for the Biology of Aging are finding new information about how Parkinson’s disease manifests itself after exposure to the herbicide paraquat, in hopes of finding ways to prevent the progression of the disease. Despite a well-established body of scientific literature linking the paraquat to Parkinson’s, and a ban on the use of the chemical in the European Union that dates back to 2007, its use is still permitted in the U.S. Many health groups, including Beyond Pesticides and organizations like the Michael J Fox Foundation are calling on the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency stop the use of paraquat by denying its upcoming reregistration.
Published in the journal Cell Reports, this new research on Parkinson‚Äôs investigates the impact of ‚Äúsenescent‚ÄĚ cells in the body. Senescent cells are those which, despite being able to divide, stop doing so in response to stress. This is an anti-cancer mechanism, as stress would otherwise cause the cells to multiply unchecked and create malignancies. Researchers suspected that despite the benefit of stopping cancer, senescent cells may be causing other problems in the body. Rather than dying, these cells can cause inflammation in the area around where the cell became senescent. ¬†Scientists focused in on one particular type of senescent cell, the astrocyte, which are essentially cells that send and receive neurons in the brain. It was hypothesized that senescent astrocytes could be causing localized inflammation that harms the neurons associated Parkinson‚Äôs disease. Parkinson‚Äôs is characterized by the death of neurons associated with dopamine production. While paraquat has long been associated with the direct death of these neurons, this new research shows that additional neurological impacts may be at play.
Scientists carried out different investigations to test the impact of senescent astrocytes on the development of Parkinson’s. First, they compared human brain tissue between Parkinson’s patients and those without the disease. Compared to those that never contracted Parkinson’s, individuals with the disease showed biomarkers associated with higher levels of senesced astrocytes. Researchers then looked at whether paraquat could cause senescence in a lab-cultured human astrocyte. Not only did paraquat stop astrocyte cell proliferation, it did better at inducing senescence than hydrogen peroxide and other traditional medical methods of inducing astrocyte senescence. Scientists found that, in line with epidemiological data that shows greater risk for Parkinson’s from chronic, low dose exposure than acute, one-time exposure, exposing the cultured astrocytes to paraquat for a longer time at a lower dose resulted in a greater number of senesced cells.
A final test was conducted on laboratory mice. After exposing mice to levels of paraquat indicated in the literature to result in Parkinson‚Äôs disease symptoms, results traced a very similar response to the human astrocyte cell culture. Senescent astrocytes increased after paraquat exposure, and mice displayed increased difficulties in movement and motor function. However, when researchers used a drug to flush senescent cells from the substantia nigra, the area of the brain where domapine-producing cells are located, the Parkinson‚Äôs-like symptoms of paraquat exposure subsided. ‚ÄúThey are almost indistinguishable from the healthy mice,‚ÄĚ said Marco Demaria, PhD, to The Guardian.
‚ÄúAs far as we know, this is the first time it‚Äôs been demonstrated in any neurodegeneration model that ablating [removing] senescent cells actually has an effect on disease progression,‚ÄĚ said study co-author Julie Anderson, PhD to The Scientist. However, Dr. Anderson also noted to TheScientist that, ‚Äúright now, we don‚Äôt know specifically what it is about paraquat that is inducing the senescence within the astrocytes.‚ÄĚ
This complex study provides a route to potentially treat not only Parkinson‚Äôs but other diseases where senescent cells may play a role, such as ALS and Alzheimer‚Äôs. Future research will need to uncover how to flush out specific senescent cells while leaving others, which may be valuable in other areas, such as healing wounds, alone. ‚ÄúWe know the cells we want to target, but at the moment we don‚Äôt have the therapeutics to do that,‚ÄĚ said Dr. Demaria to The Guardian. ‚ÄúWe cannot yet only target the bad cells.‚ÄĚ
While the treatment developed by researchers in this study is promising, a better approach to reducing and eliminating the spread of pesticide-related diseases is to simply take the chemical off the market. Any products linked to devastating diseases such as ALS, Alzheimer’s, and Parkinson’s have no place in our environment. While paraquat’s use is restricted to certified applicators in the U.S., it can still be applied to agricultural land. Despite a ban on the chemical in Europe and a planned phase-out of use in China, over seven million lbs of paraquat were applied to 15 million acres of American farmland in 2015.
Support efforts to ban the continued use of paraquat. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency is currently reviewing safety concerns about the chemical, but without public involvement, the agency’s decision could be similar to its continued allowance of another neurotoxic pesticide Рchlorpyrifos. Keep up to date with Beyond Pesticides’ action alerts for updates, and for more information on the link between pesticides and Parkinson’s, see the Pesticide-Induced Diseases Database section on Parkinson’s disease.
All unattributed positions and opinions in this piece are those of Beyond Pesticides.
Source: The Guardian, The Scientist, Cell Reports
Posted in Agriculture, Disease/Health Effects, International, Paraquat, Parkinson's, Uncategorized by: Beyond Pesticides
No Comments
31
Jan
(Beyond Pesticides, January 31, 2018) Woolworths, one of Australia’s  largest retailers, has decided to stop selling neonicotinoid products (neonics) linked to global declines in bee populations. This is the latest retailer in Australia to announce commitments to stop supplying the bee-toxic products.
largest retailers, has decided to stop selling neonicotinoid products (neonics) linked to global declines in bee populations. This is the latest retailer in Australia to announce commitments to stop supplying the bee-toxic products.
After thousands of Australians signed a petition calling on retailers to stop selling insecticides containing neonicotinoids, Woolworth announced it has, in fact, succumbed to public pressure and would join Bunnings Warehouse, Mitre 10 and Coles stores in pulling neonic products from their shelves. The week prior, retail chain Bunnings announced it would pull all items containing neonicotinoids from their shelves. Woolworth said it would stop selling the products by June 2018. The retail commitments come as a result of efforts launched by global consumer group SumOfUs that called on Australian retailers to stop selling insecticide products containing neonicotinoids, including the popular home and garden product, Confidor, which has been stocked by Woolworths and contains imidacloprid as the active ingredient.
According to Australia‚Äôs The New Daily, about one-third of Australian fruit and vegetable crops are reliant on pollination. Speaking on the ban of neonic products, Katja Hogendoorn, PhD, of University of Adelaide, who researches the behavioral ecology and evolution of native bees, is quoted as saying there was ‚Äúno doubt pesticides often kill bees. Having a beautiful garden is a luxury. Bees are not, they are essential,‚ÄĚ Dr. Hogendoorn said. ‚ÄúThe banning of neonicotinoids for home gardeners by Bunnings and Mitre 10 is a great development. I hope the other companies follow suit.‚ÄĚ
The Australian government undertook a review of neonicotinoids and the health of honey bees in 2013, which found that ‚Äúthe introduction of the neonicotinoids has led to an overall reduction in the risks to the agricultural environment from the application of insecticides,‚ÄĚ according to the Guardian
In the U.S., Walmart and True Value announced last year that they will be phasing out neonic pesticides from all retail supply chains. This follows 2015 commitments by Home Depot, the world’s largest home-improvement chain, that it will no longer use neonic pesticides in 80 percent of its flowering plants, and that it will complete its phase-out in plants by 2018. This was preceded by Lowe’s commitment to phase out the sale of neonic products within 48 months. Several regional garden stores are also working with suppliers to discontinue the use of neonicotinoids: Behnke Nurseries Co. in Maryland, Bachmans, MN, Cavano’s Perennials, MD, Blooming Nursery, OR.
Research on neonics has been consistent in linking their use to reduced learning in bees, as well as other impacts, such as those on colony size, and reproductive success. Studies looking at effects on birds reports that songbirds exposed to widely used insecticides, like neonicotinoids, fail to properly orient themselves for migration, the first such study that adds weight to arguments that pesticides are a likely cause in the decline of migratory bird populations.  U.S. beekeepers lost an unsustainable 33% of their hives between 2016 and 2017. Neonics are also detected regularly in the nation’s waterways at concentrations that exceed acute and chronic toxicity values for sensitive organisms. A new report from the U.S. Geologic Survey (USGS) finds neonic contamination of the Great Lakes that threatens aquatic life.
EPA has already released the preliminary pollinator assessment for the neonicotinoids that identified risks to pollinators from a variety of uses on agricultural crops. The aquatic assessment for imidacloprid, also released last year, finds that imidacloprid threatens the health of U.S. waterways with significant risks to aquatic insects and cascading effects on aquatic food webs. As a result of risks to aquatic organisms, the Canadian pesticide regulatory agency has recommended banning imidacloprid, a decision on which has been delayed. In Europe, a recent survey finds that streams across the United Kingdom (UK) are contaminated with neonics. The European Commission met on December 12 and 13, 2017 to decide on a proposal to extend the 2013 neonicotinoid ban to all outdoor crops, but this decision was delayed. The issue is expected to be on the agenda again in early 2018. The UK government has reversed its previous stance on neonicotinoids, now saying that it should be banned due to their harm to pollinators.
Beyond Pesticides released Poisoned Waterways, a report which documents the persistence of neonicotinoids in U.S. waterbodies and the danger they cause to aquatic organisms, resulting in complex cascading impacts on the aquatic food web. The report also highlights current regulatory failures of EPA aquatic standards, which continue to underestimate risks to sensitive species due to a reliance on test protocols that do not reflect real-world exposures or susceptibilities. Aquatic standards, which have been underestimating risks to sensitive species due to a reliance on test protocols, do not reflect real-world exposures or susceptibilities.
Eliminating the sale of harmful pesticides does not mean that retailers will have nothing left to sell their customers. Beyond Pesticides released¬†The Well-Stocked Hardware Store, an online toolkit that identifies organic compatible products for¬†hardware stores seeking to find replacement products that can be used with an organic system approach to land management. Beyond Pesticides highlights the actions of Eldredge Lumber, a hardware store in Maine, through the video¬†Making the Switch. ‚ÄúYou‚Äôre protecting the environment, your family, your children and grandchildren, and your neighbors. Nobody wants to have pesticides drifting into their front or rear yard, and people are just loving it, they‚Äôre feeding into it. I couldn‚Äôt be happier,‚ÄĚ says owner Scott Eldredge in the video.
All unattributed positions and opinions in this piece are those of Beyond Pesticides.
Source: The Guardian; The New Daily
Posted in neonicotinoids by: Beyond Pesticides
No Comments
30
Jan
(Beyond Pesticides, January 30, 2018) New data from the U.S. Geological Survey  (USGS) reveals the year-round presence of neonicotinoids (neonics) in the Great Lakes Рthe world’s largest freshwater ecosystem. Neonics, which are highly toxic to aquatic organisms and pollinators, are prevalent in the tributaries of the Great Lakes with concentrations and detections increasing during planting season. This new data adds to burgeoning demand for a federal ban of these insecticides in order to safeguard vulnerable aquatic ecosystems and pollinators.
(USGS) reveals the year-round presence of neonicotinoids (neonics) in the Great Lakes Рthe world’s largest freshwater ecosystem. Neonics, which are highly toxic to aquatic organisms and pollinators, are prevalent in the tributaries of the Great Lakes with concentrations and detections increasing during planting season. This new data adds to burgeoning demand for a federal ban of these insecticides in order to safeguard vulnerable aquatic ecosystems and pollinators.
The study, “Year-round presence of neonicotinoid insecticides in tributaries to the Great Lakes, USA,” sampled ten major tributaries to the Great Lakes from October 2015 to September 2016. Neonicotinoids were detected in every month sampled. At least one neonicotinoid was detected in 74 percent of the samples, with 10 percent of samples containing three neonicotinoids.¬†The most frequently detected neonicotinoid was imidacloprid (53%), followed by clothianidin (44%), thiamethoxam (22%), acetamiprid (2%), and dinotefuran (1%).
The detections of clothianidin and thiamethoxam are significantly correlated with the percentage of agricultural land use. Similarly, concentrations increased in the spring and summer months when the planting of neonic-coated seeds and broadcast applications are the highest. For instance, in the agriculturally dominated basin (corn and soybean) along the Maumee River, Ohio, clothianidin, imidacloprid, thiamethoxam are ubiquitously detected in all water samples collected within the basin at the highest recorded for the study; maximum individual neonicotinoid concentration is 330‚ÄĮng‚ÄĮL‚ąí1¬†and maximum total neonicotinoid concentration is 670‚ÄĮng‚ÄĮL‚ąí1; median detected individual neonicotinoid concentration is 7.0 to¬†39‚ÄĮng‚ÄĮL‚ąí1.¬†Alternatively, imidacloprid detections significantly increase as the percent of the urbanization increases, where home gardeners and golf courses use neonicotinoid turf and garden products.
Prior to the study, little was known about the chemicals’ presence in the Great Lakes region. From October 2015 to September 2016, USGS researchers took monthly samples from the following rivers that all drain into the Great Lakes: Manitowoc River (WI), Grand River (MI), St. Joseph River (MI), Indiana Harbor Canal (IN), Saginaw River (MI), River Rouge (MI), Maumee River (OH), Cuyahoga River (OH), Genesee River (NY), and Bad River (WI). Michelle Hladik, PhD, lead author of the new study and a research chemist at the USGS, said the major risk of these chemicals is to aquatic insects‚ÄĒan effect that could ripple up the food chain. “If these pesticides are affecting aquatic insects, causing lower populations, it could affect the food chain by removing a food source” for fish, she said.
Neonicotinoids are the most widely used insecticides in the U.S. and have been linked to neurological and immune system impairments in honey bees and other pollinator declines. However, emerging science is also showing that these chemicals are also highly toxic to aquatic organisms, especially aquatic insects on which whole ecosystems rely. Declines in these organisms can, therefore, have catastrophic results for organisms that depend on them for food, including fish and birds.
Last month, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) released preliminary ecological (non-pollinator) assessments for the neonicotinoids clothianidin, thiamethoxam, dinotefuran and the terrestrial ecological assessment for imidacloprid, finding that these pesticides pose both acute and chronic risks to aquatic life and birds. Treated seeds are identified as posing the highest dietary risks to birds, confirming previous research that neonics are highly hazardous not only to bees, but also, to birds, aquatic life, and other non-target organisms. EPA has already released the preliminary pollinator assessment for the neonics, which identifies risks to pollinators from a variety of uses on agricultural crops. The aquatic assessment for imidacloprid, also released last year, finds that it threatens the health of U.S. waterways with significant risks to aquatic insects and cascading effects on aquatic food webs.
Neonics are detected regularly in the nation’s waterways at concentrations that exceed acute and chronic toxicity values for sensitive organisms. As a result of risks to aquatic organisms, the Canadian pesticide regulatory agency has recommended banning imidacloprid, a decision that has been delayed. In Europe, a recent survey finds that streams across the United Kingdom (UK) are contaminated with neonics. The Beyond Pesticides report Poisoned Waterways documents the persistence of neonicotinoids in U.S. waterbodies and the danger they cause to aquatic organisms, resulting in complex cascading impacts on the aquatic food web. The report also highlights current regulatory failures of EPA aquatic standards, which continue to underestimate risks to sensitive species, due to a reliance on test protocols that do not reflect real-world exposures or susceptibilities.
Take Action: Tell EPA that neonics pose unacceptable risks to pollinators, aquatic life, and birds! And, ask your Congressional delegation push EPA to stop the use of neonicotinoids.
All unattributed positions and opinions in this piece are those of Beyond Pesticides.
Source: Environmental Health News
Posted in contamination, neonicotinoids, Water by: Beyond Pesticides
No Comments
29
Jan
(Beyond Pesticides, January 29, 2018)¬†Scientists, public health managers, and others charged with protecting the health  of the public and the environment at the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) are being encouraged to exit the agency ‚Äďas EPA Administrator Scott Pruitt plans to meet his goal of cutting agency staff and programs by 50 percent.
of the public and the environment at the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) are being encouraged to exit the agency ‚Äďas EPA Administrator Scott Pruitt plans to meet his goal of cutting agency staff and programs by 50 percent.
Tell your Congressional delegation that EPA’s staff and budget cuts are false economy!
Aides to Mr. Pruitt confirmed to the Washington Examiner that by the end of President Trump‚Äôs first term, the agency‚Äôs staff will be cut by nearly half. Administrator Pruitt told the Washington Examiner he was ‚Äúproud‚ÄĚ of his efforts to dismantle ‚Äďsome say cripple‚ÄĒ the very agency he leads. This is false economy. It endangers the American public and its air, land, water, and biodiversity.
EPA is responsible for enforcing the Safe Drinking Water Act, with a goal of making the nation’s waters fishable and swimmable. EPA enforces the Clean Air Act, which has cleaned up American cities, reducing illness and property damage from smog. And EPA is responsible for overseeing the clean-up of contaminated sites, thus preventing further pollution and illness.
The agency also regulates pesticides under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA).
All of EPA‚Äôs programs require the application of science to public policy. Among the people who are being encouraged to retire ‚ÄĒvia ‚Äúbuyouts‚ÄĚ and attractive retirement benefits to incentivize exits‚ÄĒ are more than 200 scientists and nearly 100 environmental protection specialists.
Since the Trump administration took office, more than 700 employees have left EPA. According to the Washington Examiner, as of January 3, 2018, the EPA had 14,162 employees. In fiscal year 1988, when Ronald Reagan was President, the EPA employee level was 14,440. Twenty-three percent of EPA employees are currently eligible to retire with full benefits, and another 4 percent can retire at the end of 2018. Additionally, another 20 percentwill be eligible to retire in the next five years. Taken together, nearly 50 percent of EPA staff will be encouraged to leave, in one way or another, over the next five years. One administration official is quoted, in the Washington Examiner, as saying, ‚ÄúWe‚Äôre happy to be at Reagan-level employment numbers and the future retirements show a preview of how low we could get during this administration. It would be fair to say that anywhere from 25 to 47 percent of EPA could retire during this administration.‚ÄĚ
EPA has been plagued with budget constraints for many years, but now, with such drastic cuts (both personnel and budgetary), programs spearheaded by EPA to protect air, water, people, and wildlife from toxic pollution will suffer ‚ÄĒa goal made clear by the Trump Administration. Eliminating resources needed to prevent problems means that more money will need to be spent repairing damage and treating disease.
Although, as documented by Beyond Pesticides, EPA’s regulation of pesticides is flawed, the agency plays a critical role in reviewing science and implementing laws protecting human health and the environment. Science itself has been under attack by the Trump Administration, as evidenced by its issuance of scientific grant and hiring freezes at EPA and other agencies nationwide, along with a ban on science communications through social media platforms. Under a dismantled EPA, experts say that even the limited advances made will be undermined. For instance, the neurotoxic pesticide chlorpyrifos, which endangers children, was proposed to be revoked in 2015 due to findings and recommendations of EPA’s own scientists and a 2016 Scientific Advisory Panel (SAP). However, one of Administrator Scott Pruitt’s first acts in office was to rescind the proposal, claiming more evidence was needed.
Though environmentalists and public health experts have criticized EPA for lax or inadequate regulation of pesticides, the clear attacks on public health and the environment through proposed budget cuts, by the Trump administration and EPA’s Mr. Pruitt, demand urgent action.
Tell your Congressional delegation to hold the line on EPA’s budget to protect health, resources, and the economy!
All unattributed positions and opinions in this piece are those of Beyond Pesticides.
Posted in Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), Uncategorized by: Beyond Pesticides
No Comments
 and on-farm profit can be maintained and improved by replacing these toxic chemicals with alternative pest management strategies. The new study is part of an ongoing update to the 2014 Worldwide Integrated Assessment undertaken by an international team of scientists called the Task Force on Systemic Pesticides. The results of this review point to the need for strong action against these chemicals by all levels of government.
and on-farm profit can be maintained and improved by replacing these toxic chemicals with alternative pest management strategies. The new study is part of an ongoing update to the 2014 Worldwide Integrated Assessment undertaken by an international team of scientists called the Task Force on Systemic Pesticides. The results of this review point to the need for strong action against these chemicals by all levels of government.








 decrease air pollution from cars and other vehicles, scientists are finding that the use of pesticides and other household chemicals represent an increasing proportion of smog-forming pollution in the U.S. Research published in the journal
decrease air pollution from cars and other vehicles, scientists are finding that the use of pesticides and other household chemicals represent an increasing proportion of smog-forming pollution in the U.S. Research published in the journal  20,000 cows or more dot the Western US in California, Colorado and Texas in particular. They have repeatedly come under fire from watchdog groups, journalists and farmers who have observed and documented the absence of cows on pasture during grazing season, as required by the Organic Foods Production Act (OFPA). This circumventing of the law could soon change with the commercialization of the fluorescene spectroscopy (FS), which detects the amount of forage a dairy herd is eating by measuring the luminescence of metabolized grass in milk. The law requires that herds graze daily during a given region’s growing season, at least 120 days per year, and consume a minimum of 30% grass in their daily diet.
20,000 cows or more dot the Western US in California, Colorado and Texas in particular. They have repeatedly come under fire from watchdog groups, journalists and farmers who have observed and documented the absence of cows on pasture during grazing season, as required by the Organic Foods Production Act (OFPA). This circumventing of the law could soon change with the commercialization of the fluorescene spectroscopy (FS), which detects the amount of forage a dairy herd is eating by measuring the luminescence of metabolized grass in milk. The law requires that herds graze daily during a given region’s growing season, at least 120 days per year, and consume a minimum of 30% grass in their daily diet.
 statewide ban on the use of its specialty dicamba herbicide in Arkansas. Despite a lengthy process of evaluation and public comment that led to a prohibition on the use of drift-prone dicamba herbicides during the growing season on Arkansas farms, Monsanto made one last-ditch attempt to stop the law from going into effect by suing the entire state. With the industry’s loss, Arkansas is on track to implement the
statewide ban on the use of its specialty dicamba herbicide in Arkansas. Despite a lengthy process of evaluation and public comment that led to a prohibition on the use of drift-prone dicamba herbicides during the growing season on Arkansas farms, Monsanto made one last-ditch attempt to stop the law from going into effect by suing the entire state. With the industry’s loss, Arkansas is on track to implement the  to settle violations to U.S. regulations for selling illegal and misbranded pesticides in its online store. Under the terms of the settlement, Amazon will monitor and remove illegal pesticide products from its website. These products, mostly imported, were not registered for use and sale in the U.S. and can pose hazards to unsuspecting consumers.
to settle violations to U.S. regulations for selling illegal and misbranded pesticides in its online store. Under the terms of the settlement, Amazon will monitor and remove illegal pesticide products from its website. These products, mostly imported, were not registered for use and sale in the U.S. and can pose hazards to unsuspecting consumers. Canadian province will implement new restrictions on the use of five highly toxic pesticides. As part of efforts to fulfill the vision of the
Canadian province will implement new restrictions on the use of five highly toxic pesticides. As part of efforts to fulfill the vision of the  Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) label restrictions on total release foggers, otherwise known as ‚Äúbug bombs,‚ÄĚ are a public health failure. Bug bombs pose a significant risk of acute illness to individuals even when they attempt to follow new label instructions. Beyond Pesticides has long called for bug bombs to be banned, as there are
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) label restrictions on total release foggers, otherwise known as ‚Äúbug bombs,‚ÄĚ are a public health failure. Bug bombs pose a significant risk of acute illness to individuals even when they attempt to follow new label instructions. Beyond Pesticides has long called for bug bombs to be banned, as there are  claims against pesticide giant, Syngenta, after dozens of workers in Kuai, Hawaii were exposed to the neurotoxic pesticide chlorpyrifos in 2016 and 2017. EPA backed away from the $4.8 million settlement that it was initially seeking from Syngenta and negotiated a civil penalty of $150,000.
claims against pesticide giant, Syngenta, after dozens of workers in Kuai, Hawaii were exposed to the neurotoxic pesticide chlorpyrifos in 2016 and 2017. EPA backed away from the $4.8 million settlement that it was initially seeking from Syngenta and negotiated a civil penalty of $150,000.
 (Beyond Pesticides, February 13, 2018) Arguments by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to withhold from public and court review key documents revealing how it approved the first genetically engineered (GE) salmon were rejected by the Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals. Now, documents detailing how the agency reviewed and approved the GE animal will have to be produced for court review in the ongoing case challenging its controversial approval.
(Beyond Pesticides, February 13, 2018) Arguments by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to withhold from public and court review key documents revealing how it approved the first genetically engineered (GE) salmon were rejected by the Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals. Now, documents detailing how the agency reviewed and approved the GE animal will have to be produced for court review in the ongoing case challenging its controversial approval. exposure to the highly toxic paraquat add to the
exposure to the highly toxic paraquat add to the  National Wheat Growers Association last month in challenging California’s listing of glyphosate as a carcinogen under the state’s Proposition 65 law. California added glyphosate to the list of cancer-causing chemicals in July 2017, but has since been attacked by Monsanto and its allies for carrying out state law that requires carcinogens to be labeled and monitored.
National Wheat Growers Association last month in challenging California’s listing of glyphosate as a carcinogen under the state’s Proposition 65 law. California added glyphosate to the list of cancer-causing chemicals in July 2017, but has since been attacked by Monsanto and its allies for carrying out state law that requires carcinogens to be labeled and monitored. (Beyond Pesticides, February 8, 2018) New trials are being launched in the United Kingdom (UK) to monitor fields that have long strips of wildflowers planted through croplands to boost natural predators and potentially reduce pesticide spraying. The large-scale trials are meant to determine how effective these strips can be as a tool for practitioners wishing to enhance biological pest control in the field.
(Beyond Pesticides, February 8, 2018) New trials are being launched in the United Kingdom (UK) to monitor fields that have long strips of wildflowers planted through croplands to boost natural predators and potentially reduce pesticide spraying. The large-scale trials are meant to determine how effective these strips can be as a tool for practitioners wishing to enhance biological pest control in the field. population of the species is continuing to decline at an alarming rate, with scientists and conservation groups pointing to man-made factors like logging, climate change, and herbicide use on genetically engineered (GE) crop fields as primary drivers. The annual California count of western monarch butterflies stationed volunteers at 262 sites, more than ever before, yet at 200,000 butterflies counted, the numbers nearly matched the lowest level recorded this decade, when only 145,000 butterflies were seen in 2012. The decline of these iconic butterflies demands swift action from lawmakers and regulators to protect their dwindling numbers.
population of the species is continuing to decline at an alarming rate, with scientists and conservation groups pointing to man-made factors like logging, climate change, and herbicide use on genetically engineered (GE) crop fields as primary drivers. The annual California count of western monarch butterflies stationed volunteers at 262 sites, more than ever before, yet at 200,000 butterflies counted, the numbers nearly matched the lowest level recorded this decade, when only 145,000 butterflies were seen in 2012. The decline of these iconic butterflies demands swift action from lawmakers and regulators to protect their dwindling numbers. Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) efforts to purge academic scientists who had previously received EPA grants from sitting on the agency’s advisory committees. Last October, EPA issued a new policy that changes the makeup of its advisory boards by limiting the participation of scientists from academia and nonpartisan nonprofit organizations. Critics say the change attempts to fill these advisory committees with more industry-friendly officials whose belief systems are anti-environmental protection. On January 23, 2018, a group of scientists 
Environmental Protection Agency‚Äôs (EPA) efforts to purge academic scientists who had previously received EPA grants from sitting on the agency‚Äôs advisory committees.¬†Last October, EPA issued a new policy that changes the makeup of its advisory boards by limiting the participation of scientists from academia and nonpartisan nonprofit organizations.¬†Critics say the change attempts to fill these advisory committees with more industry-friendly officials whose belief systems are anti-environmental protection.¬†On January 23, 2018, a group of scientists¬† who grow and harvest our food. A sustainable food system must protect the land and the people who work the land, including the children and families of farmworkers. In two related actions, EPA is proposing to remove age requirements for application of pesticides. The actions involve changes to the Agricultural Worker Protection Standard (WPS), which went into effect this January and covers farmworkers hired to apply pesticides, and the Certification of Applicators (CA) rule, which will go into effect May 22 and covers those allowed to apply highly toxic restricted use pesticides (RUPs), the most toxic pesticides. The proposals to remove the age requirements present unacceptable risks to teenagers, who ‚Äúare still developing in critical physical and emotional areas, with particular regard to their brains and reproductive systems,‚ÄĚ according to the
who grow and harvest our food. A sustainable food system must protect the land and the people who work the land, including the children and families of farmworkers. In two related actions, EPA is proposing to remove age requirements for application of pesticides. The actions involve changes to the Agricultural Worker Protection Standard (WPS), which went into effect this January and covers farmworkers hired to apply pesticides, and the Certification of Applicators (CA) rule, which will go into effect May 22 and covers those allowed to apply highly toxic restricted use pesticides (RUPs), the most toxic pesticides. The proposals to remove the age requirements present unacceptable risks to teenagers, who ‚Äúare still developing in critical physical and emotional areas, with particular regard to their brains and reproductive systems,‚ÄĚ according to the  drastically underestimating chemical-intensive agriculture‚Äôs contribution to nitrogen oxide (NOx) caused air pollution, acid rain, and respiratory illness in the state, according to a
drastically underestimating chemical-intensive agriculture’s contribution to nitrogen oxide (NOx) caused air pollution, acid rain, and respiratory illness in the state, according to a  for the Biology of Aging are finding new information about how Parkinson’s disease manifests itself after exposure to the herbicide paraquat, in hopes of finding ways to prevent the progression of the disease. Despite a
for the Biology of Aging are finding new information about how Parkinson’s disease manifests itself after exposure to the herbicide paraquat, in hopes of finding ways to prevent the progression of the disease. Despite a  (USGS) reveals the year-round presence of neonicotinoids (neonics) in the Great Lakes Рthe world’s largest freshwater ecosystem. Neonics, which are highly toxic to aquatic organisms and pollinators, are prevalent in the tributaries of the Great Lakes with concentrations and detections increasing during planting season. This new data adds to burgeoning demand for a federal ban of these insecticides in order to safeguard vulnerable aquatic ecosystems and pollinators.
(USGS) reveals the year-round presence of neonicotinoids (neonics) in the Great Lakes – the world‚Äôs largest freshwater ecosystem. Neonics, which are highly toxic to aquatic organisms and pollinators, are prevalent in the tributaries of the Great Lakes with concentrations and detections increasing during planting season. This new data adds to burgeoning demand for a federal ban of these insecticides in order to safeguard vulnerable aquatic ecosystems and pollinators. of the public and the environment at the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) are being encouraged to exit the agency ‚Äďas EPA Administrator Scott Pruitt plans to meet his goal of cutting agency staff and programs by 50 percent.
of the public and the environment at the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) are being encouraged to exit the agency ‚Äďas EPA Administrator Scott Pruitt plans to meet his goal of cutting agency staff and programs by 50 percent.
